Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Severe inflammatory-erosive arthritis in tumor necrosis factor transgenic (TNF-Tg) mice is associated with B-cell translocation into sinuses of joint-draining popliteal lymph nodes (PLNs) via unknown mechanisms (1). Thus, we characterized transcriptional changes in PLNs of TNF-Tg mice with Early vs. Advanced stages of arthritis combining spatial and single-cell transcriptomics to assess the potential mechanisms orchestrating B-cell translocation.
Methods: PLNs from TNF-Tg male mice with Early (5-7-months, n=6 PLNs) and Advanced (Adv, >8-months, n=12 PLNs) arthritis were processed for spatial transcriptomics. In addition, 8-9k cells from pooled PLNs of Early and Adv TNF-Tg groups were subjected to droplet-based single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNAseq, n=6 PLNs/group) and immune profiling scRNAseq (n=2 PLNs/group, 2 replicates). Data were analyzed with Seurat, NicheNet (cell interaction), and scRepertoire (clonality) R packages. PLN immunofluorescence (IF) and ankle μCT measures were utilized to validate RNA detection and evaluate bone loss, respectively.
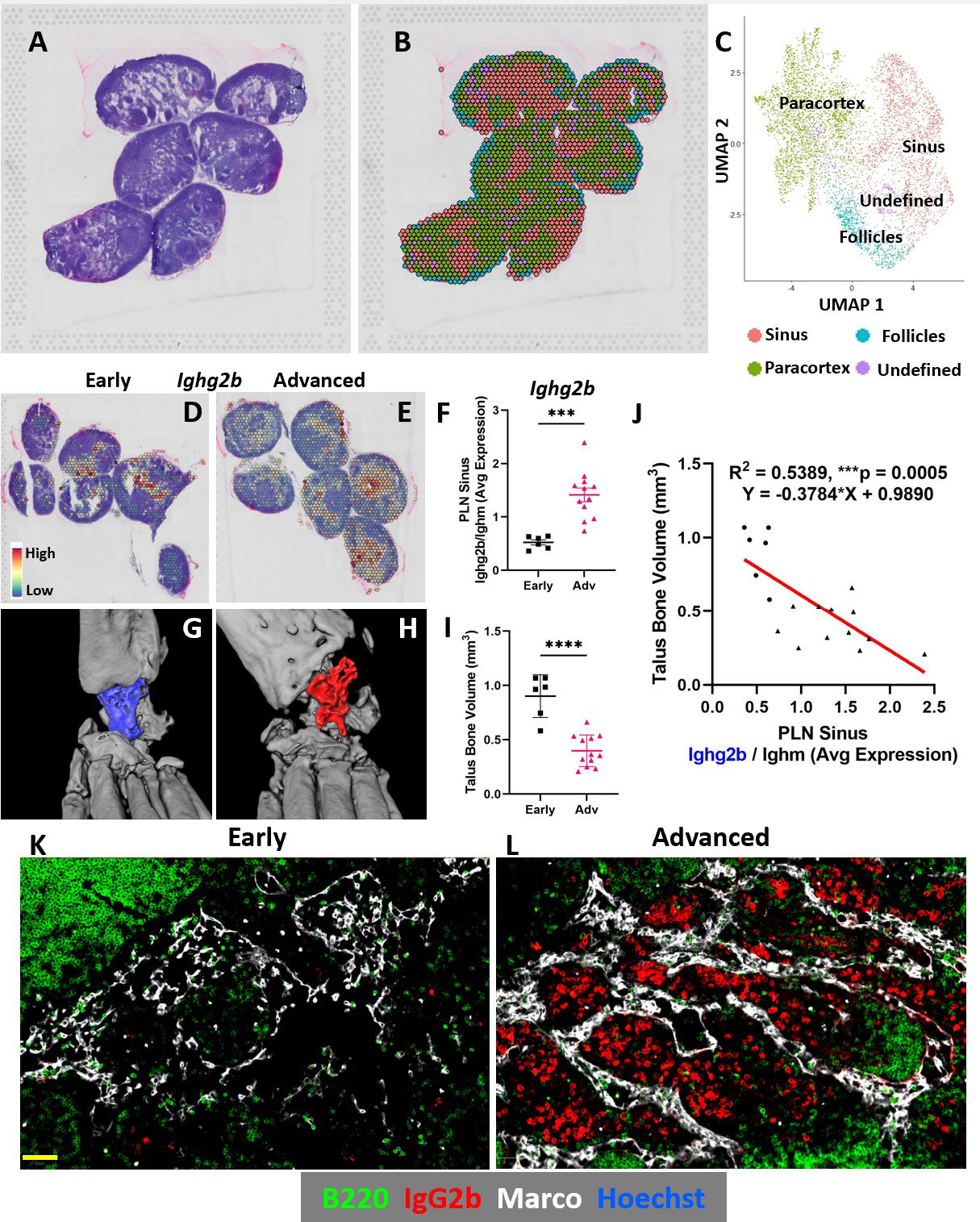
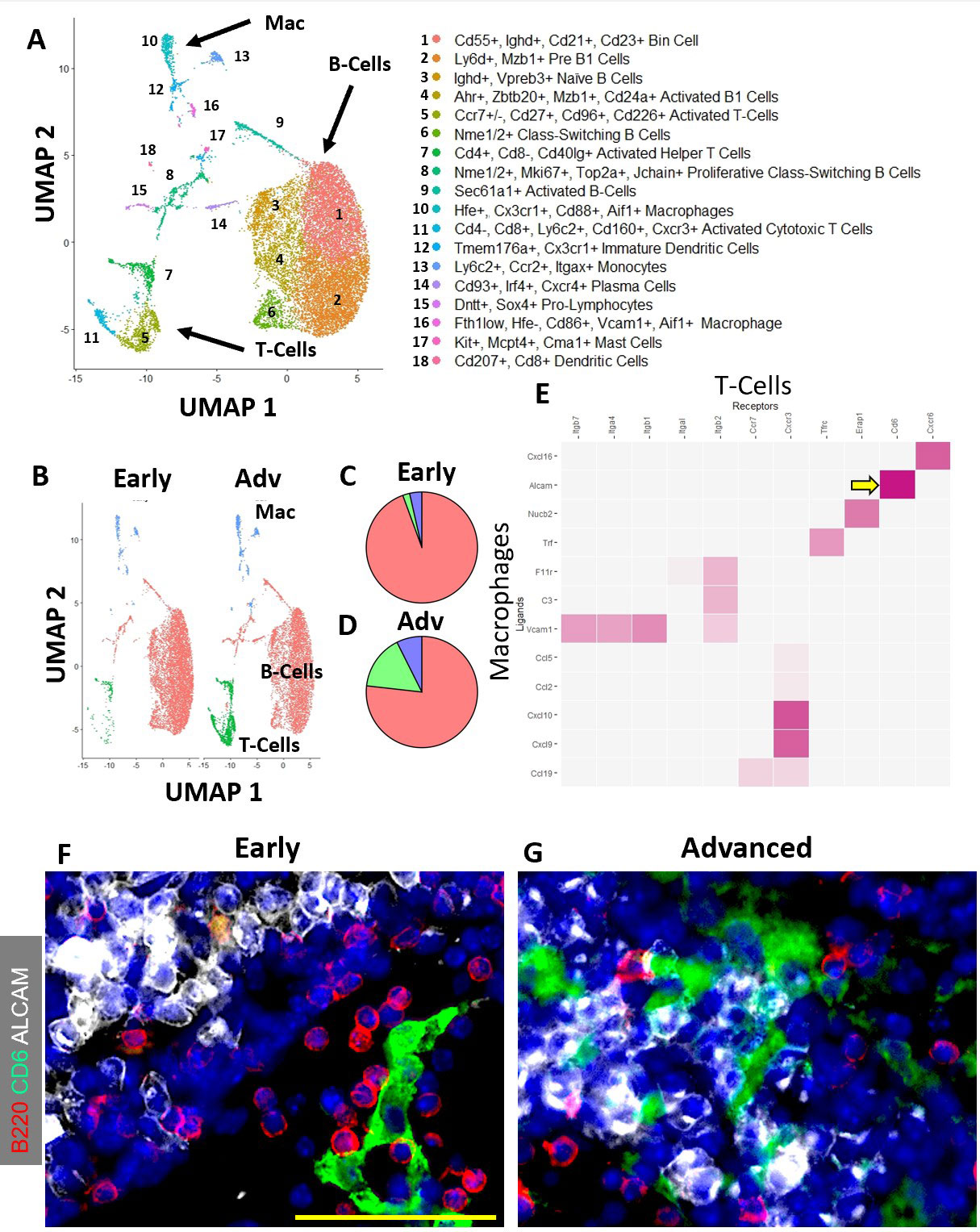
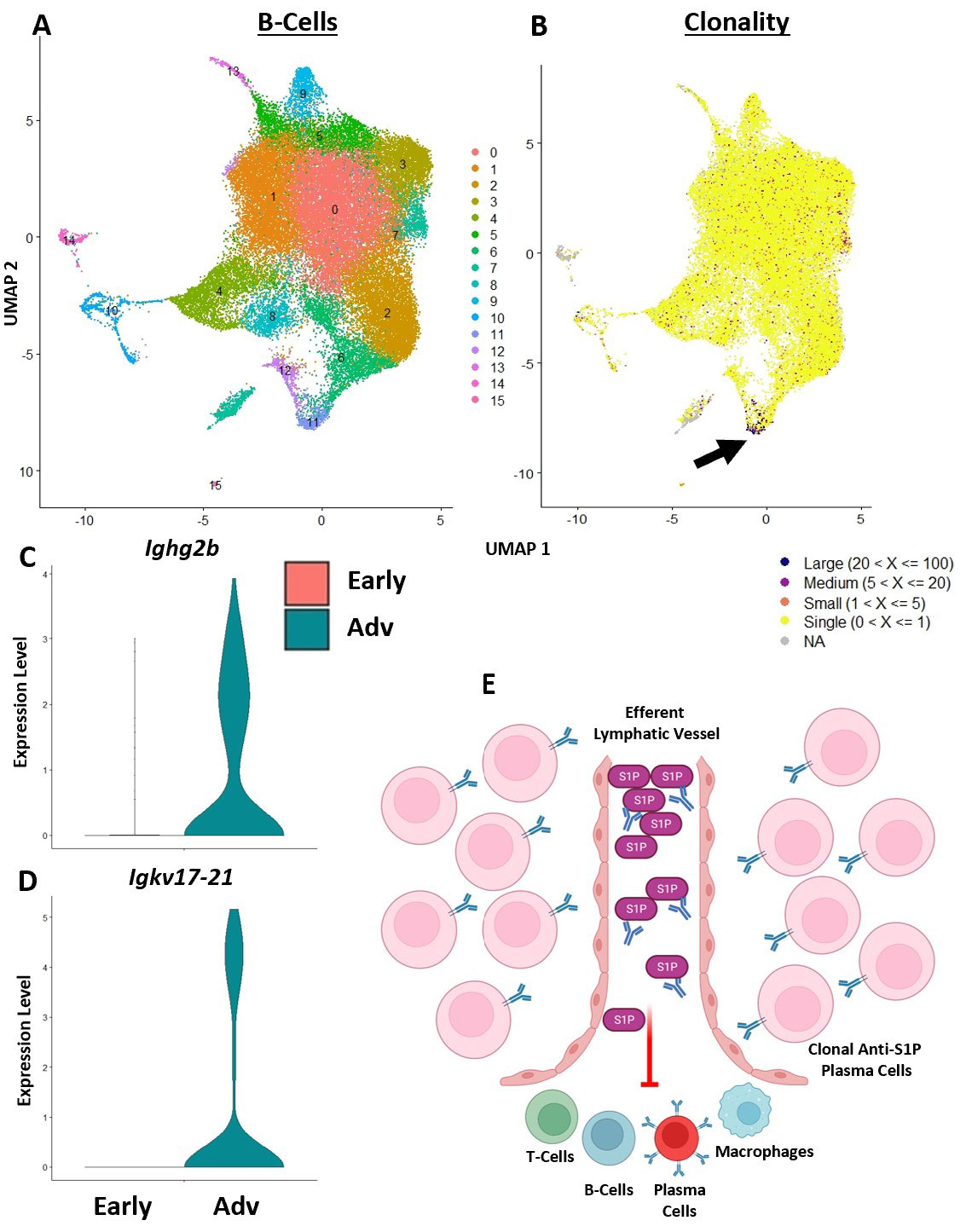
Results: Spatial transcriptomics revealed a significant and selective increase in Ighg2b/Ighm expression ratio in PLN sinuses of Adv vs Early conditions (0.5±0.1 vs 1.4±0.5 counts/counts; p< 0.001). Ighg2b expression significantly correlated with increased bone erosions and reduced talus bone volumes in the afferent ankle joint (R2=0.54, p< 0.001). IF confirmed the accumulation of IgG2b+/B220– plasma cells adjacent to Marco+ peri-follicular medullary sinuses (Figure 1). scRNAseq resolved 18 distinct cell populations with a dramatic increase in T-cells in Adv vs Early PLNs (15.8% vs 2.0%). Bioinformatics indicated a high probability interaction between Alcam+ macrophages and CD6+ T-cells. IF confirmed the close proximity of Alcam+/CD6+ cells only in the Adv condition (Figure 2). Assessment of B-cell clonality revealed 15 polyclonal clusters and a single oligoclonal population ( >20 cells of same clonotype). Differential gene expression analysis of the oligoclonal population showed increased Ighg2b expression along with unique variable light chain expression (Igkv17-21) in the Adv condition, which has been previously associated with antigen specificity to sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) (2) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: B-cell translocation into PLN sinuses is associated with the generation of IgG2b+ plasma cells in Advanced but not Early arthritis. These B-cell changes are concomitant with T-cell accumulation and activation via Alcam+/CD6+ interaction. Bioinformatic analysis and previous studies (2) suggest the presence of clonal S1P-specific plasma cells that may compromise S1P-dependent cell egress in PLNs and alter lymphatic function in inflammatory arthritis. Ongoing studies will confirm the existence of S1P-specific plasma cells and evaluate the therapeutic potential of CD6 blockade in TNF-Tg arthritis, similar to recent clinical trials (3).
References
1. Bouta et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 14(2):94-106. 2018.
2. Farokhi et al. Antibodies (Basel). 9(2):10. 2020.
3. Rodriguez et al., Clin Exp Immunology. 191(2):229-39. 2018.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kenney H, Peng Y, Chen K, Rangel-Moreno J, Pritchett E, Fox J, Korman B, Anolik J, Xing L, Ritchlin C, Schwarz E, Wu C. Spatial and Single-Cell Transcriptomics Identify Alcam+ Macrophage / CD6+ T-Cell Interactions and Accumulation of IgG2b+ Class-Switched Plasma Cells in Marco+ Medullary Sinuses of Joint-Draining Popliteal Lymph Nodes in TNF-Tg Mice with Advanced Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spatial-and-single-cell-transcriptomics-identify-alcam-macrophage-cd6-t-cell-interactions-and-accumulation-of-igg2b-class-switched-plasma-cells-in-marco-medullary-sinuses-of-joint-draining-popli/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spatial-and-single-cell-transcriptomics-identify-alcam-macrophage-cd6-t-cell-interactions-and-accumulation-of-igg2b-class-switched-plasma-cells-in-marco-medullary-sinuses-of-joint-draining-popli/