Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Our observational cohort study aimed at assessing the effectiveness and safety of the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib in refractory IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD).
Methods: Seven patients admitted to the Rheumatology and Immunology Department of Peking University People’s Hospital were enrolled. All the patients fulfilled the 2019 American College of Rheumatology(ACR)/ European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) classification criteria for IgG4-RD. Refractory IgG4-RD was defined to be resistant to conventional treatment of at least 3 months’ duration. Patients received tofacitinib twice daily, with simultaneous continuation of immune-suppressants and glucocorticoids. They were followed-up for the shortest 3 months and the longest 12 months by the same medical team. At each visit, IgG4-RD responder index (IgG4-RD RI) 5, physician’s global assessment (PGA), serum IgG4 levels (≥201mg/dL) and adverse events (AEs) were measured and assessed. Clinical remission was assessed by evaluating the changes of IgG4-RD RI scores.
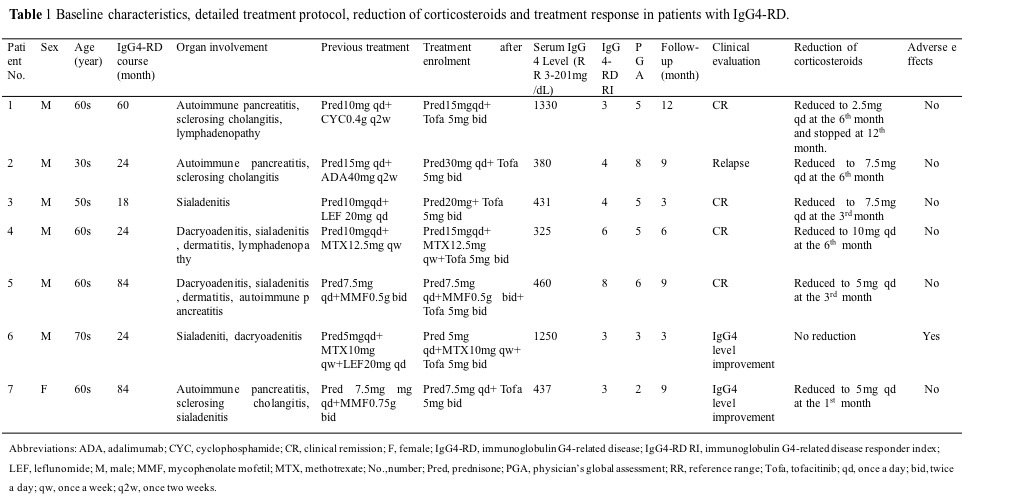
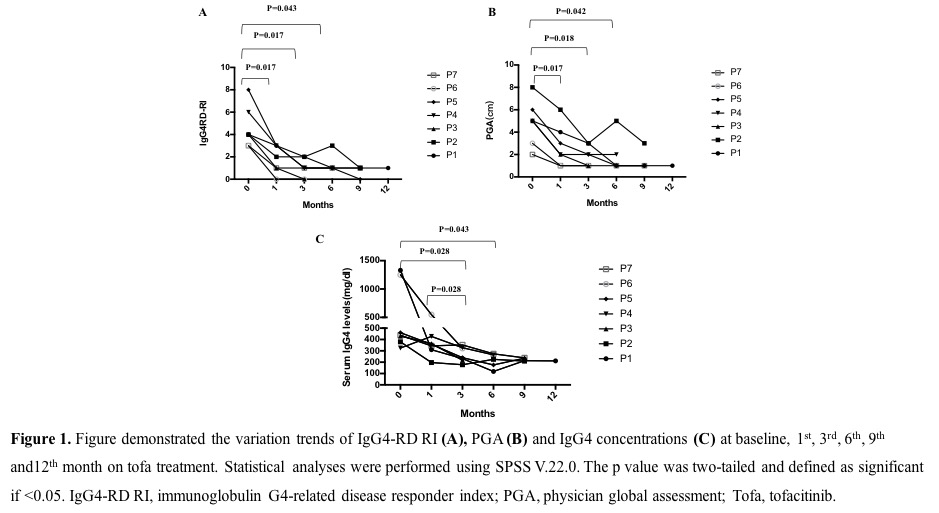
Results: The demographic data and clinical features of the seven patients are described in table 1. Prednisone were increased from 5-10mg/d to 15-20mg/d in 4 patients with clinical recurrence at entry and the other three received previous steroids dose. Concomitant immunosuppressive treatment was continued or withdrawn. Four patients received clinical remission and two patients achieved serum IgG4 concentration improvement after tofacitinib treatment; one experienced a flare during the follow-up (table 1). All patients tapered their baseline prednisone dose, with 4 patients receiving doses less than or equal to 5 mg/day, and 1 even withdrawing steroids during the follow-up(table 1). Both IgG4-RD RI score (p=0.017, p=0.017, p=0.043, respectively) and PGA (p=0.017, p=0.018, p=0.042, respectively) were significantly improved at 1st, 3rd and 6th month (figure 1A, B). Three patients (Patients 3, 5 and 6) achieved complete remission with IgG4-RD RI scores of 0 during the follow-up. Except the improvement of clinical manifestations, the serum IgG4 levels declined significantly at 3 months (p=0.028) and 6 months (p=0.043) (figure 1C). In addition, serum IgG4 levels decreased at 3rd month when compared to their levels at 1st month (p=0.028) (figure 1C). The serum IgG4 levels of patient 6 dramatically decreased from 1250mg/dL to 549 mg/dL at 1st month after tofacitinib therapy without steroid increase. Except for one patient who suffered an activation of herpes varicella zoster without serious prognosis, no probable drug-related adverse effect was reported among our other patients enrolled in the study during the follow-up visits (table 1).
Conclusion: Our results proved that tofacitinib was effective for the treatment of refractory IgG4-RD, sparing steroid to reach clinical remission. Tofacitinib offers a promising treatment approach to IgG4-RD. Findings from this study may inform future’s studies of other small-molecular targeted drugs for the treatment of IgG4-RD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhu H, Tang S, Li Y, Sun F, Gan Y, Ye H. Successful Treatment of Refractory IgG4-Related Disease with Tofacitinib: Experiences from 7 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/successful-treatment-of-refractory-igg4-related-disease-with-tofacitinib-experiences-from-7-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/successful-treatment-of-refractory-igg4-related-disease-with-tofacitinib-experiences-from-7-patients/