Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is an intricate interplay between the microbiome and the immune response impacting the development of normal immunity and autoimmunity. However, we do not fully understand how the microbiome affects the production of natural-like and pathogenic autoantibodies. Peptidoglycan (PGN) is a component of the bacterial cell wall that is highly antigenic. PGNs from different bacteria can differ in their immune regulatory activities.
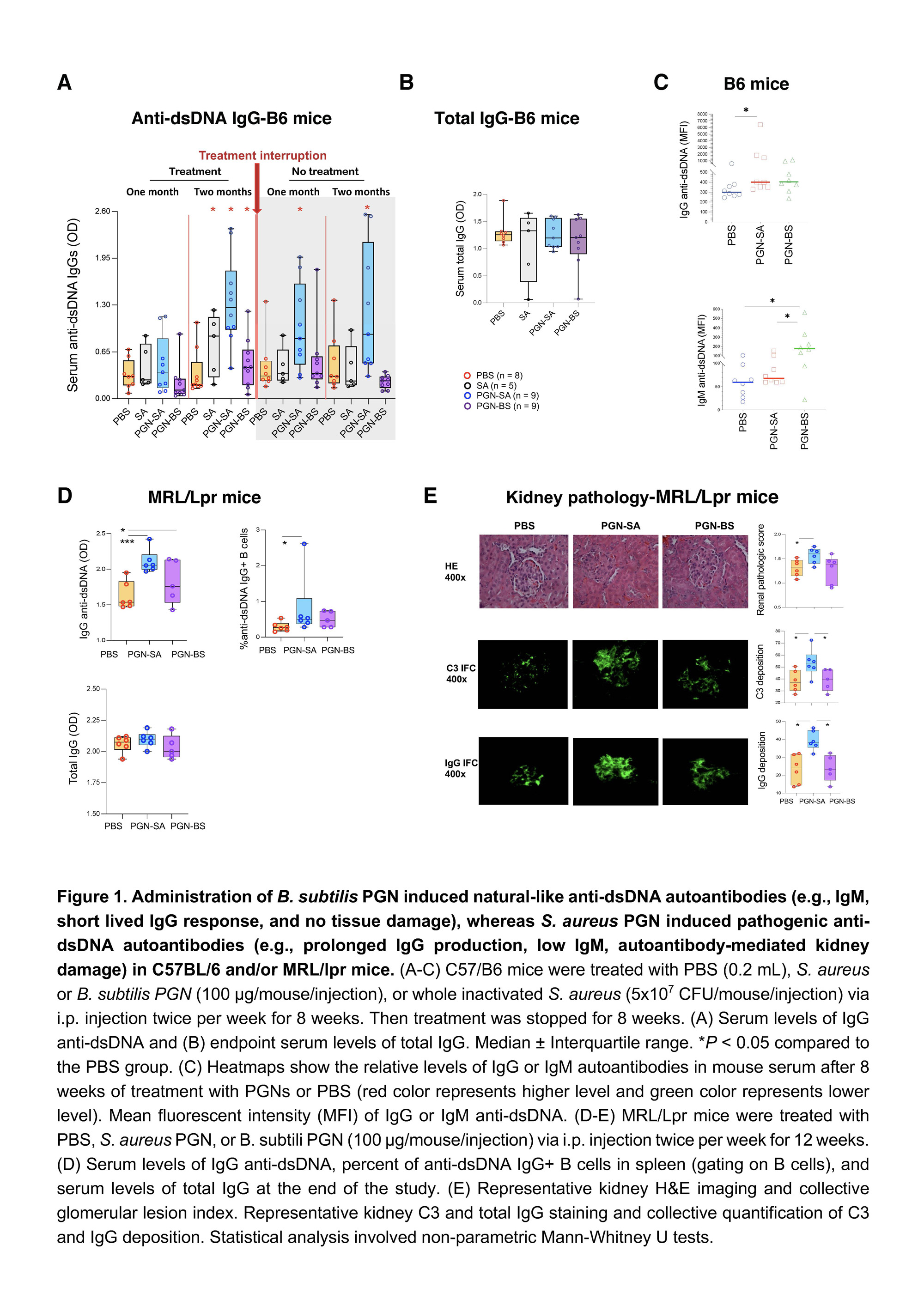
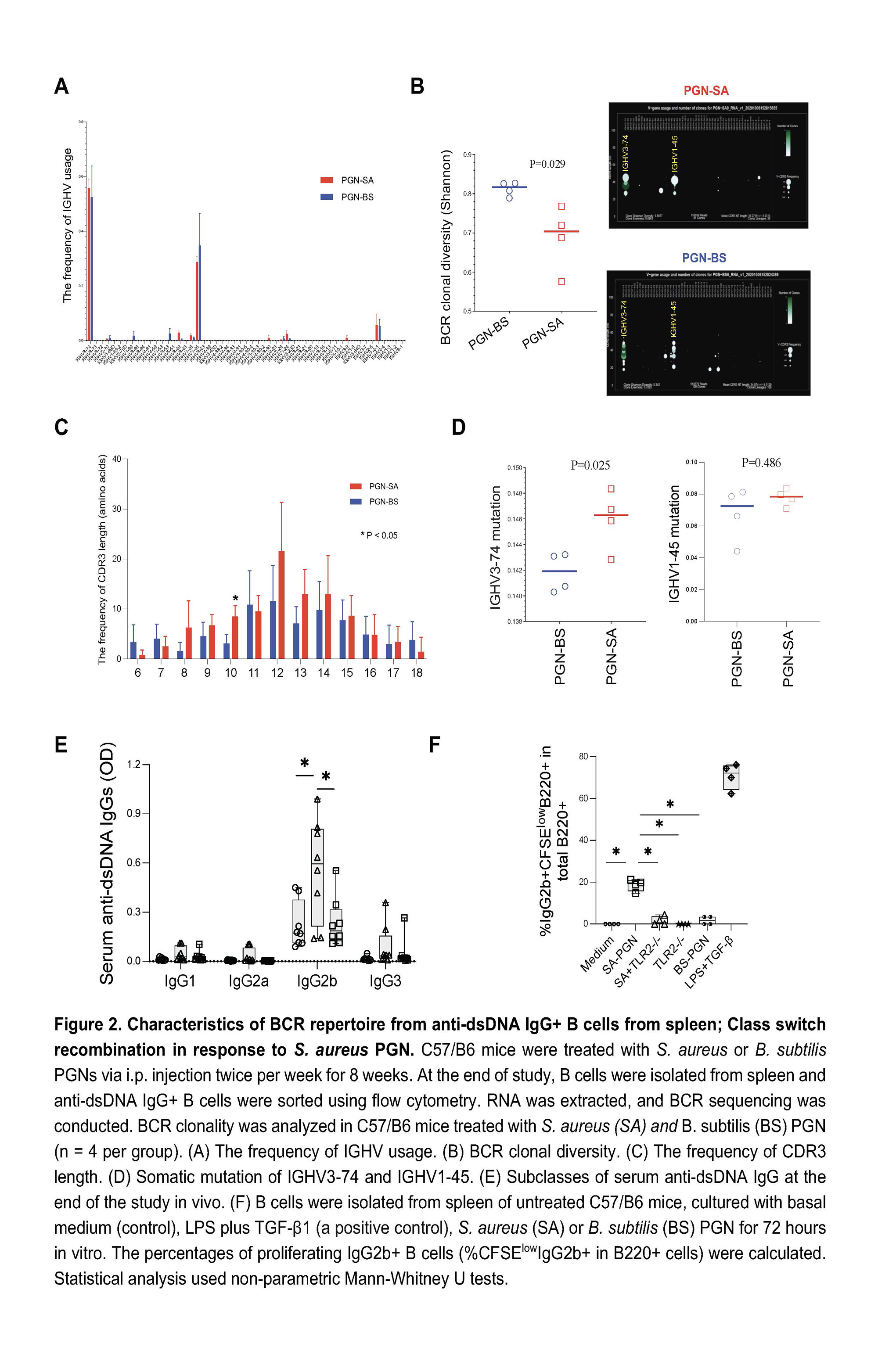
Methods: Female C57BL/6 and MRL/lpr mice were intraperitoneally injected (i.p.) with PBS, Staphylococcus aureus PGN, or Bacillus subtilis PGN (100 μg/time). C57BL/6 mice (6-week-old) were treated with PGNs and PBS twice per week for 8 weeks; then the treatment was stopped for another 8 weeks. MRL/lpr lupus-prone mice (6-week-old) were treated with PBS and PGNs twice per week for 12 weeks. Spleen anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) IgG+ B cells were sorted for B-cell receptor sequencing. Serum autoantibody levels and kidney damage were analyzed.
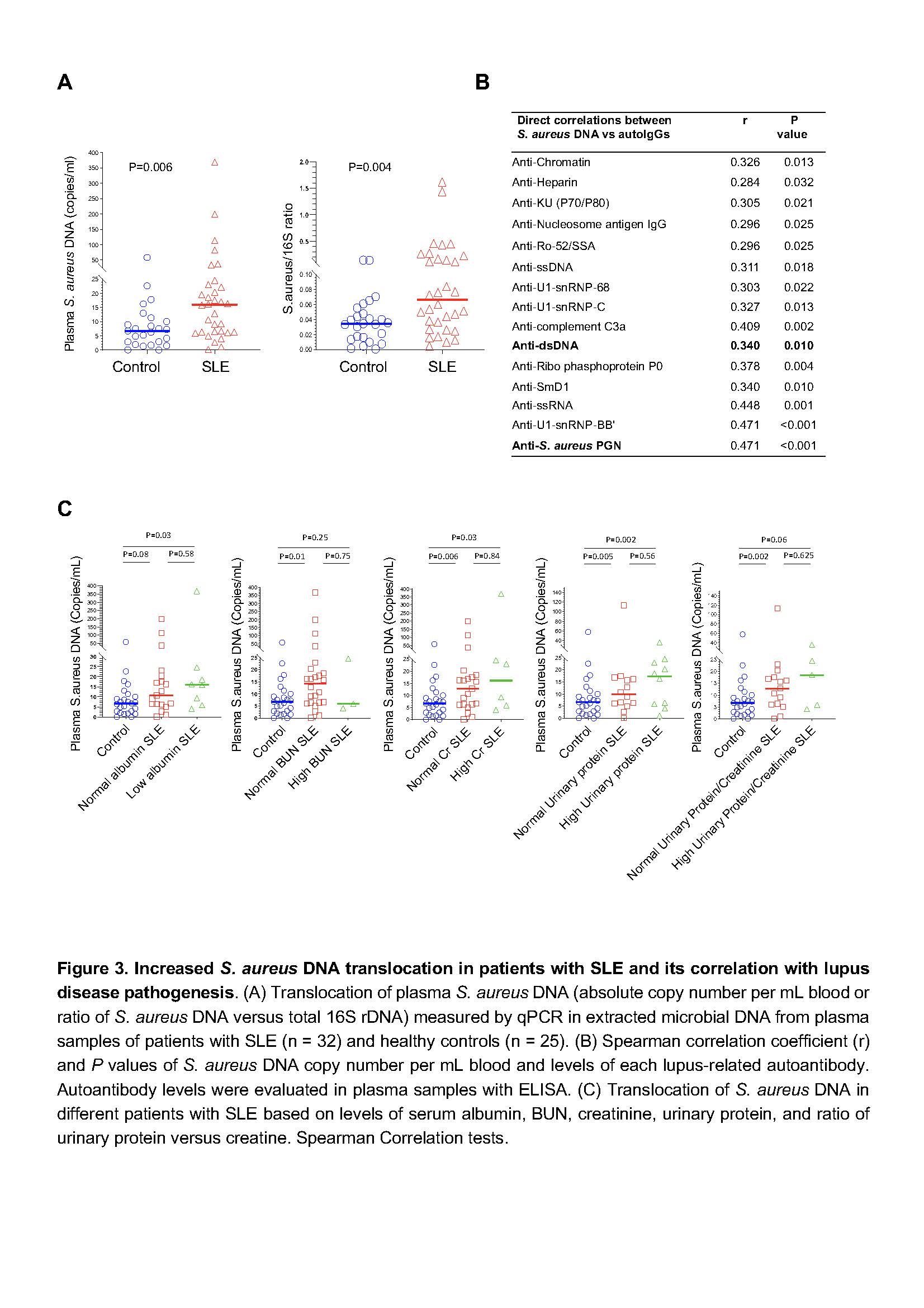
In a human study, we recruited unrelated controls (n = 25) or lupus patients (n = 32) as defined by the updated American College of Rheumatology classification criteria. All participants were premenopausal females (age ≥18 years). Pregnant or breastfeeding, recent severe illness, contraindications for blood withdrawals, or received antibiotics within the past 90 days were excluded. The method for determining plasma S. aureus DNA levels was evaluated by qPCR usingprimersfor S. aureus were forward:5′-TTCGCTACTAGTTGCTTA-3′ and reverse: 5′-GCACTATATACTGTTGGATC-3′.
We applied non-parametric Mann-Whitney U tests to compare differences between two groups, and Spearman’s correlation tests to evaluate associations. All tests were two-sided, and P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Administration of B. subtilis PGN-induced natural-like anti-dsDNA autoantibodies (e.g., IgM, short-lived IgG response, and no tissue damage), whereas S. aureus PGN-induced pathogenic anti-dsDNA autoantibodies (e.g., prolonged IgG production, low IgM, autoantibody-mediated kidney damage) in C57BL/6 and/or MRL/lpr mice (Figures 1-2, P < 0.05, non-parametric MannWhitney U tests). However, serum total IgG did not differ (P > 0.05, Figure 1B). S. aureus PGN drives specific clonal expansion, somatic hypermutation of IGHV3-74, and TLR2-dependent Class switch recombination in splenic anti-dsDNA autoreactive B cells (P < 0.05, Figure 2). In women with SLE, plasma S. aureus DNA levels were increased compared to control women (P < 0.05, Figure 3) and plasma S. aureus DNA levels were correlated with levels of lupus-related autoantibodies and renal involvement (P < 0.05, Spearman Correlation tests, Figure 3).
Conclusion: S. aureus PGN induces pathogenic autoantibody production, whereas B. subtilis PGN drives the production of natural nonpathogenic autoantibodies. The higher plasma S. aureus DNA in patients, we postulate, is one factor that induces autoantibody production and disease development in susceptible individuals. Therapeutics aimed at blocking TLR2 or Staphylococcus colonization may have a role in treating lupus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ning W, Gilkeson G, Jiang W. Staphylococcus Aureus Peptidoglycan Induces Pathogenic Autoantibody Production via Autoreactive B Cell Receptor Clonal Selection, Implications in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/staphylococcus-aureus-peptidoglycan-induces-pathogenic-autoantibody-production-via-autoreactive-b-cell-receptor-clonal-selection-implications-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/staphylococcus-aureus-peptidoglycan-induces-pathogenic-autoantibody-production-via-autoreactive-b-cell-receptor-clonal-selection-implications-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/