Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: B Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: T peripheral helper (Tph) cells accumulate in the joints of children with ANA+ oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (oligo JIA) and may provide pathogenic help to B cells. To understand Tph cell-B cell interactions in oligo JIA, we immunophenotyped and characterized the repertoire of synovial fluid (SF) B cells.
Methods: Peripheral blood (PB) and/or SF samples were obtained from children with oligo JIA (ILAR criteria) and adult/pediatric controls. To compare to other follicular lymphocytes, discard tonsils were collected from children undergoing tonsillectomy for indications such as sleep apnea. Flow cytometry was used to immunophenotype B cells and data were analyzed with FlowJo and OMIQ. Uniform manifold approximation and projections (UMAP) were created by downsampling to 2,000, live CD19+ B cells from each sample. Cluster analysis was performed with FlowSOM. Genomic DNA was extracted from sorted naïve, CD21lo, non-switched memory, and switched memory B cells and the immunoglobulin heavy chain was sequenced (Adaptive Biotechnologies). GraphPad Prism was used for statistical analysis.
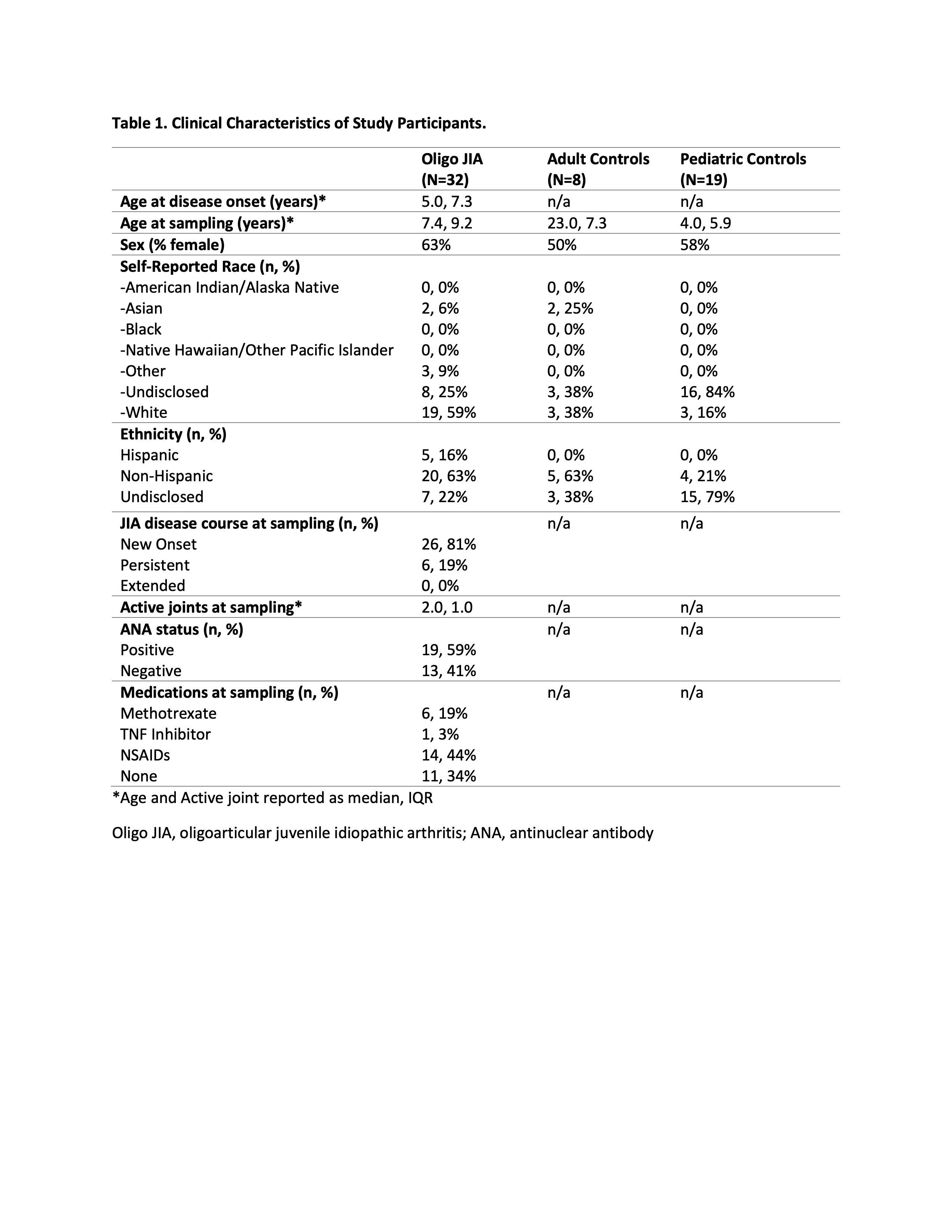
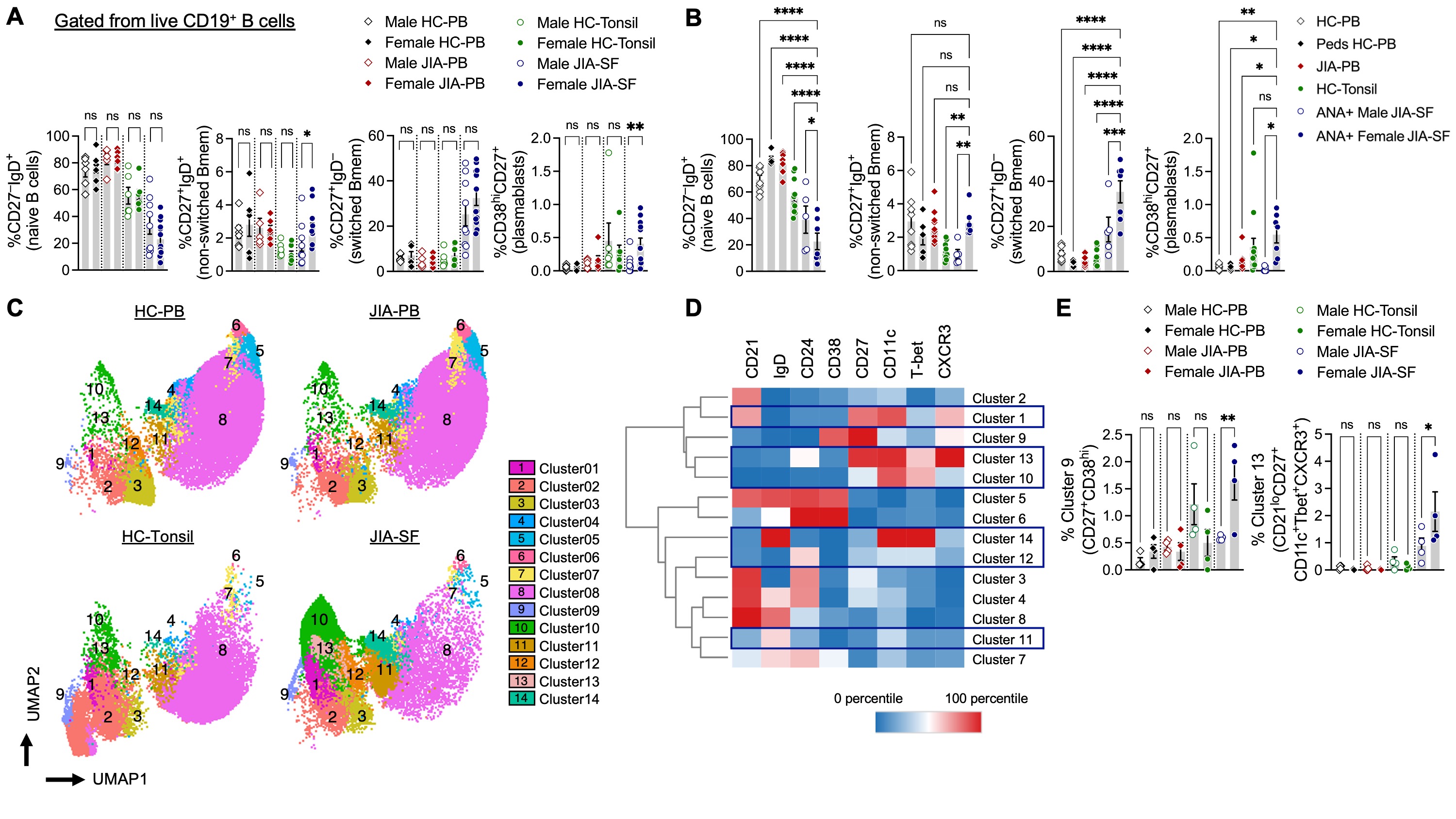
Results: Table 1 summarizes study participants. We found immunophenotypic differences in SF B cells from male vs. female oligo JIA patients that were not observed in male vs. female PB and tonsil (Fig1A). When comparing SF from ANA+ oligo JIA patients, females had significantly more non-switched Bmem, switched Bmem, and plasmablast cells (Fig1B). There were no differences in B cell subsets of oligo JIA patients stratified by age of disease onset or ANA status alone. Next, an unsupervised clustering algorithm was used to identify 14 distinct population of B cells across the study groups. Six of these metaclusters were significantly and uniquely expanded in oligo JIA SF, including 5 clusters of CD21lo B cells of varying phenotype (Fig1C-D). In the SF of females with oligo JIA, there was enrichment of CD21lo B cells that expressed memory (CD27+) and age-associated B cell (ABC) (CD11chiTbet+CXCR3+) features (cluster 13) as well as plasmablasts (cluster 9) (Fig1E).
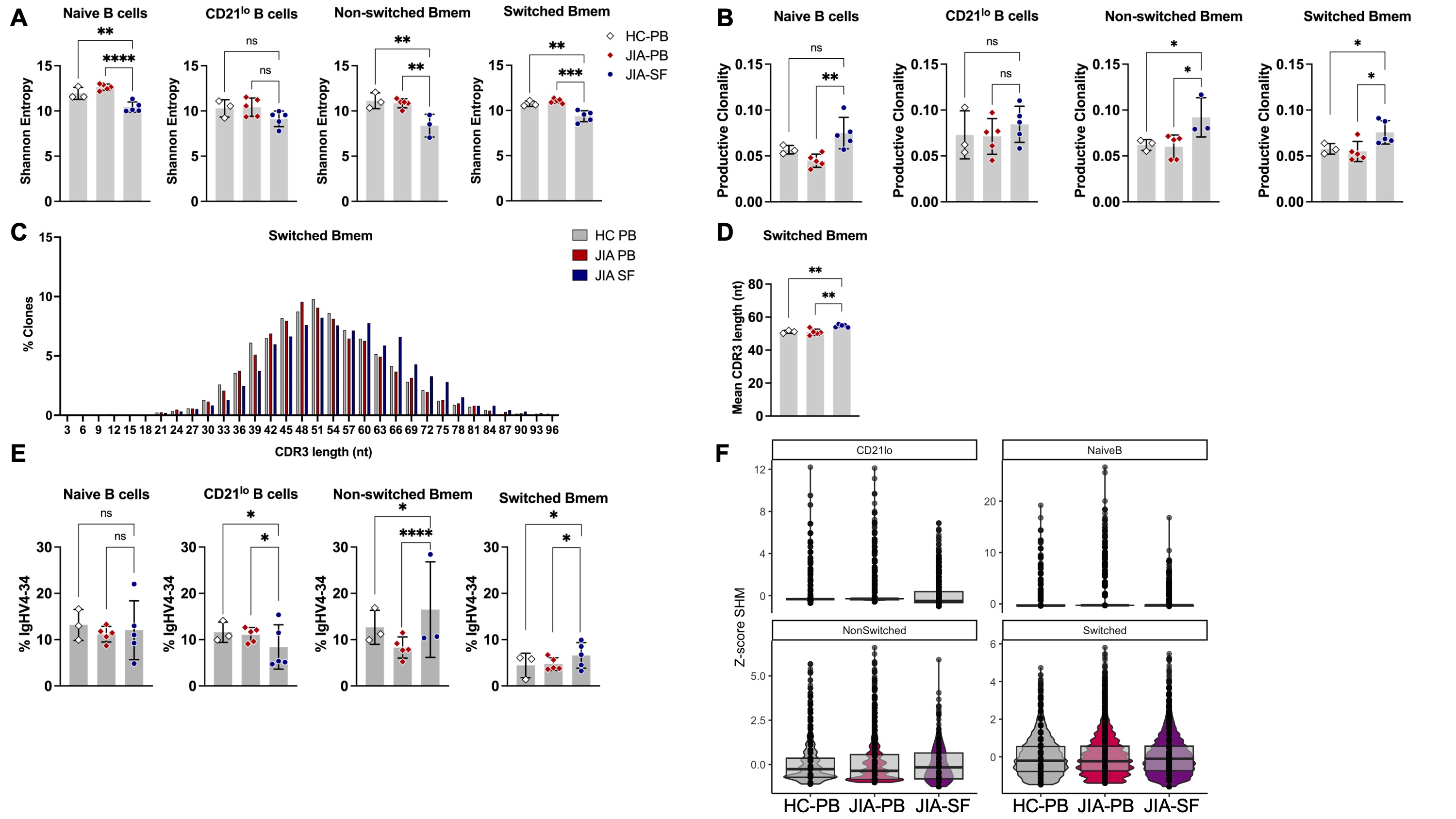
BCR repertoire analysis of females with oligo JIA showed that naïve, non-switched Bmem, and switched Bmem were less diverse and more clonal than their counterparts in the PB of controls and oligo JIA patients (Fig2A-B). Switched Bmem cells from oligo JIA SF had longer mean CDR3 lengths compared to oligo JIA and control PB, a feature associated with autoreactivity (Fig2C-D). Skewing of VH and JH genes was observed in Bmem cells from oligo JIA SF, including increased usage of the intrinsically autoreactive IgVH4-34 gene (Fig2E). Bmem cells from oligo JIA SF had BCRs with high frequencies of somatic hypermutation (SHM), comparable to Bmem cells in PB that are known to result from germinal center (GC) reactions (Fig2F).
Conclusion:
Abnormalities in the SF B cell compartment were prominent in female vs. male oligo JIA patients, including enrichment of plasmablasts and CD21lo B cells with features of ABCs. The BCR repertoire of females with oligo JIA displayed evidence of autoreactivity and high rates of SHM indicative of T cell-dependent GC reactions. Thus, sex may play a role in oligo JIA B cells responses, which may explain the predilection of this disease to affect females.
Summary data on bar graphs is mean ± standard error. P value, ns, >0.05; *, ≤ 0.05; **, ≤ 0.01; ***, ≤ 0.001; ****, ≤ 0.0001.
Oligo JIA, oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Bmem, memory B cells; SF, synovial fluid; ANA, antinuclear antibody; UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projections; HC, healthy control; PB, peripheral blood.
Statistical analysis for A, B, D: one-way ANOVA with correction for multiple comparisons with all groups compared to oligo JIA SF. Statistical analysis for E: two-way ANOVA corrected for multiple comparisons with all groups compared to oligo JIA SF.
Summary data on bar graphs is mean ± standard deviation (SD). P value, *, ≤ 0.05; **, ≤ 0.01; ***, ≤ 0.001; ****, ≤ 0.0001.
Oligo JIA, oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis; PB, peripheral blood; SF, synovial fluid; HC, healthy controls; HC, healthy controls; SF, synovial fluid; Bmem, memory B cells; CDR3, complementarity-determining region 3; SHM, somatic hypermutation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lam K, Harris C, Fernandez-Salinas D, Hahn M, Ashoor M, Bakhsh A, Bryant C, Case S, Chandler M, Chang J, Cohen E, Dedeoglu F, Halyabar O, Hausmann J, Hazen M, Ibanez D, Kim L, Lo J, Lo M, Meidan E, Perron M, Powers H, Son M, Wobma H, Lee P, Nigrovic P, Ohlms L, Chang M, Gutierrez-Arcelus M, Henderson L. Sex Differences in the B Cell Compartment of Patients with Oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-differences-in-the-b-cell-compartment-of-patients-with-oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sex-differences-in-the-b-cell-compartment-of-patients-with-oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/