Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Accurate assessment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) disease activity in clinical practice requires a feasible, continuous, multidimensional composite instrument to assess key domains of this heterogeneous disease. While currently available composite tools used in PsA, including the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Composite Exercise (GRACE) and the PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS), are useful in clinical trials, their complexity and time required to complete limit their use in clinical practice.1 Abbreviated instruments, known as 3 visual analogue scale (VAS) and 4VAS, have demonstrated good performance in an observational study, but further testing was recommended.2 The purpose of this analysis is to explore the correlation between 3VAS or 4VAS and GRACE, PASDAS and measures of quality of life using data from COSMOS.
Methods: The Phase 3b COSMOS study assessed guselkumab (GUS) 100mg Q8W versus placebo (PBO) in tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) inadequate response (IR, inadequate efficacy or intolerance) pts with active PsA.3 Pts who received PBO crossed over to GUS at either Week (W) 16 (early escape [EE], n=45/96) or W24 (planned, n=51/96). Each domain of the 3VAS (physician global, pt global, pt skin) and 4VAS (physician global, pt pain, pt joint, pt skin) was evaluated using a 0–10 VAS (higher score=more active disease), and calculated mean scores were plotted over time in a pt-continuer population (those with W0 and W48 data). Pearson correlation assessed relationships between observed values over time for 3VAS/4VAS versus GRACE, PASDAS, the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and the 36-item Short Form Health Survey Physical Component Summary (SF-36 PCS) score.
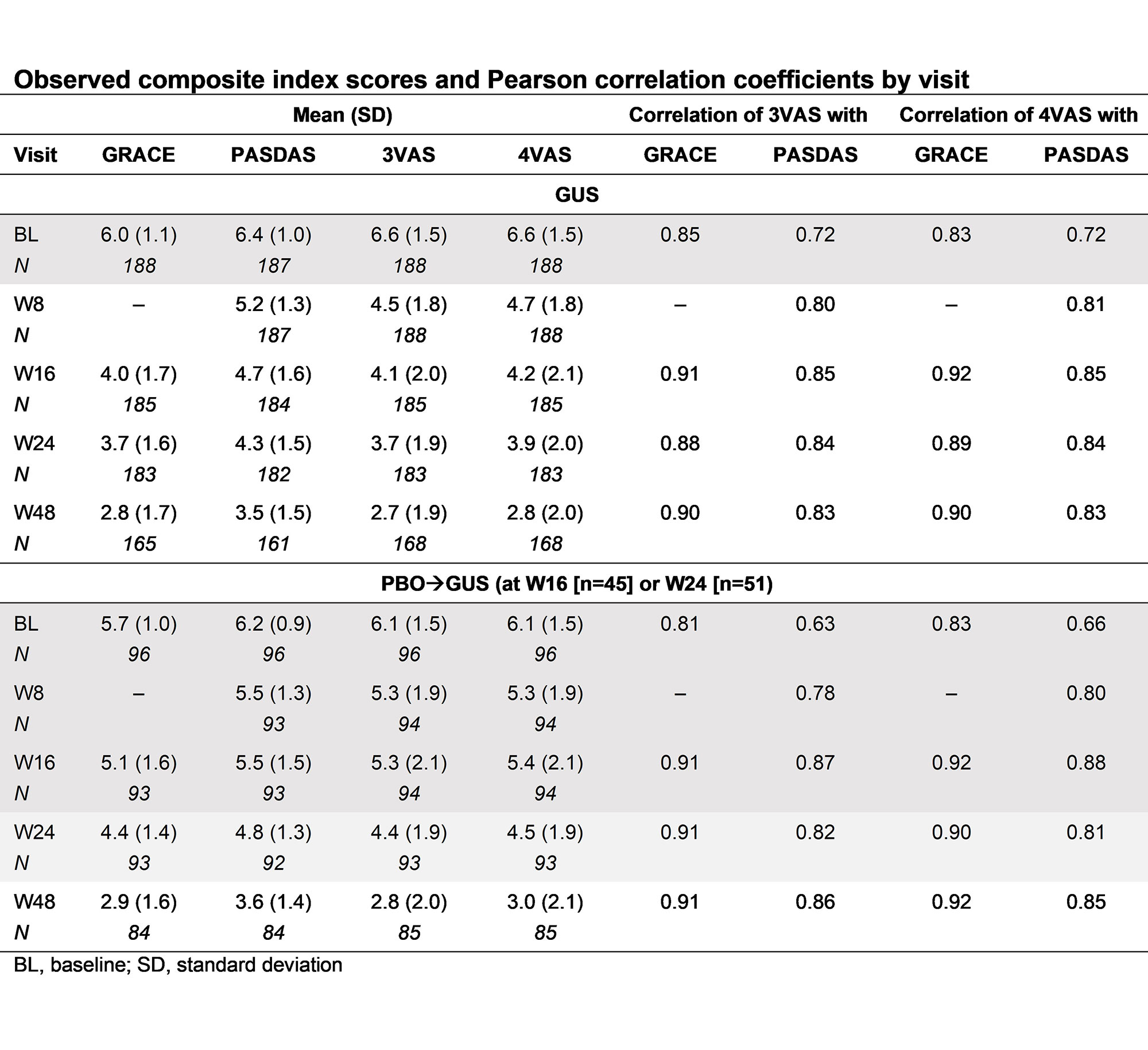
Results: Data from 285 pts were examined (GUS, n=189; PBO, n=96). Substantial improvements ( >45%) were seen in GRACE, PASDAS, 3VAS and 4VAS scores through W48 in GUS‑treated pts (Table), with separation from PBO as early as W8 (Fig). Strong correlations between 3VAS/4VAS and GRACE (r=0.83–0.92)/PASDAS (r=0.72–0.85) were observed in GUS-randomized pts at each visit (Table). 3VAS/4VAS showed moderate correlation with HAQ-DI (r=0.45–0.63) and SF-36 PCS (r=–0.40 to –0.65). Consistent results were observed in PBOàGUS pts.
Conclusion: In these TNFi-IR pts, GUS treatment led to substantial improvements in PsA disease activity through 1 year using several composite indices. All indices, including the 3VAS/4VAS, allowed early discrimination between the GUS and PBO cohorts. The strong correlation between 3VAS/4VAS and GRACE/PASDAS in this pt population is promising and highlights that abbreviated composite indices can provide an accurate assessment of disease activity that may, because of better feasibility, lead to a wider use of such instruments and thus improve pt care. As a next step, thresholds for disease states should be further evaluated.
References
1. Tillett W et al. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2020;96:11–8
2. Tillett W et al. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2021;97:45–9
3. Coates LC et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 (epub)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tillett W, Coates L, Sharaf M, Neuhold M, Theander E, Bergmans P, Shawi M, Perate M, Contré C, Helliwell P. Strong Correlation Between Short- vs Long-form Composite Measures of Psoriatic Arthritis Disease Activity in a TNFi-IR Population Treated with Guselkumab: Data from the Phase 3b COSMOS Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strong-correlation-between-short-vs-long-form-composite-measures-of-psoriatic-arthritis-disease-activity-in-a-tnfi-ir-population-treated-with-guselkumab-data-from-the-phase-3b-cosmos-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/strong-correlation-between-short-vs-long-form-composite-measures-of-psoriatic-arthritis-disease-activity-in-a-tnfi-ir-population-treated-with-guselkumab-data-from-the-phase-3b-cosmos-trial/