Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The quality of life, as measured by the Short Form-36 (SF-36), is reduced in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM). Although endorsed by the International Myositis Assessment and Clinical Studies Group (IMACS) for evaluating myositis patients, SF-36 has not been fully validated in IIM. This study aimed to investigate the psychometric properties of the SF-36 in a large cohort of IIM patients.
Methods: Patients fulfilling the EULAR/ACR classification criteria were enrolled in the study utilizing a database of patients enrolled in two clinical trials (Tocilizumab in Myositis and Acthar in Myositis) and one prospective observational study (PAMPRO). The SF-36 evaluates eight subdomains: physical function, bodily pain, physical health limitations, emotional problems, emotional well-being, social functioning, energy/fatigue, and general health, along with physical health summary score (PCS) and a mental health summary score (MCS). Data collection included demographic and clinical parameters, encompassing all myositis core set measures (CSMs): MMT-8, patient and physician global assessments, HAQ, muscle enzymes, and extra-muscular disease activity scores.
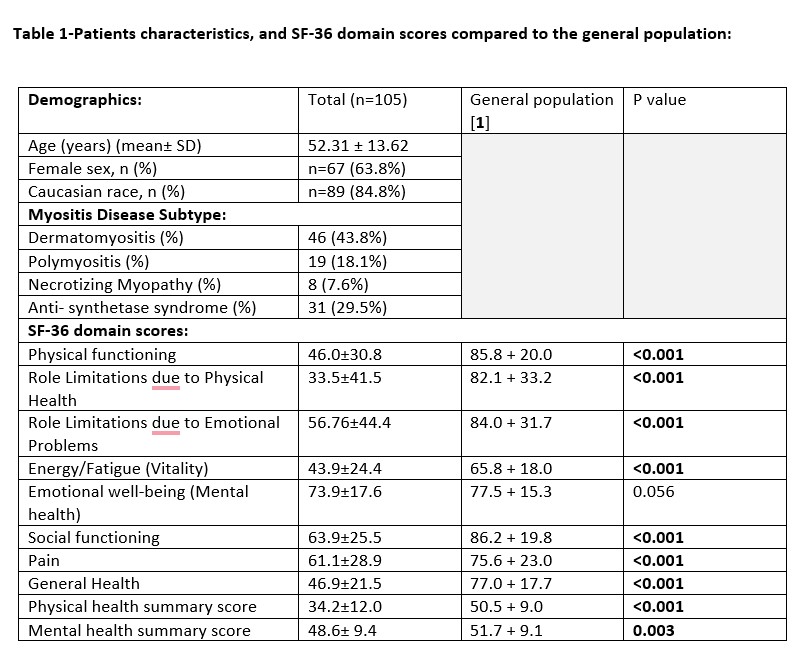
Results: One hundred and five IIM patients were included (44% dermatomyositis, 30% anti-synthetase syndrome, 18% polymyositis, 8% necrotizing myopathy), mean age of 52.31 ± 13.62, 64% females and 85% Caucasians. Most SF-36 domain and summary scores were significantly lower compared to the general population [1] (Table 1). SF-36 components were similar among IIM sub-types, except for significantly lower physical function scores in necrotizing myopathy patients (p=0.02). No association was found between SF-36 scores and age, sex, or race. All SF-36 domain scores were significantly lower in patients with abnormal MMT, active disease by physician global, and increased disability by HAQ score ≥ 0.5.
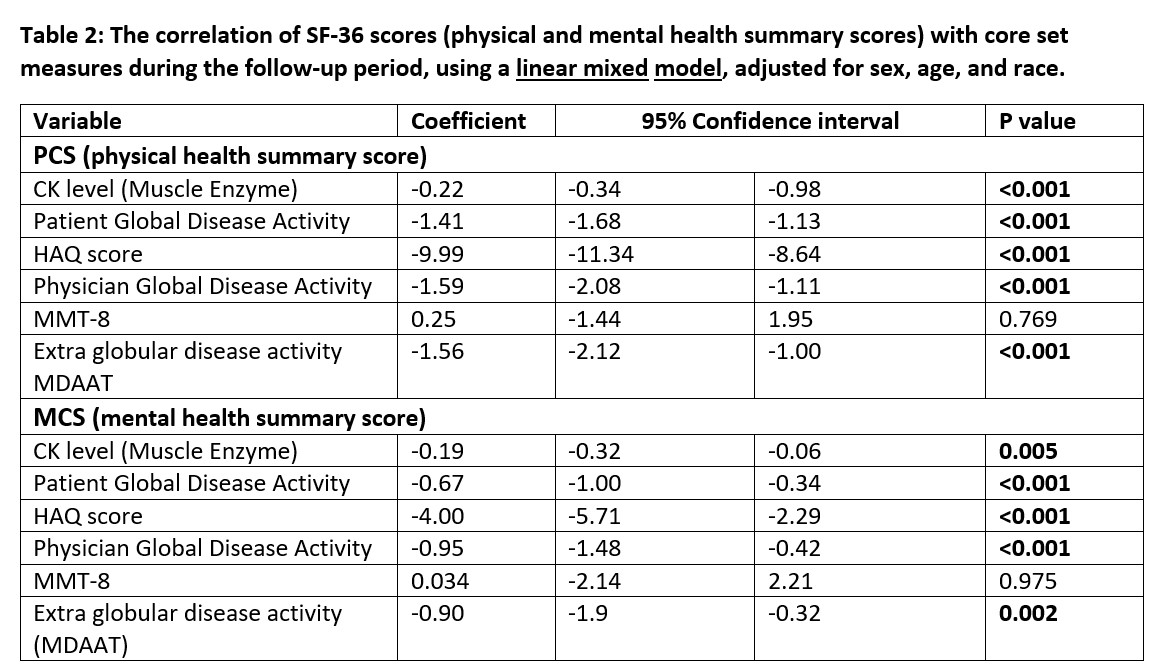
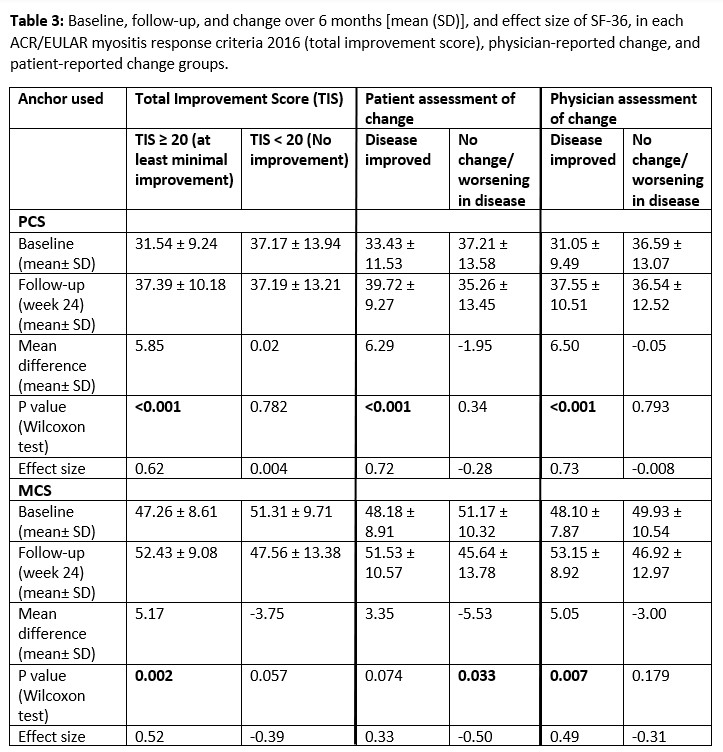
SF-36 PCS and MCS components demonstrated good test-retest reliability at 1 month (r=0.874 p< 0.001 and r=0.731 p< 0.001, respectively). Strong associations of PCS and MCS with other CSMs were demonstrated, including patient and physician-global assessments, HAQ score, and extra-muscular disease activity, indicating good validity. Longitudinal correlations were significant between PCS and MCS for all CSMs, except for MMT-8 (Table 2). SF-36 illustrated significant and concordant change with myositis response criteria and physician/patient assessments of change, with a large effect size (Table 3). The clinically important difference (CID) of SF-36 PCS score using the anchors patient/physician-reported change at 6 months and the 2016 ACR/EULAR myositis response criteria were 8.2, 6.5, and 5.8, respectively. The CID of SF-36 MCS score using the same anchors were 8.8, 8.1, and 8.9, respectively.
Conclusion: SF-36 demonstrates good reliability, validity and responsiveness in a large cohort of IIM patients. This important patient-reported outcome should be utilized for assessing health-related quality of life in clinical practice and trials.
References:
1. Hopman WM, et al. Canadian normative data for the SF-36 health survey. CMAJ. 2000;163(3):265-71.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
keret s, Aggarwal A, Almackenzie M, Chandra T, Silva R, Gkiaouraki E, Pongtarakulpanit N, Sriram s, Oddis C, Aggarwal R. Short Form-36 Psychometric Properties in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Reliability, Validity and Responsiveness [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-form-36-psychometric-properties-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-reliability-validity-and-responsiveness/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/short-form-36-psychometric-properties-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-reliability-validity-and-responsiveness/