Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders I: Translational
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Growing evidence supports a critical role for innate immunity in systemic sclerosis (SSc) pathogenesis. Altered myeloid cell numbers and functions have been implicated in the initiation and progression of SSc, but their functional characterization and relationship with specify disease manifestations such as interstitial lung disease (ILD) remain poorly understood. We sought to characterize specific myeloid populations associated with SSc-ILD and investigate how disease severity affects the transcriptional regimen.
Methods: Single cell RNA-seq was performed on peripheral blood obtained from 60 SSc patients meeting 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria. Unsupervised clustering identified dendritic/monocyte populations which were then selected for further sub-clustering analysis and annotation. Differential expression analysis and sub-type frequency analysis was conducted between 40 patients with SSc-ILD and 20 patients without (non-SSc-ILD). Using the worst recorded forced vital capacity (fvc) value (%-predicted), correlation analysis against pseudo-bulk expression was performed for an unbiased genome-wide assessment of SSc-ILD severity associations.
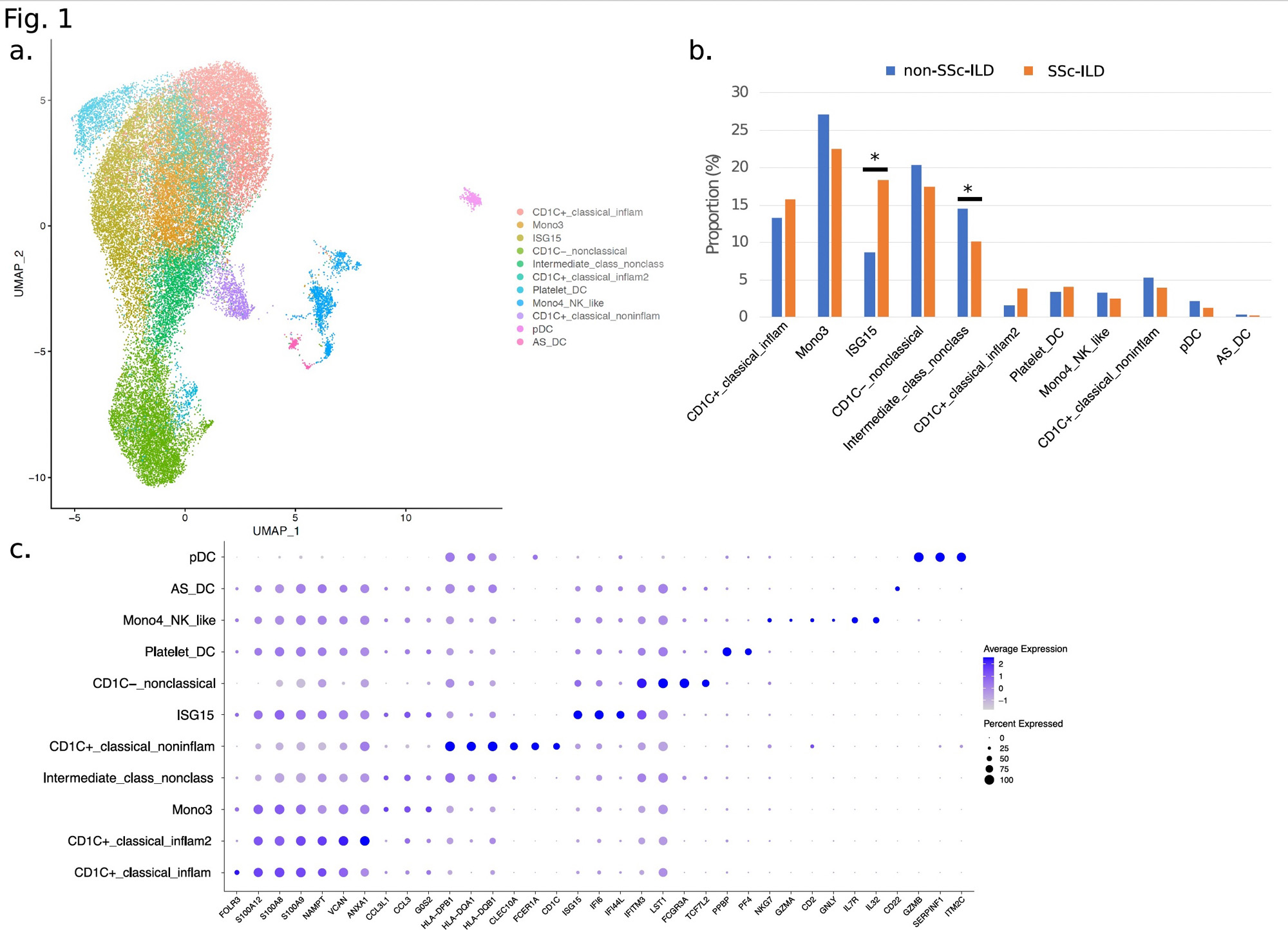
Results: Clustering and annotation of 39,582 dendritic/monocyte cells identified 11 myeloid cell types (Fig.1a). Comparison of relative cell type proportions between SSc-ILD and non-SSc-ILD (Fig.1b) revealed a 2.1-fold increase (p-value=1.7×10-2) in a “ISG15-hi” monocyte population expressing high levels of interferon (IFN)-inducible markers (i.e. IFI6 and IFI44L, Fig.1c). Concomitantly, an “Intermediate” monocyte population (expressing classical NAMPT and non-classical IFITM3, Fig.1c) showed a significantly decreased frequency (1.4-fold, p-value=2.8×10-2) in SSc-ILD subjects, and a strong negative correlation with ISG15hi subset counts (Pearson r=-0.70; p-value=2.45×10-7). Differential expression analysis identified 33 genes (1.2-fold, FDR < 2×10-2) between SSc-ILD and non-SSc-ILD in ISG15-hi monocytes (Fig.2a), with robust enrichment in the “Interferon signaling” pathway (FDR=1.5×10-10) (Fig.2b). For the Intermediate monocyte population, 61 genes had a significant negative correlation (-0.50 < Pearson r< -0.31; p-value < 0.05) associated with SSc-ILD severity and were enriched in pathways including “Cytokine signaling in immune system” (FDR=3.27×10-5) and “Innate immune system” (FDR=8.07×10-3). Of note, 18/61 genes were found to be significantly differentially expressed in SSc-ILD patients with the highest ILD severity (fvc < 55%), including the innate immunity gene FPR1 (Pearson r =-0.48, p-value=1.15×10-3).
Conclusion: Using single cell analysis, we identified a novel cluster of circulating monocytes expressing high levels of type I IFN-inducible markers that exhibits a significant association with presence and severity of SSc-ILD. Our findings suggest that these ISG15-hi monocytes may be cellular effectors critically involved in the dysregulated type I IFN activation driving SSc pathogenesis and identify them as promising targets for disease-specific therapeutic intervention.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ainsworth R, Taylor K, Cao Y, Sasaki T, Rao D, Bottini N, Boin F. Single Cell RNA-seq of Myeloid Cells from Systemic Sclerosis Patients Identifies Circulating Monocyte Population with Interferon Signature Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-of-myeloid-cells-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-identifies-circulating-monocyte-population-with-interferon-signature-associated-with-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-seq-of-myeloid-cells-from-systemic-sclerosis-patients-identifies-circulating-monocyte-population-with-interferon-signature-associated-with-interstitial-lung-disease/