Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0671–0710) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) disease models that faithfully recapitulate endothelial mediated vasculopathy are critical for testing and developing novel treatments. The generation of inducible pluripotential stem cells (IPSC) from SSc patients’ serum and the ability to develop those into patient specific endothelial cells (EC) allows for vasculopathy analysis. The objective of this study was to examine iPSC-EC-barrier function at baseline and in response to an inflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 (IL-1α), which may have a cardinal role in SSc cardiopulmonary dysfunction and tissue fibrosis.
Methods: SSc patients with an abnormal echocardiogram and age-and sex matched healthy controls (HC) were consented at a two SSc Centers. Peripheral blood monocytes cells (PBMC) were collected at the time of a routine care visit and clinical features were recorded. PBMC were differentiated into iPSC-EC at the Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine Program (CellReGenTM) at the University of Utah, which adheres to quality control metrics including specimen karyotyping. Measures of mitochondrial superoxide using MitoSox in SSc-IPSC-ECs and HC were determined by the intensity of protein expression as observed through immunofluorescence. We cultured the reprogrammed cells on electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) to provide a platform to properly study vascular barrier function. Baseline impedance and response to IL-1α was measured.
Results: IPSC-EC reprogramming was attempted in 22 SSc registry patients with abnormal echocardiograms. Thirteen of 22 individual SSc cell lines were successfully reprogrammed. The SSc clinical features are shown in Table 1. For these 13 SSc patients, 9 age- and sex-matched HC samples were selected and successfully reprogrammed. Samples that did not have PBMC isolation in less than 12 hours of collection failed to reprogram. There was no significant difference in clinical features of the SSc patients that reprogrammed successfully. Under baseline conditions, IPSC-EC from SSc patients had ~20% reduced EC resistance (enhanced endothelial permeability) compared to healthy controls over the length of the experiment (Figure 1a). The treatment effect of EC with IL-1α demonstrated that there was a significant decrease in endothelial resistance (higher permeability) response to IL-1α in the HC patients, but IL-1α had no influence on SSc endothelial resistance (Figure 1b). There were no differences in Mitosox between SSc and HC patient EC (Figure 2), suggesting the baseline permeability differences in the SSc EC were not due to mitochondrial ROS.
Conclusion: In this largest to date study of SSc-IPSC-EC, we identified increased baseline permeability in SSc compared to HC. While HC had a typical IL-α increase in permeability, SSc lacked this typical physiological response. We found that despite some alterations in EC phenotype, mitochondrial ROS were similar in SSc and HC ECs. Our data suggests that genetic or epigenetic changes were preserved in SSc patient IPSCs as a patient vascular phenotype was recapitulated in cells developed into EC. IPSC-EC generated from PBMCs hold high potential in elucidating the role of vascular endothelium in the pathogenesis of SSc.
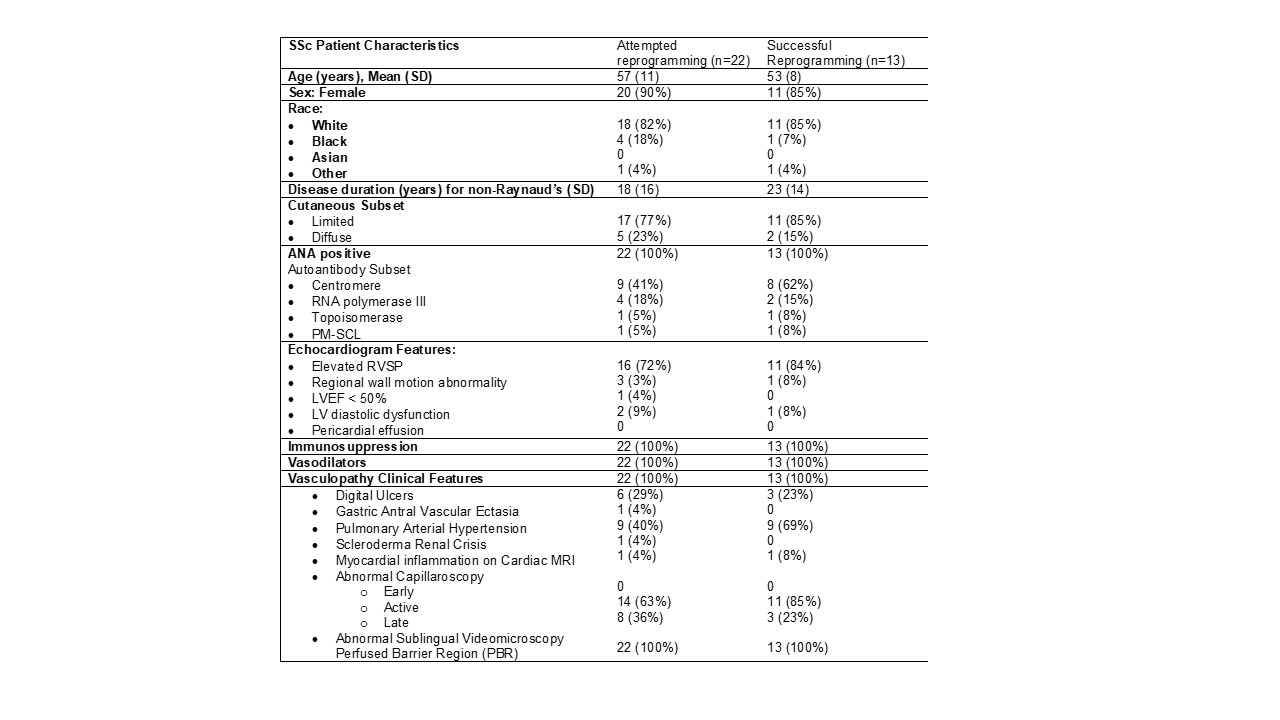 Systemic Sclerosis Registry Patients with an Abnormal Echocardiogram Referred to the Cardio-Rheum Clinic or Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Clinic
Systemic Sclerosis Registry Patients with an Abnormal Echocardiogram Referred to the Cardio-Rheum Clinic or Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Clinic
.jpg) Measure of permeability in inducible pluripotential stem cells (iPSC) generated from healthy controls (HC) and systemic sclerosis (SSC) and cultured on the electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) platform at baseline (a) and in response to interleukin-(IL) 1 alpha 10ng and 15 ng over 72 hours (b)
Measure of permeability in inducible pluripotential stem cells (iPSC) generated from healthy controls (HC) and systemic sclerosis (SSC) and cultured on the electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) platform at baseline (a) and in response to interleukin-(IL) 1 alpha 10ng and 15 ng over 72 hours (b)
.jpg) Measures of mitochondrial superoxide in reprogrammed SSc-iPSC-EC (n=13) when compared to HC (n=9).
Measures of mitochondrial superoxide in reprogrammed SSc-iPSC-EC (n=13) when compared to HC (n=9).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Frech T, Gogulamudi V, Moreno D, Austin E, Frech C, Hemnes A, Ruiz T, Shahin A, Talati M, Maguire C, Donato A. Systemic Sclerosis Inducible Pluripotential Stem Cells Reprogrammed into Endothelial Cells Identify Vascular Permeability May Not Be Cytokine Driven [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-sclerosis-inducible-pluripotential-stem-cells-reprogrammed-into-endothelial-cells-identify-vascular-permeability-may-not-be-cytokine-driven/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-sclerosis-inducible-pluripotential-stem-cells-reprogrammed-into-endothelial-cells-identify-vascular-permeability-may-not-be-cytokine-driven/
