Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baseline and cumulative inflammation have both been associated with increased cardiovascular event (CVE) risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Statin therapy reduced systemic inflammation, attenuated coronary atherosclerosis progression and promoted plaque calcification and stabilization1 both in general as well as RA patients. We here explored whether baseline statin use influenced the impact of baseline C-reactive protein (CRP) on long-term cardiovascular risk in patients with RA.
Methods: We evaluated 4,357 patients without known cardiovascular disease upon registration to An International Cardiovascular Consortium for people with RA (ATACC-RA) and who were followed prospectively. The primary outcome was ischemic CVE defined as the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, coronary revascularization, stable angina pectoris, transient ischemic attack, and peripheral arterial disease with or without revascularization. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation with 10 repetitions. Multivariable Cox models stratified by center evaluated the effect of natural logarithm of CRP, statin use and their interaction on CVE risk after adjusting for age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, family history, smoking, age at RA diagnosis, and total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein (TC/HDL)ratio. A sensitivity analysis was performed using inverse probability of treatment weights to balance differences between statin treated and untreated patients.
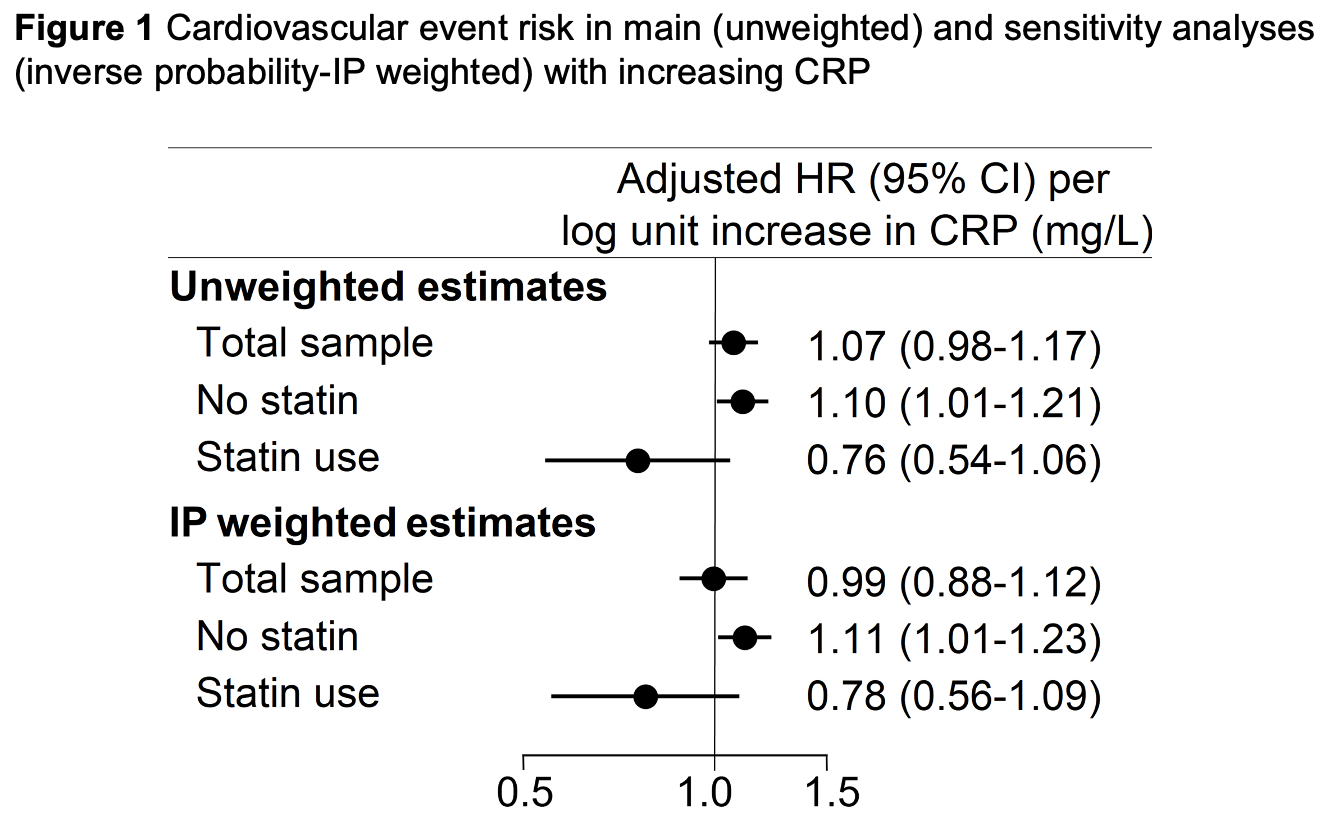
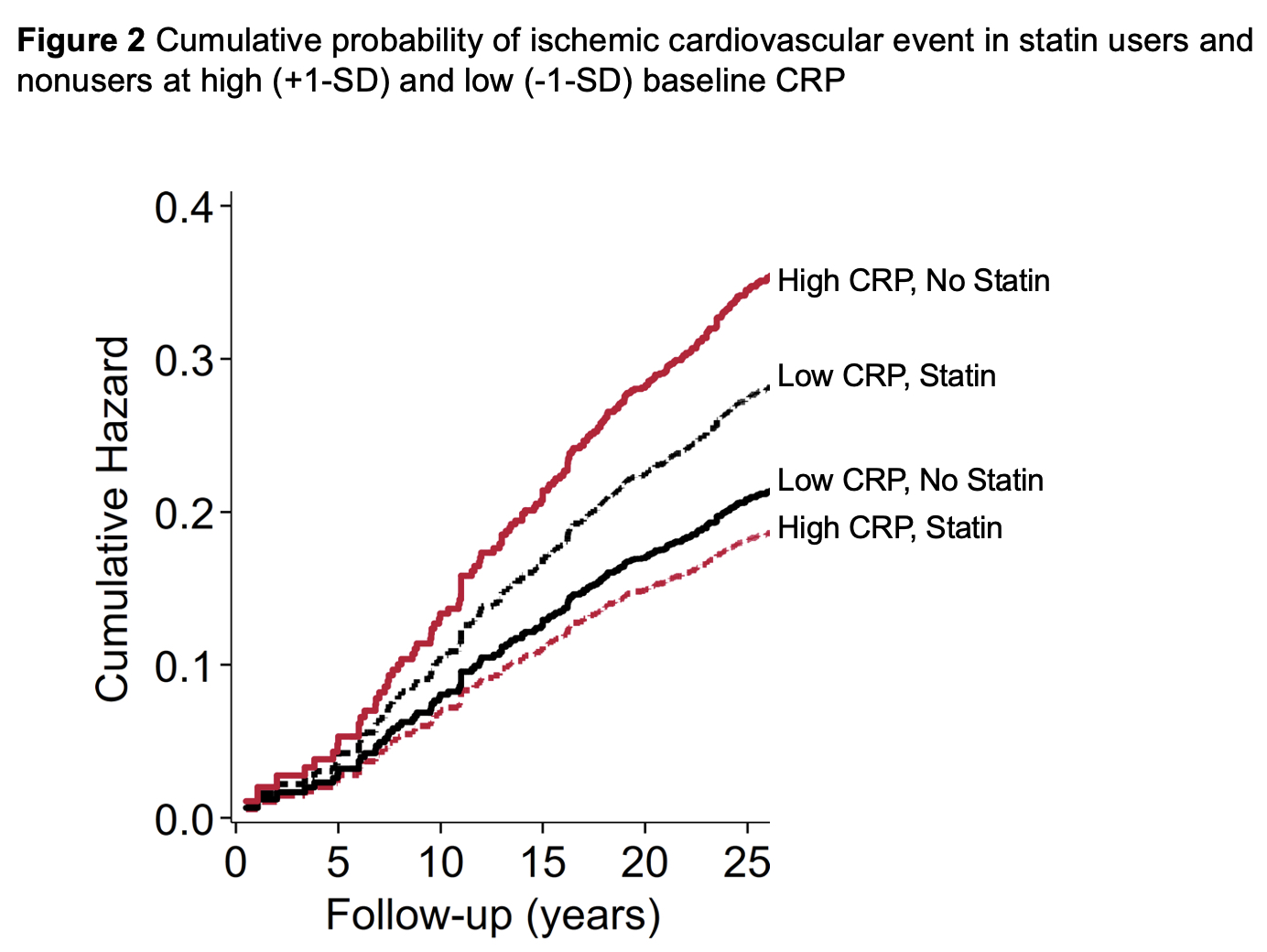
Results: At baseline 462 patients were treated with statins whereas 3,895 were not. Statin therapy inversely associated with low density lipoprotein cholesterol (p< 0.001), TC/HDL ratio (p< 0.001) and CRP(ln) (p=0.048). Over 26,356 patient years (PY) of follow-up, 361 total ischemic CVE were recorded, 321 over 24,235 PY in statin nonusers and 40 over 2,121 PY in statin users. Incidence of any ischemic CVE was 13.3 (95% CI 11.9-14.8)/1000PY among statin nonusers and 18.9 (95% CI 13.8-25.7)/1000PY in statin users (incidence rate difference 5.62 [95% CI -0.41 to 11.64]). In the entire cohort, baseline CRP(ln) was not associated with ischemic CVE risk, [adjusted hazards ratio- aHR 1.07 (95% CI 0.98-1.17), p=0.138]. However, higher CRP(ln) associated with greater risk of the composite outcome exclusively in statin nonusers [aHR 1.10 (95% CI 1.01-1.21), p=0.036] but not in statin users (p-interaction=0.032, Figures 1 and 2). While CRP(ln) was not different between statin groups after inverse probability weighting adjustment (p=0.333), the sensitivity analysis yielded similar results: higher CRP(ln) associated with greater ischemic CVE risk in statin nonusers [aHR 1.11 (95% CI 1.01-1.22), p=0.030] but not among statin users (p-interaction=0.046).
Conclusion: Higher inflammation at baseline associated with greater risk of any ischemic CVE among statin nonusers but not in users. This points to the potential of statin-specific effects directly on atherosclerotic plaque—such as lower progression and stabilization1—above and beyond effects on cholesterol metabolism and systemic inflammation.
Reference: Karpouzas GA et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022;61(5):1857-1866
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Ormseth S, Van Riel P, Myasoedova E, Gonzalez-Gay M, Corrales A, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Sfikakis P, Dessein P, Tsang L, Hitchon C, El Gabalawi H, Pascual Ramos V, Contreras Yañez I, Colunga I, Galarza-Delgado D, Azpiri-López J, Rolefstad S, Semb A, Misra D, Kitas G, Hauge E. Statin Use Attenuates the Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Ischemic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/statin-use-attenuates-the-impact-of-systemic-inflammation-on-ischemic-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/statin-use-attenuates-the-impact-of-systemic-inflammation-on-ischemic-cardiovascular-risk-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/