Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
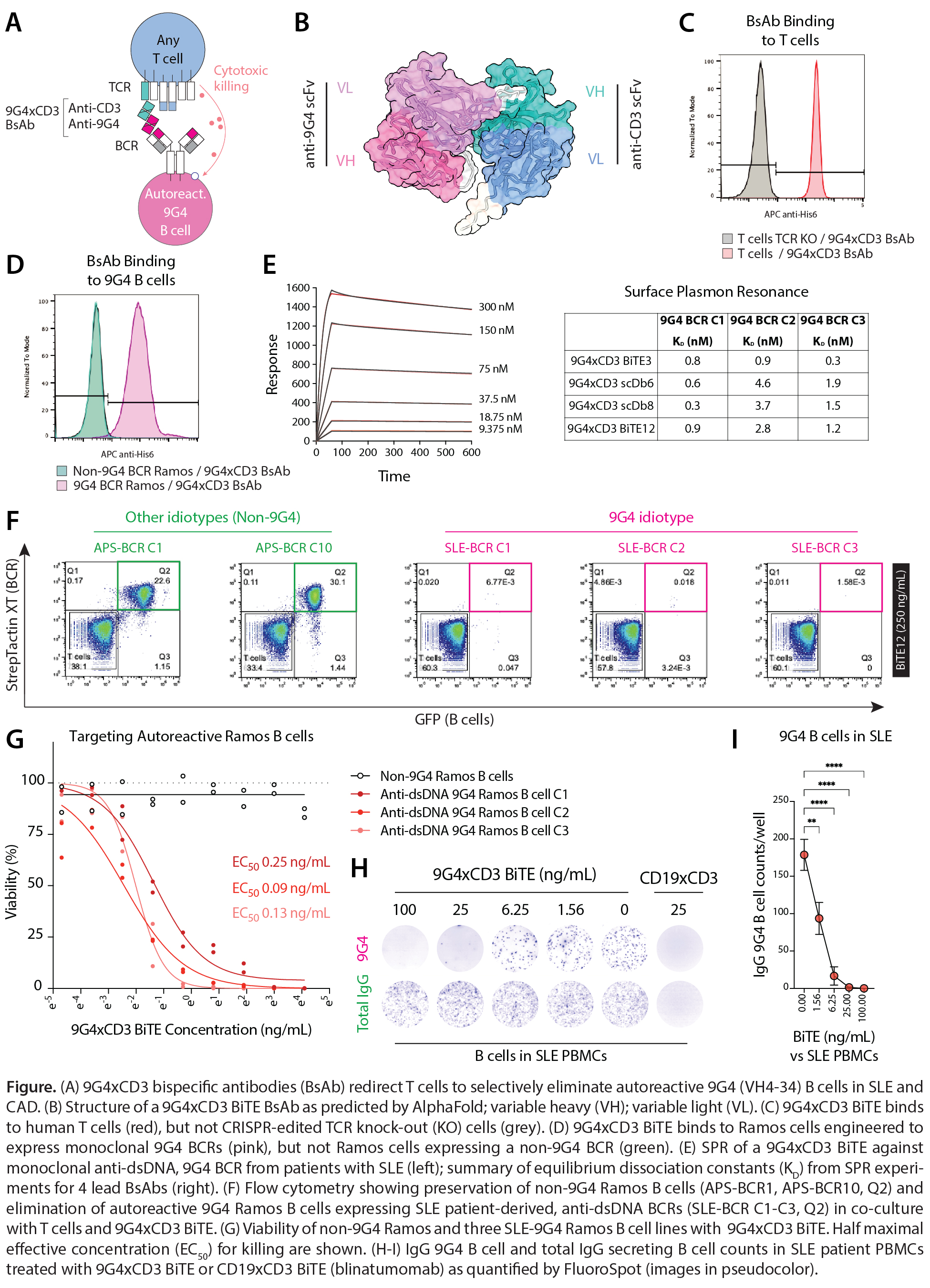
Background/Purpose: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapies hold promise for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) but are critically limited by scalability and long-term safety (e.g., risk of transformation). Therapies that indiscriminately deplete all B cells and require cytotoxic conditioning are further limited by toxicity and infection risk. Immunotherapies that engage T cells to eliminate autoreactive B cells with precision offer an alternative to CAR-T cell therapies. The autoreactive B cell compartment in active SLE is characterized by the expansion of B cells expressing the 9G4 idiotope (9G4, VH4-34), a major source of disease-relevant autoantibodies (e.g., dsDNA, DNAse1L3). We hypothesized that bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) can redirect T cells to selectively kill 9G4 B cells via their B cell receptors (BCRs). We therefore developed an off-the-shelf, precision T cell-engaging BsAbs therapy that selectively eliminates 9G4 B cells.
Methods: Anti-9G4 and anti-CD3 single-chain variable fragment (scFv) sequences were synthesized, cloned, and 9G4xCD3 BsAbs expressed in single-chain diabody (scDb) or bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) formats in ExpiCHO cells. Ramos B cells were CRISPR-Cas9-edited to replace their endogenous BCR with monoclonal 9G4 and non-9G4 BCRs cloned from patients with SLE or antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). Binding of BsAbs to Ramos B cells and polyclonal T cells was determined by flow cytometry. Binding affinities of BsAbs were quantified by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The potency and specificity of 9G4xCD3 BsAbs against edited Ramos cells expressing 9G4 or non-9G4 BCRs were interrogated in co-culture, and cytotoxicity was quantified by live-cell imaging, flow cytometry, and cytokine assays. PBMCs from patients with SLE were treated with 9G4xCD3 BsAbs, and depletion of 9G4 B cells was quantified by IgG anti-9G4 FluoroSpot following differentiation to antibody-secreting cells (ASC). Depletion of lupus-relevant autoantibodies was quantified.
Results: BsAbs were developed to redirect T cells to precisely kill 9G4 B cells (A-B). Binding of BsAbs to human T cells was dependent on TCR-CD3ε surface expression (C). 9G4xCD3 BsAbs, expressed as scDbs and BiTEs, selectively bound 9G4, but not non-9G4 Ramos B cells (D). Equilibrium dissociation constants (KD) for 9G4xCD3 BsAbs against SLE-9G4 BCRs reactive to dsDNA/DNAse1L3 were 0.3-4.6 nM by SPR (E). In co-culture of T cells with SLE-9G4 or non-9G4 Ramos B cells, 9G4xCD3 BsAbs selectively eliminated 9G4 B cells (F). Target cell killing was observed at low BsAb concentrations (EC50 0.08-1.56 ng/mL) but maintained specificity across a wide range of titration (60 ng/mL) (G). In co-culture with SLE PBMCs, 9G4xCD3 BiTE eliminated 9G4 B cells in a dose-dependent manner while maintaining other ASCs (H-I).
Conclusion: We describe an off-the-shelf, precision immunotherapy approach for the selective depletion of autoreactive B cells in SLE. 9G4xCD3 BsAbs are efficient and specific at eliminating 9G4 B cells—an opportunity to treat SLE without increasing the risk of infection. Different to CAR-T cells, 9G4xCD3 BsAbs can be produced and administered at scale. Beyond autoimmune diseases, these BsAbs have utility in the treatment of B cell lymphomas.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liu J, Xia Y, Ferris D, Shaw E, Mog B, Pearlman A, Moritz B, Kaeo K, Gliech C, Awosika T, DiNapoli S, Nichakawade T, Li Y, Ge J, Glavaris S, Marcou N, Ahmedna T, Bugrovsky R, Jenks S, Bettegowda C, Goldman D, Petri M, Sanz I, Kinzler K, Zhou S, Vogelstein B, Paul S, Andrade F, Konig M. T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibodies to Target Autoreactive 9G4 Idiotope B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/t-cell-engaging-bispecific-antibodies-to-target-autoreactive-9g4-idiotope-b-cells-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/t-cell-engaging-bispecific-antibodies-to-target-autoreactive-9g4-idiotope-b-cells-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/