Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects - Poster II: Co-morbidities and Complications
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The excess risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in patients with inflammatory joint diseases (IJD) is attributable to several risk factors, including a high prevalence of hypertension. However, there is limited knowledge on the effect of antihypertensive treatment (a-HTT) in these patients. Our objective was to initiate a-HTT when indicated and treat to guideline recommended blood pressure (BP) goal in IJD patients. We also aimed to evaluate the effect of a-HTT in this patient population, and which factors were associated with BP goal attainment.
Methods: Patients with IJD (n=765) were referred from a rheumatology outpatient clinic or general practitioners to a preventive cardio-rheuma clinic. All patients underwent a CVD risk evaluation, including BP measurements (performed using and Omron M7 apparatus). Antihypertensive treatment was initiated in accordance with guidelines, and the BP treatment goal was <140/90 mmHg.
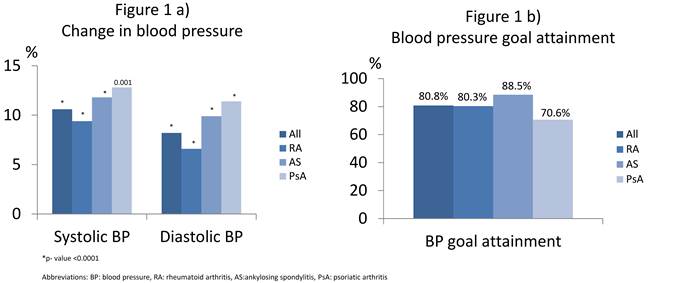
Results: Of the 765 IJD patients referred (rheumatoid arthritis n= 450, ankylosing spondylitis n=210 and psoriatic arthritis n=105), 104 (13.6%) had an indication for BP lowering, while 224 (29.3%) were already using a-HTT at the first consultation. For those where a-HTT was initiated at baseline (n=104), there was a highly significant change in BP from first to final consultation (Fig 1a). BP goal was achieved in 84 (80.8%) patients (Fig 1b), using mean±SD 3.1±1.7 consultations. Dose adjustments was done in 38 (36.5%) of the patients with median (IQR) a-HTT dose adjustments of 1 (1, 1.25). In 9 (8.7%) patients the a-HTT was changed. Systolic BP (p <0.0001), but not use of anti-rheumatic medication or inflammatory biomarkers at baseline, was significantly associated with BP goal attainment in age- and sex adjusted logistic regression analyses. Patients with the lowest systolic BP were more likely to achieve BP goals. For patients already on a-HTT (n=224), only 52.7% had a BP <140/90 mmHg at baseline. After up titration or change of a-HTT, the percentage of patients achieving BP goal in this group increased to 82.6%.
Conclusion: This is to our knowledge the first prospective report on success rate of BP goal achievement in patients with IJD. Approximately 80% reached BP target, which is even a higher proportion than what is shown in the general population. Treatment to BP goal is feasible in patients with IJD, and is not complicated by inflammation or use of anti-rheumatic medication.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rollefstad S, Norheim P, Ikdahl E, Semb AG. Success Rate of Blood Pressure Goal Achievement in Patients with Inflammatory Joint Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/success-rate-of-blood-pressure-goal-achievement-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/success-rate-of-blood-pressure-goal-achievement-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-diseases/