Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1612–1632) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) and giant cell arteritis (GCA) are chronic inflammatory disorders predominantly affecting patients over 50. Despite unclear etiopathogenesis, both conditions share central immunopathogenic pathways. Recent evidence indicates they might constitute a continuum of a single disease with diverse clinical manifestations, highlighting the importance of identifying reliable inflammatory biomarkers. Both disorders drive systemic inflammation, impair patient functionality, and potentially lead to severe complications like ischemic optic neuropathy or aneurysms from vascular involvement. Thus, accessible and cost-effective biomarkers for monitoring disease activity remain critical. This study evaluates the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) as novel hematological indices for assessing inflammatory activity in PMR and GCA.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional observational study including consecutive PMR and/or GCA patients fulfilling ACR-EULAR classification criteria. Patient demographics, clinical data (symptomatic systemic activity, treatment status), and laboratory parameters, including C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), NLR (neutrophils/lymphocytes), and SII (platelets × neutrophils/lymphocytes), were collected during a single assessment. Correlation analyses were performed using Spearman’s test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and Youden’s index identified optimal diagnostic cut-offs. Sensitivity, specificity, positive (LR+) and negative (LR–) likelihood ratios, and odds ratios (OR) were calculated.
Results: A total of 68 patients were analyzed (mean age 76 ± 7 years; 53% female; PMR 85%, cranial GCA 19%, extracranial GCA 9%). Active systemic symptoms were present in 36 (53%) patients. Both NLR and SII were significantly higher in active compared to inactive patients (median NLR 2.63 vs. 1.84, p = 0.002; median SII 701 vs. 460, p < 0.001). Each index correlated moderately with CRP (NLR ρ = 0.55, SII ρ = 0.62; p < 0.001) but did not correlate significantly with ESR (ρ ≤ 0.19; p > 0.10), nor were they affected by glucocorticoid therapy. ROC analysis showed SII had superior discriminatory power compared to NLR (AUC 0.76 vs. 0.72; p < 0.05). The optimal SII cut-off (≥560) demonstrated a sensitivity of 72%, specificity of 84%, LR+ of 4.6, LR– of 0.34, and OR of 14.0, significantly outperforming NLR ≥ 2.2 (sensitivity 67%, specificity 69%, LR+ 2.1). Each 100-unit increase in SII was associated with a 28% increased odds of activity (OR 1.28, 95% CI 1.13–1.45), while each unit increase in NLR raised odds 1.6-fold (OR 1.63, 95% CI 1.11–2.39).
Conclusion: The SII emerges as a superior, glucocorticoid-independent marker of systemic disease activity in PMR/GCA compared to the NLR, providing additional clinical utility beyond ESR and complementing CRP. Its simple calculation from routine complete blood counts positions SII as an accessible and promising biomarker warranting prospective validation in longitudinal monitoring studies
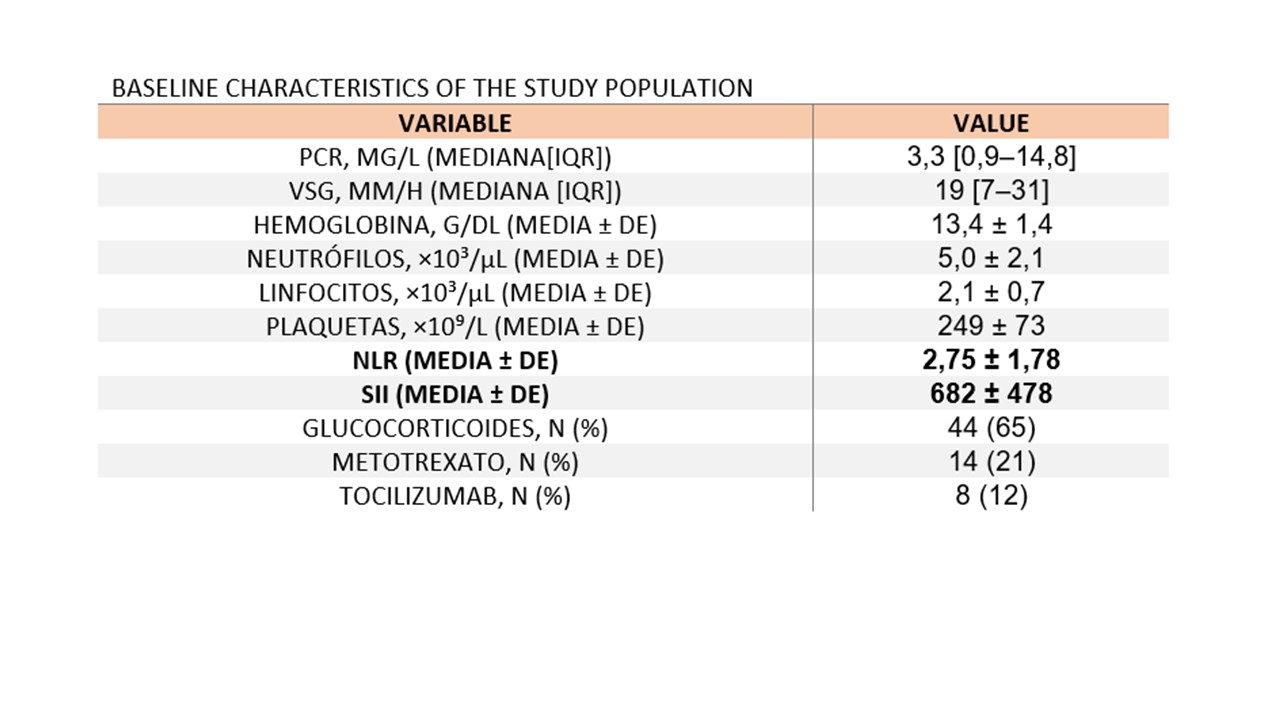 BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY POPULATION
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY POPULATION
*NLR (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte rati) SII ( systemic immune-inflammation index)
.jpg) SII Outperforms NLR in ROC Analysis for Disease Activity Discrimination
SII Outperforms NLR in ROC Analysis for Disease Activity Discrimination
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghio G, Paz Machado M, Encalada E, Perez Nadales I, Salvador Alarcón G, Riera Alonso E, pujol m, Pujol Teixidor M, Martinez Pardo S. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Is Superior to Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Assessing Disease Activity in Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-immune-inflammation-index-is-superior-to-neutrophil-to-lymphocyte-ratio-for-assessing-disease-activity-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica-and-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-immune-inflammation-index-is-superior-to-neutrophil-to-lymphocyte-ratio-for-assessing-disease-activity-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica-and-giant-cell-arteritis/
