Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Title: 6W011 ACR Abstract: Spondyloarthritis Incl PsA–Clinical VI: Imaging of Axial SpA (2922–2927)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Spinal radiographic progression has been investigated in patients with r-axSpA, but not yet as thoroughly in early axSpA. We aimed to analyse the progression of spinal radiographic damage in patients with early axSpA.
Methods: Five-year spinal radiographs from patients with early axSpA from the DESIR cohort were scored by 3 readers (average) according to the mSASSS (0-72). Change scores for all available intervals were calculated. The development of new syndesmophytes (2 out of 3 readers) was calculated as a net change: number of patients with positive change minus number of patients with negative change divided by total number of patients. Two- and 5-year mSASSS progression and development of new syndesmophytes were assessed in subgroups defined at baseline according to the ASAS axSpA criteria and its arms, mNYC and also to the presence of syndesmophytes.
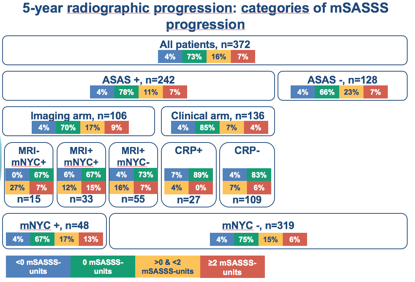
Results: In total, 549 patients (mean age 34 (SD 9) years, 46% males, 63% fulfilling ASAS axSpA criteria, baseline mSASSS 0.5(1.5)) were included. Thirty-eight patients (7%) showed syndesmophytes at baseline, 42% of which were ASAS axSpA criteria negative. Mean mSASSS progression was 0.2(0.9) at 2 years and 0.4(1.8) at 5 years. 18% of the patients fulfilling the ASAS axSpA criteria showed a 5-year positive mSASSS change (>0), compared to 30% in those not fulfilling the criteria (Figure). 26% of the patients fulfilling the imaging arm had a positive change: highest positive change in MRI-mNYC+ (34%), followed by MRI+mNYC+ (27%) and lastly MRI+mNYC– (23%). Mean mSASSS progression was highest in the mNYC+MRI+ group (1.3(4.0)). Eleven percent of the patients fulfilling only the clinical arm of the ASAS criteria had a positive change in mSASSS at 5 years, mean change of 0.1(0.7). Patients with baseline syndesmophytes (across all subgroups) had the highest progression: 2.7(5.0) mSASSS-units. At 5 years, 7% of all patients had a net change of any new syndesmophyte; this was 6% for ASAS+, 9% for ASAS-, 10% for the imaging arm (18% for mNYC+MRI+) and 3% for patients fulfilling the clinical arm only. Seventeen percent of the mNYC+ patients had a net change in new syndesmophytes as well as 42% of the patients with baseline syndesmophytes.
Conclusion: Spinal radiographic progression, though limited in early axSpA, can be captured already at 2 years of follow-up. Inflammation and damage in the SIJ are associated with a higher radiographic progression. The presence of baseline syndesmophytes strongly predicts the development of further structural damage already early in the disease.
Figure: Five-year mSASSS radiographic progression categories according to the subgroups of the ASAS criteria, arms of the ASAS criteria and fulfillment of mNYC at baseline.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, Sepriano A, van Lunteren M, Molto A, D'Agostino MA, Loeuille D, Dougados M, Reijnierse M, Claudepierre P. Spinal Radiographic Progression in Early Axial Spondyloarthritis: 5-Year Data from the DESIR Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spinal-radiographic-progression-in-early-axial-spondyloarthritis-5-year-data-from-the-desir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spinal-radiographic-progression-in-early-axial-spondyloarthritis-5-year-data-from-the-desir-cohort/