Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lung tissues from patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) have greater levels of malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts (MAA) that co-localize with citrullinated (CIT) and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins compared to lung tissues from individuals with RA without lung disease or other forms of ILD. Moreover, stimulation of macrophages with MAA- and CIT-modified fibrinogen (FIB) induces the release of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) that activates joint fibroblast. Along with PDGF-BB, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) has emerged as a pivotal mediator in promoting fibrotic responses in human lung fibroblasts (HLF). The objective of this study was to assess the potential of macrophages derived from patients with RA-ILD to elicit the release of PDGF-BB or TGF-β in response to stimulation with MAA and/or CIT modified proteins, and subsequently to evaluate their impact upregulation downstream pro-fibrotic markers in HLF.
Methods: PBMCs were isolated from 3 healthy donors and 4 patients with RA-ILD. PBMCs were differentiated into M0 macrophages (MP) and stimulated with 25μg/mL of unmodified FIB, FIB-MAA, FIB-CIT, or FIB-MAA-CIT. Supernatants were collected (MP-SN) and measured for PDGF-BB and TGF-β using ELISA. HLF cells were then treated with MP-SN for 8-hours. HLF expression of collagen 6 (Col6A3) and metalloproteinase-12 (MMP12) was quantified using RT-PCR as the fold increase relative to stimulation with MP-SNFIB. Statistical analyses included t-tests between healthy controls and RA-ILD patients, and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for intergroup comparisons.
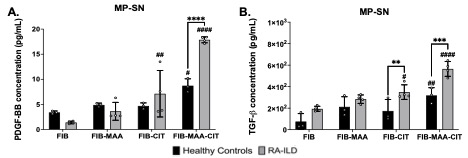
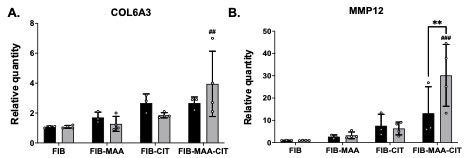
Results: MP-SN generated from FIB-MAA-CIT stimulation showed significantly higher concentrations of TGF-β and PDGF-BB compared to MP-SN generated from stimulations with all other antigens in both controls and patients RA-ILD (Fig. 1; p< 0.05). Moreover, concentrations of TGF-β and PDGF-BB were higher in most supernatants derived from RA-ILD macrophages compared to those from controls, a difference that reached significance for MP-SNFIB-MAA-CIT (p< 0.0001 for both) and MP-SNFIB-CIT (p< 0.001 for TGF-β). Stimulation of HLF cells with MP-SNFIB-MAA-CIT derived from patients with RA-ILD resulted in substantial 4- and 30-fold increases in expression of COL6A3 and MMP12, respectively (Fig.2). Notably, only MMP12 upregulation reached statistical significance in HLF cells stimulated with MP-SN derived from RA-ILD vs. controls (p< 0.01).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that macrophages stimulated with FIB-MAA-CIT exhibit the greatest release of PDGF-BB and TGF-β. Notably, this response was augmented in macrophages derived from patients with RA-ILD when compared to controls. The presence of PDGF-BB and TGF-β in the MP-SN suggests a role in activating fibrotic responses in HLFs. Moreover, our findings suggest that MAA and CIT modifications conspire, playing a pivotal role in instigating fibrotic pathways in RA-ILD pathogenesis, mediated through macrophage release of TGF-β and PDGF-BB. Thus, targeting the formation MAA and CIT modified proteins or inhibiting PDGF-BB or TGF-β could represent a promising therapeutic approach for RA-ILD treatment.
Abbreviations: CIT, citrulline; FIB, fibrinogen; MAA, malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts; MP, macrophages derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PDGF-BB, platelet derived growth factor isoform BB; RA-ILD, rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease; SN, supernatants; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.
Abbreviations: CIT, citrulline; COL6A3, type 6 collagen; FIB, fibrinogen; MAA, malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts; MMP12, metalloproteinase 12; MP, macrophages derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PDGF-BB, platelet derived growth factor isoform BB; RA-ILD, rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease; SN, supernatants; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aripova N, Duryee M, England B, Hunter C, Klingemann L, Aripova N, Nelson A, Poole J, Katafiasz D, Bailey K, Thiele G, Mikuls T. Supernatants from Macrophages Stimulated with Citrullinated and MAA-Modified Fibrinogen Contain PDGF-BB and TGF-b and Upregulate Fibrotic Markers in Human Lung Fibroblasts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/supernatants-from-macrophages-stimulated-with-citrullinated-and-maa-modified-fibrinogen-contain-pdgf-bb-and-tgf-b-and-upregulate-fibrotic-markers-in-human-lung-fibroblasts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/supernatants-from-macrophages-stimulated-with-citrullinated-and-maa-modified-fibrinogen-contain-pdgf-bb-and-tgf-b-and-upregulate-fibrotic-markers-in-human-lung-fibroblasts/