Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: IL-36 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthropathies (SpA) like psoriasis and IBD. Enthesitis related arthritis (ERA) category of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is a form of juvenile SpA; however, no data is available regarding the role of IL-36 in this disease. Thus, we studied the involvement of IL-36 in ERA.
Methods: 84 patients with ERA (ILAR criteria), 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 24 healthy subjects were enrolled in the study after ethics approval and informed consent.
IL-36α, β, γ and IL-36R was determined in PBMCs and SFMCs at the mRNA levels using RTqPCR; and IL-36α, γ, IL-36Ra, IL-6 and IL-17 levels were measured in serum and synovial fluids (SF) by ELISA. Fibroblast like synoviocytes (FLS) were stimulated with recombinant IL-36γ, IL-6, IL-17, IL-6+IL-17 and TNF-α as well as with SF from patients with ERA in presence or absence of IL-36Ra. For ELISA, cells were stimulated for 8 h and supernatants were removed, cells were washed and further cultured for 16 h. Post stimulation expression of IL-6 and IL-36γ levels were measured at mRNA and protein levels. All results are expressed as median ±IQR.
Results: Among 84 JIA-ERA patients, 77 were boys. Their mean age was 16.8 ± 3.5 years and mean disease duration was 60.3 ± 48.8 months. All had active disease with mean ESR of 62.3 ± 34.9 mm and mean Juvenile Spa disease activity score of 3.4 ± 1.4.
mRNA levels of IL-36α, IL-36γ and IL-36R were increased in PBMCs of ERA patients as compared to healthy controls. However, at protein level only IL-36γ was detectable in a significant proportion of subjects and was higher (0 ± 42.1 pg/mL) than controls (0 ± 0) (p< 0.01) but lower than RA patients (198.2 ± 672.9 pg/mL).
In SFMCs, all 4 mRNA were detectable with levels lower than RA patients. SF levels of IL-36γ were also enhanced (0 ± 26.78 pg/mL) but were lower than RA patients (460 ± 1345 pg/mL). SF IL-36γ levels correlated significantly with disease activity (JSpaDA) (r=0.51, p< 0.0001), and with SF levels of IL-6 (r=0.4, p= 0.0063) and IL-17 (r=0.57, p=0.0018). Patients on treatment with DMARDs had significantly lower SF IL-36γ levels than those not receiving DMARDs.
When FLS were stimulated with IL-36γ and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, mRNA expression of IL-36γ; and mRNA and protein expressions of IL-6 were found increased. Protein expression of IL-36γ was not detectable by ELISA in cell supernatants and no expression of IL-17 at RNA or protein level was noted.
When FLS were stimulated with SFs from JIA-ERA patients (n=5), increased expressions of IL-36γ mRNA and IL-6 mRNA and protein were seen, compared to controls. However, in presence of IL-36Ra, expressions of both cytokines were significantly reduced (p< 0.0001 in all cases).
Conclusion: The data suggests that pro-inflammatory cytokines aid in upregulation of IL-36γ which in turn upregulates expression of IL-6 and this might lead to a positive feedback loop leading to amplification of inflammation in ERA. Association of SF levels of IL-36g with disease activity further supports this possibility.
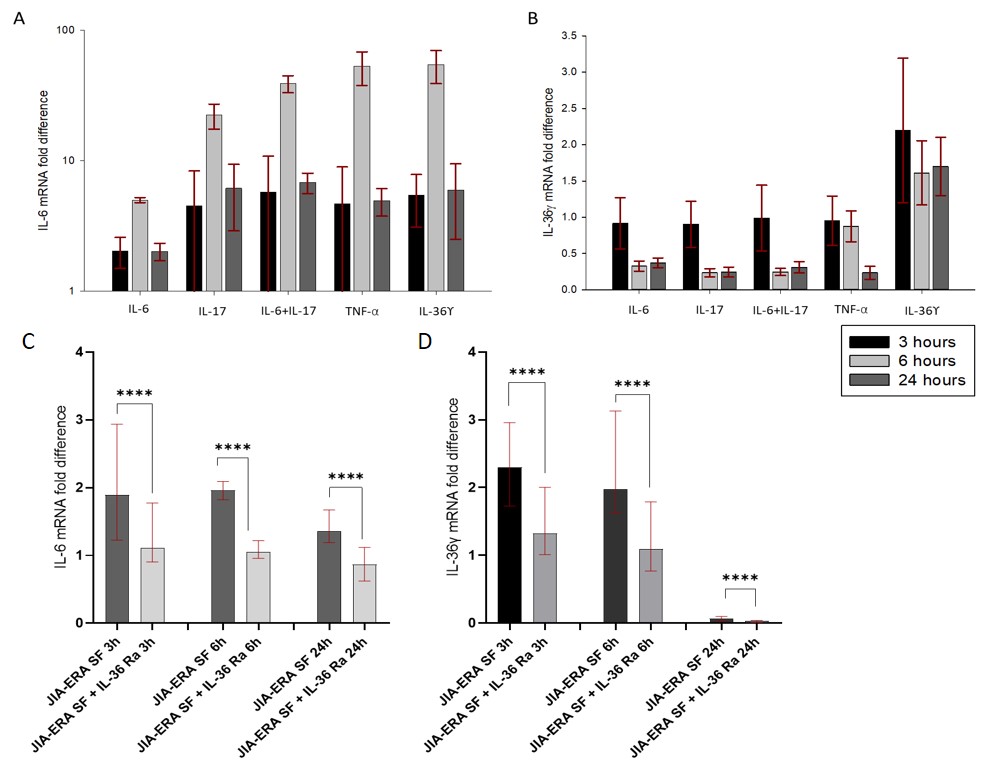 Figure: Fold difference in mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL_36γ in FLS post stimulation. (A) mRNA expression of IL-6 upon stimulation of FLS with pro-inflammatory cytokines. (B) mRNA expression of IL_36γ upon stimulation of FLS with pro-inflammatory cytokines. (C) mRNA expression of IL-6 in FLS upon stimulation with SF from JIA-ERA patients in presence or absence of IL_36Ra. (D) mRNA expression of IL_36γ in FLS upon stimulation with SF from JIA-ERA patients in presence or absence of IL_36Ra.
Figure: Fold difference in mRNA expression of IL-6 and IL_36γ in FLS post stimulation. (A) mRNA expression of IL-6 upon stimulation of FLS with pro-inflammatory cytokines. (B) mRNA expression of IL_36γ upon stimulation of FLS with pro-inflammatory cytokines. (C) mRNA expression of IL-6 in FLS upon stimulation with SF from JIA-ERA patients in presence or absence of IL_36Ra. (D) mRNA expression of IL_36γ in FLS upon stimulation with SF from JIA-ERA patients in presence or absence of IL_36Ra.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aggarwal A, Majumder S, Guleria S. Synovial Fluid IL-36γ in Patients with Enthesitis Related Arthritis (ERA) Correlates with Disease Activity and Leads to Production of IL-6 by Fibroblast Like Synoviocytes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-il-36%ce%b3-in-patients-with-enthesitis-related-arthritis-era-correlates-with-disease-activity-and-leads-to-production-of-il-6-by-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-il-36%ce%b3-in-patients-with-enthesitis-related-arthritis-era-correlates-with-disease-activity-and-leads-to-production-of-il-6-by-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes/
