Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Treatment adherence is crucial to optimizing outcomes in rheumatic diseases. Suboptimal adherence is common with inflammatory and chronic diseases, often treated with biologics, including biosimilars. Over 30 new biosimilars have been approved in North America alone in the past 5 years. However, population-based comparisons of biosimilar and bio-originator adherence remain scarce. Our objective is to compare etanercept (ETA) adherence among patients with rheumatic disease treated with biosimilar (ETA-B) and bio-originator (ETA-O).
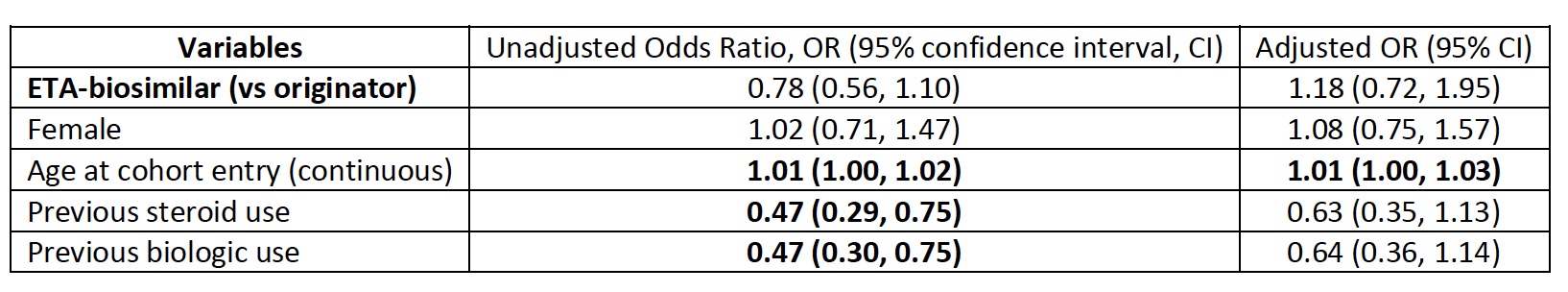
Methods: We used data from the National Prescription Drug Utilization Information System (NPDUIS), which contains pan-Canadian (except Quebec) claims-level data on prescriptions from public drug programs. We studied ETA-naive adults (18+) with hospital discharge diagnostic codes for rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis (ICD-10 codes M05-06, M45, M070-M073, L40), initiating ETA between Jan. 2015-Dec. 2019. ETA-O (Enbrel) and ETA-B (Brenzys, Erelzi) were defined using Drug Identification Numbers. From the date of first ETA dispensation, adherence was measured by the medication possession ratio (MPR) during the first year of treatment (sum of all supply days divided by 365). MPR ≥80% was considered good adherence. Using logistic regression models, we assessed adherence during the first year for bio-originator versus biosimilar initiators. We adjusted for sex at birth, age at ETA initiation, and biologic use and prednisone use prior to ETA initiation.
Results: Among 615 ETA initiators, 50.8% initiated ETA-B. Most were female (68%), with a median age of 66 (interquartile range 57-73) at drug initiation. Within the first year, an MPR of >80% was seen in 30.7% of biosimilar and 36.1% of originator users. The odds of having an MPR ≥=80% were similar for ETA-B versus ETA-O initiators (adjusted odds ratio, aOR, 0.83, 95% confidence interval, CI 0.59-1.17). The covariate most clearly correlated with achieving MPR ≥80% was age (continuous) at ETA initiation (aOR 1.01, 95% CI 1.00-1.03).
Conclusion: In this Canadian population-based study of ETA initiators with rheumatic disease, ETA-B and ETA-O had similar adherence. Low adherence is common among these individuals but is better in older individuals. A potential limitation was our assumption that every individual was under the same maintenance regimen (50 mg sc weekly). Also, reasons for nonadherence/treatment gaps are not available in NPDUIS data. However, our study adds to the real-world evidence of biosimilar/bio-originator adherence for individuals with rheumatic disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tsyruk O, Birck M, Bernatsky S, Lukusa L, Choquette D, Boire G, Maksymowych W. Similar Etanercept Adherence in Individuals with Rheumatic Disease Initiating Originator and Biosimilar: A Population-Based Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/similar-etanercept-adherence-in-individuals-with-rheumatic-disease-initiating-originator-and-biosimilar-a-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/similar-etanercept-adherence-in-individuals-with-rheumatic-disease-initiating-originator-and-biosimilar-a-population-based-study/