Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) are a heterogeneous group of autoimmune diseases primarily affecting skeletal muscle, with potential involvement of other organs. They are classified into five distinct subsets: dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), inclusion body myositis (IBM), immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), and anti-synthetase syndrome (ASyS). Diagnosing IIMs remains challenging due to overlapping clinical features and limitations in current diagnostic modalities. Emerging evidence implicates Type 1 interferons (IFNs), particularly in the pathogenesis of DM. Identifying IFN-related markers in muscle biopsies may enhance diagnostic precision and guide targeted therapy.
Methods: A cross-sectional observational study was conducted involving patients who met the 2017 EULAR/ACR classification criteria or the Bohan and Peter criteria for IIMs. Muscle biopsy samples were analyzed via immunohistochemistry for the expression of Type 1 IFN-inducible genes—Myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA), Interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), and Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I). The expression patterns of these markers were compared between DM and non-DM IIM subgroups.
Results: The study included 50 patients: 25 with DM and 25 with non-DM IIMs (18 IMNM, 4 ASyS, 2 IBM, and 1 PM). A distinct differential expression of all three Type 1 IFN markers was observed, with significantly higher expression in the DM group.In DM patients, MxA expression was predominantly perifascicular, while ISG15 and RIG-I showed focal or scattered sarcoplasmic distribution.Thirteen DM patients were myositis-specific antibody (MSA) negative; a majority of these exhibited significant expression of Type 1 IFN markers.MHC Class I upregulation was observed in all DM cases and in 84% of non-DM cases.Among seven DM patients negative for perifascicular atrophy (PFA), six showed positive expression of at least one Type 1 IFN marker.Of the four ASyS patients, all were PFA-positive, but only one exhibited Type 1 IFN expression.These findings highlight the pathological relevance of Type 1 IFN markers, suggesting they may offer superior specificity for DM diagnosis compared to traditional histopathological features like PFA.
Conclusion: This study underscores the diagnostic utility of Type 1 IFN markers—MxA, ISG15, and RIG-I—in distinguishing DM from other IIMs. Among these, MxA showed the most pronounced differential expression and demonstrated sensitivity and specificity comparable to PFA. Notably, MxA was positive in 72% of MSA-negative DM cases. While PFA remains a hallmark of DM, our findings suggest that IFN markers, particularly MxA, may serve as valuable adjuncts or alternatives in diagnostic evaluation. These insights support the incorporation of IFN markers into routine histopathological assessment and highlight their potential role in advancing precision medicine for DM.
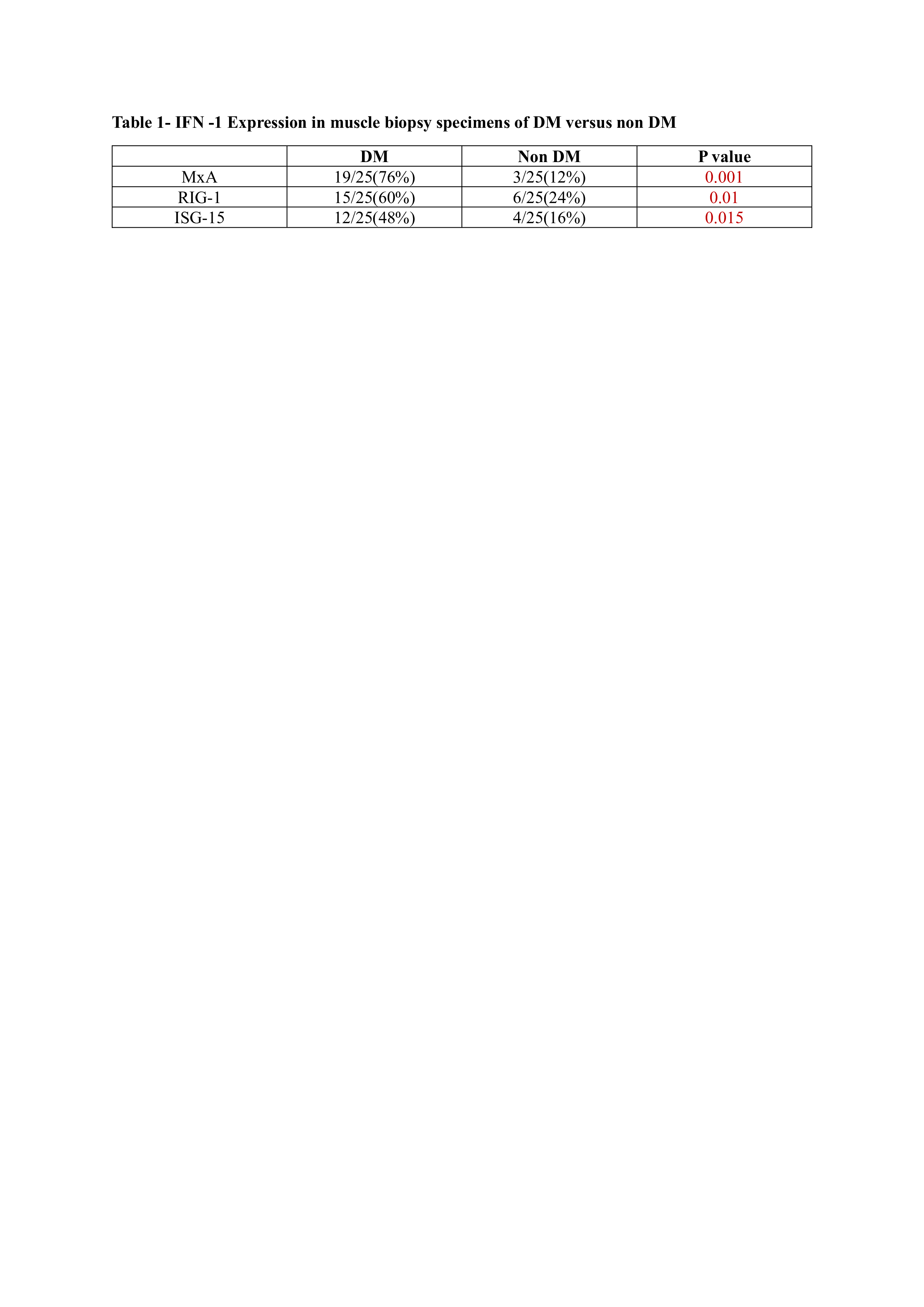 Expression in muscle biopsy specimens of DM and Non DM
Expression in muscle biopsy specimens of DM and Non DM
.jpg) IFN-1 expression in MSA negative subset of DM
IFN-1 expression in MSA negative subset of DM
.jpg) Histopathological images showing all 3 IFN-1 markers
Histopathological images showing all 3 IFN-1 markers
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
sosigowda p, D P, Uppin M, rajasekhar L. Study Of Type -1 Interferon Gene Signature Markers In Muscle Biopsy Samples Of Patients With IIM [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/study-of-type-1-interferon-gene-signature-markers-in-muscle-biopsy-samples-of-patients-with-iim/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/study-of-type-1-interferon-gene-signature-markers-in-muscle-biopsy-samples-of-patients-with-iim/
