Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Calcinosis occurs in ~25% of
patients with Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) and causes pain, morbidity, and
decreased quality of life. The treatment of calcinosis is a major challenge in
the treatment of patients with SSc. The pathogenesis of calcinosis is not fully
understood but shares similarities to calciphylaxis, an ischemic vasculopathy
with arteriolar calcification seen in end-stage renal disease, which has been
successfully treated with intravenous sodium thiosulfate (STS). Suggested
mechanisms of action of STS include calcium chelation, reduction of
pro-inflammatory cytokines through anti-oxidant properties, and vasodilation. Previous
case studies have reported positive outcomes for calcinosis patients treated
with intravenous (IV) or intralesional STS. We report here a retrospective
chart review of calcinosis patients in our practice treated with STS.
Methods:
We included all patients at our
site that had been treated with STS (topical and IV) and had follow-up data
available. Patient charts were reviewed for clinical and demographic data. X-rays
were retrospectively assessed by a physician blinded to pre or post treatment
status using the SCTC Calcinosis Working Group’s scoring system accounting for
density of calcinosis and relative area involved. A paired t-test was used to assess
significance.
Results:
A total of 5 patients were
identified, 4 of whom met 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria for SSc and 1 met criteria
for juvenile dermatomyositis. All SSc patients were treated with topical STS
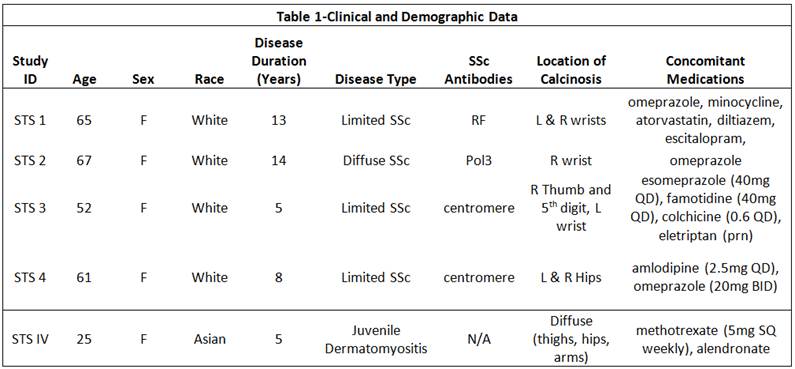
while the dermatomyositis patient was treated with IV STS. Table 1 summarizes
clinical and demographic characteristics of patients. Treatment time ranged
from 3-7 months. 1 patient (STS 4) discontinued use after 2 days due to erythema
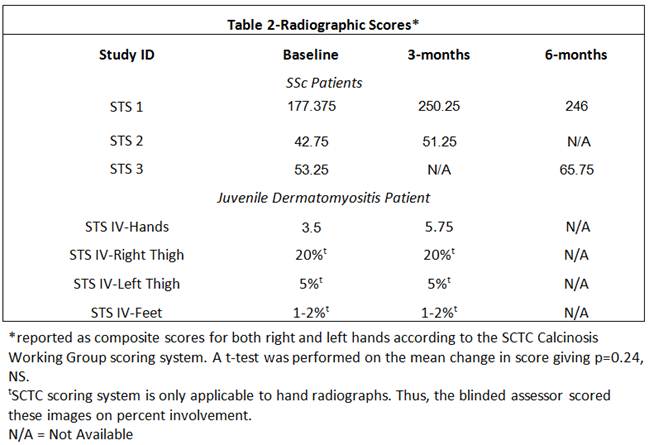
and inflammation of ulcerating calcinosis. No significant change in calcinosis
scores was seen between baseline and follow-up x-rays (Table 2, p=0.24).
Conclusion:
In this small retrospective study
no significant changes in radiographic calcinosis score were observed, but the
duration of treatment was relatively short and STS was generally well
tolerated. Further evaluation of STS in calcinosis may be considered recognizing
the limitations of this study, in particular the relatively short treatment
period.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pelrine E, Gordon JK, Baron M, Spiera RF. Sodium Thiosulfate in Calcinosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sodium-thiosulfate-in-calcinosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sodium-thiosulfate-in-calcinosis/