Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The EULAR cardiovascular screening recommendations advocate for the use of carotid dopplers in patients with inflammatory joint diseases to detect subclinical atherosclerosis. Despite these guidelines, there is no clear consensus on which specific patients should undergo carotid doppler screening. This study aims to identify significant predictors that can help define criteria for performing carotid doppler ultrasound in axial spondyloarthritis patients without conventional cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: 30 patients were recruited for this observational cross-sectional study. Patients aged between 18-60 with a diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) were evaluated for cardiovascular risk markers and carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT), defined as abnormal ( >0.8mm) and normal (< 0.8mm). Exclusion criteria included pregnancy, prior cardiovascular conditions, and other rheumatic diseases. Significant predictors of abnormal cIMT (p< 0.05) were identified through statistical analysis using Microsoft Excel
Results:
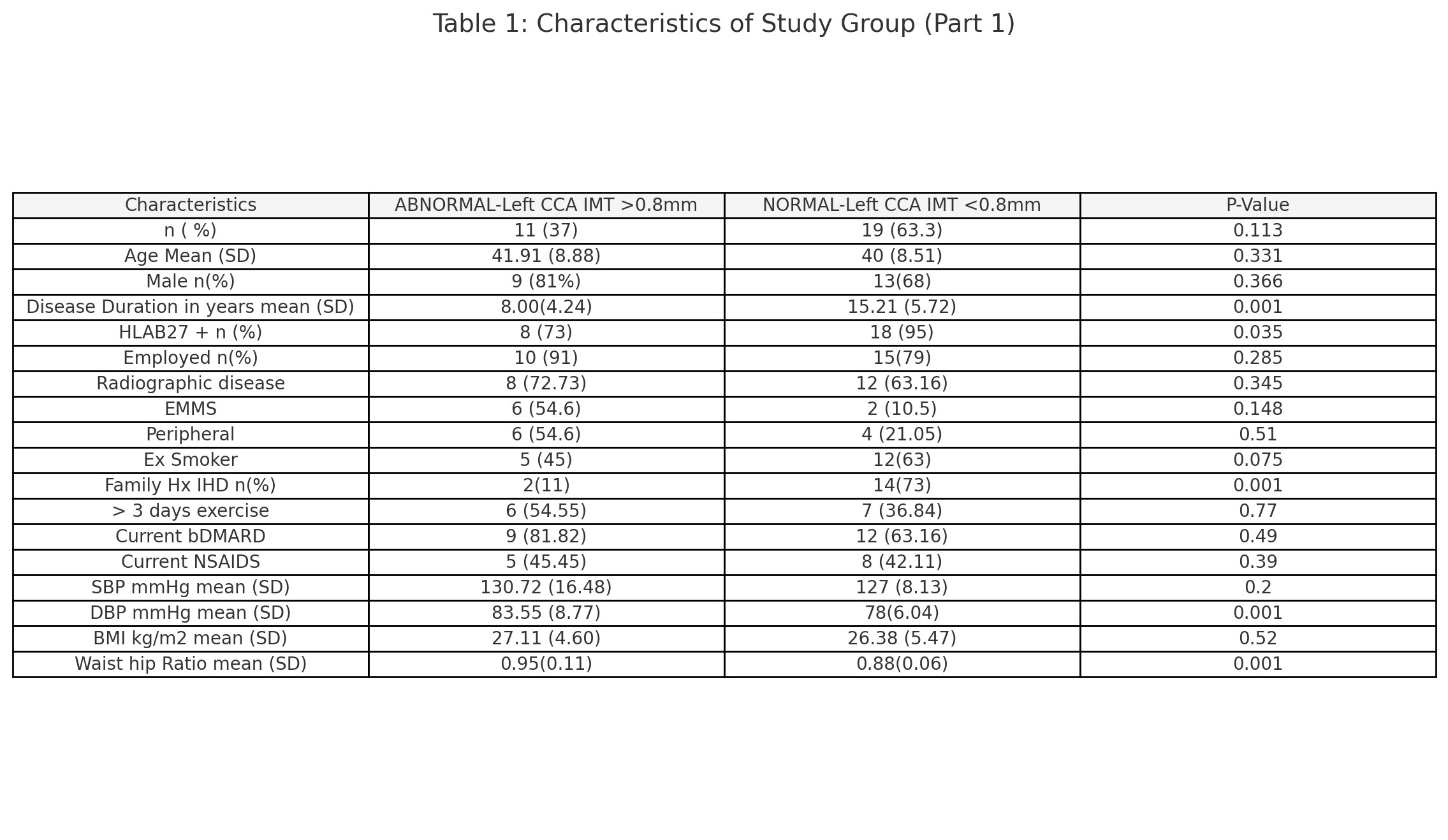
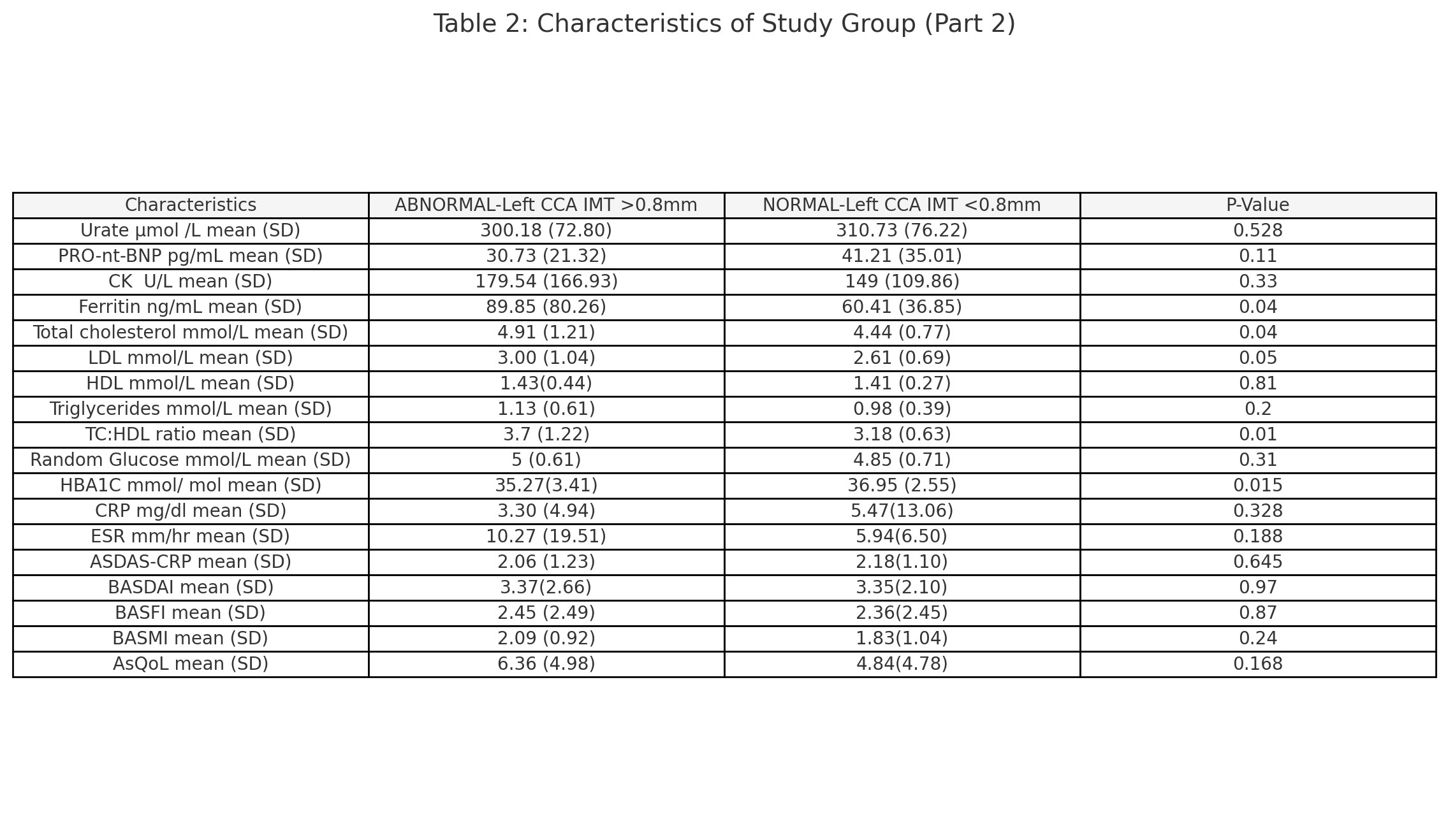
Table 1 and 2 present the general characteristics of the study group, comparing patients with normal and abnormal cIMT. Statistically significant predictors of abnormal cIMT ( >0.8mm) include shorter disease duration (8.00 vs. 15.21 years, p=0.001), HLAB27 status (73% HLAB27+ vs 95 % HLAB27+, p=0.035), negative family history of ischemic heart disease (11% vs. 73% with positive family history, p=0.0017), higher diastolic blood pressure (83.55 vs. 78 mmHg, p=0.001), higher waist-hip ratio (0.95 vs. 0.88, p=0.001), higher ferritin levels (89.85 vs. 60.41 ng/mL, p=0.04), higher total cholesterol (4.91 vs. 4.44 mmol/L, p=0.04), higher LDL (3.00 vs. 2.61 mmol/L, p=0.05), and higher Total Cholesterol:HDL ratio (3.7 vs. 3.18, p=0.01)
Conclusion: These findings suggest that simple standard-of-care examinations can effectively identify axSpA patients, deemed to be at low risk for cardiovascular disease, for carotid doppler ultrasound screening. By utilizing predictors such as HLAB27 status, family history of ischemic heart disease, blood pressure, waist-hip ratio, ferritin levels, and cholesterol levels, healthcare providers can better stratify risk. Several factors traditionally associated with cardiovascular risk did not show significant differences between the groups with normal and abnormal cIMT. Disease activity scores, such as ASDAS-CRP and BASDAI, along with inflammatory markers like CRP and ESR, did not differ significantly, suggesting that active inflammation or disease severity might not directly correlate with subclinical atherosclerosis in this cohort.
This study can facilitate the development of appropriate utilization of carotid doppler ultrasound in detecting subclinical atherosclerosis, enhancing early cardiovascular disease detection and management in axSpA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dinneen B, O'Shea F. Significant Indicators Identified for Carotid Doppler Ultrasound Use in Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients Without Conventional Cardiovascular Risk Factors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/significant-indicators-identified-for-carotid-doppler-ultrasound-use-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-without-conventional-cardiovascular-risk-factors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/significant-indicators-identified-for-carotid-doppler-ultrasound-use-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-without-conventional-cardiovascular-risk-factors/