Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) can lead to neuropsychiatric manifestations including cognitive impairment (CI). The gold standard for assessment of SLE cognitive function is the American College of Rheumatology comprehensive neuropsychological battery (NB), which was introduced in 1996 and assesses 6 cognitive domains. COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) define structural validity as “the degree to which the scores of an instrument are an adequate reflection of the dimensionality of the construct being measured”. Our primary aims were to explore the number of latent factors encompassed by the NB and assess the battery’s structural validity, i.e., determine if identified latent factors can be mapped to NB’s intended cognitive domains.
Methods: 300 consecutive consenting SLE patients aged 18-65 years attending a single center, were enrolled (Jul 2016 – Nov 2019) and completed the NB. The NB includes the following tests: Finger tapping, Trail Making Test A and B, Stroop Color and Word Test, Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT), Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT), Animal Naming, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test – Revised (HVLT-R), Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Digit Symbol Substitution Test (WAIS III), Letter-Number Sequencing, and Consonant Trigrams.Structural validity was examined with exploratory factor analysis (EFA) using squared multiple correlations as prior communality estimates. The maximum likelihood method was used to extract factors, followed by a varimax (orthogonal) rotation. A scree plot was developed to examine the underlying factors of NB. Factors with Eigenvalues of >1 were extracted. The sample size met standards for EFA of more than 100 participants or at least 5 times the number of variables being analyzed. A multiple imputation model was used to account for missing data.
Results: 300 participants entered the cohort (89.0% female, mean age at enrollment 41.1±12.1 years, mean disease duration 14.1±10.0 years) (Table 1). 54 (18.0%) of patients had at least one test score missing.
EFA model fitting indicated a six-factor model as the best fit, with Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) -24 and Tucker and Lewis Reliability Coefficient of 95% comparing to models with less or more factors. The choice of model was confirmed with Scree and Variance Explained plots with cumulative variance of 100% explained by six factors (Figure 1).
Individual NB tests primarily loaded on the factors representing the intended cognitive domains (Table 2), although the strength of weights of individual tests varied within each factor. The one exception was Consonant Trigrams, which loaded on the Memory factor, although its second highest loading was on its intended factor.
Conclusion: EFA indicates that a six-factor model fits the structure of the NB. The factors identified by EFA closely resemble the structure of the 1996 NB and confirms its structural validity. Variations in strength of weights raises the possibility of reducing the number of tests to those with the highest loadings, which might increase the feasibility of administering the NB.
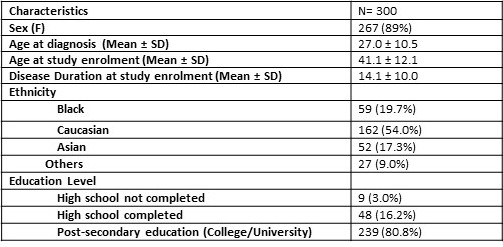 Table 1- Patient demographics at enrolment
Table 1- Patient demographics at enrolment
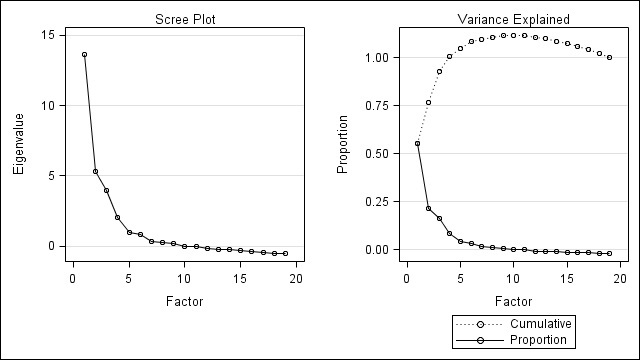 Figure 1. Scree and Variance Plots confirming a 6 factor model
Figure 1. Scree and Variance Plots confirming a 6 factor model
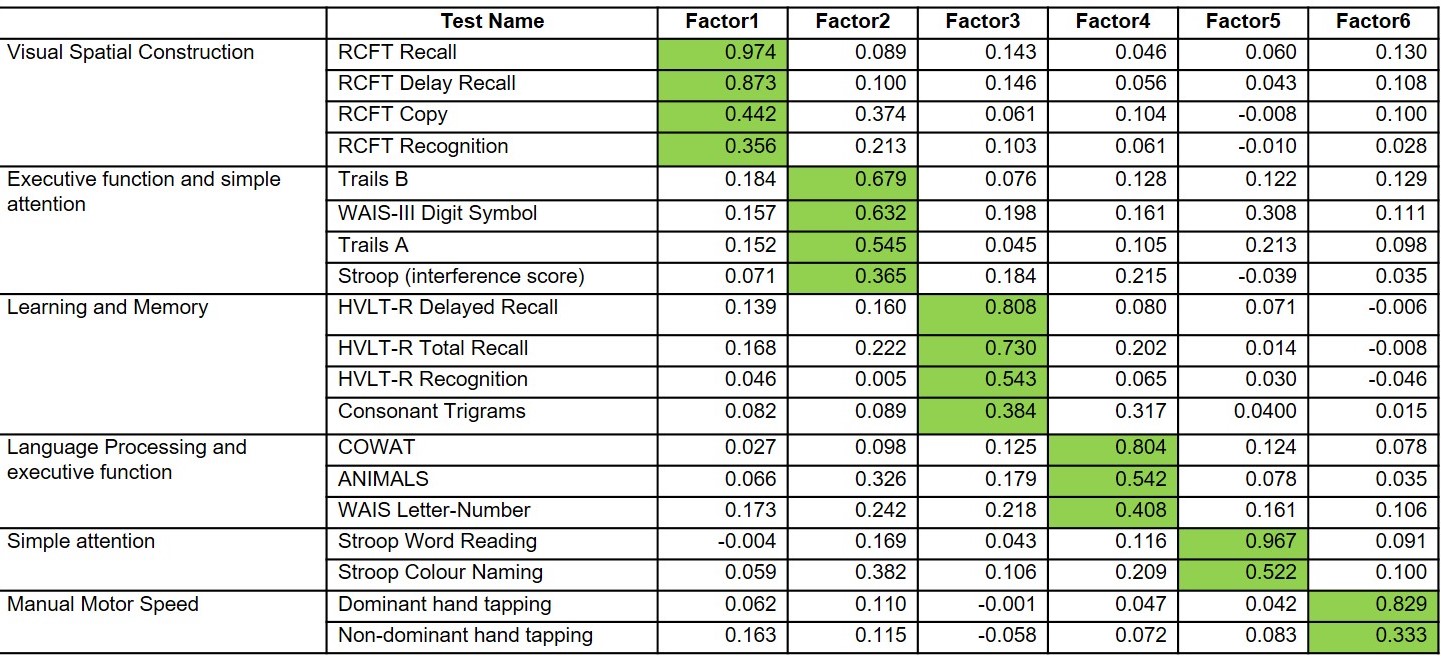 Table 2. EFA model fitting with 6 factors Abbreviations: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT), Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT), Animal Naming, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test – Revised (HVLT-R), Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Digit Symbol Substitution Test (WAIS III)
Table 2. EFA model fitting with 6 factors Abbreviations: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT), Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT), Animal Naming, Hopkins Verbal Learning Test – Revised (HVLT-R), Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Digit Symbol Substitution Test (WAIS III)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moghaddam B, Green R, Beaton D, Bingham K, Kakvan M, Ruttan L, Tartaglia C, Fritzler M, Choi M, Su J, Diaz-Martinez J, Bonilla D, Anderson N, Wither J, Katz P, Touma Z. Structural Validity of a Comprehensive Neuropsychological Battery for Assessment of Cognitive Impairment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Exploratory Factor Analysis Confirms Six Cognitive Domains [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-validity-of-a-comprehensive-neuropsychological-battery-for-assessment-of-cognitive-impairment-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-exploratory-factor-analysis-confirms-six-cognitive-domains/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/structural-validity-of-a-comprehensive-neuropsychological-battery-for-assessment-of-cognitive-impairment-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-exploratory-factor-analysis-confirms-six-cognitive-domains/
