Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Biomarkers
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Our objective was to identify the clinical significance of serum interferon-alpha levels in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Serum samples and clinical data including demographic information, body mass index measured in kg/m2, seropositivity, medications were obtained for 173 RA patients who were enrolled in the University of Pittsburgh Rheumatoid Arthritis Comparative Effectiveness Registry (RACER). Patients who underwent clinical evaluations and completed three self-report questionnaires (PainDETECT, Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) 29, Widespread Pain Index/Symptom Severity Scale) were included. Serum cytokines including interleukin (IL)-1 beta, IL-6, and interferon (IFN)-alpha were measured on serum samples using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
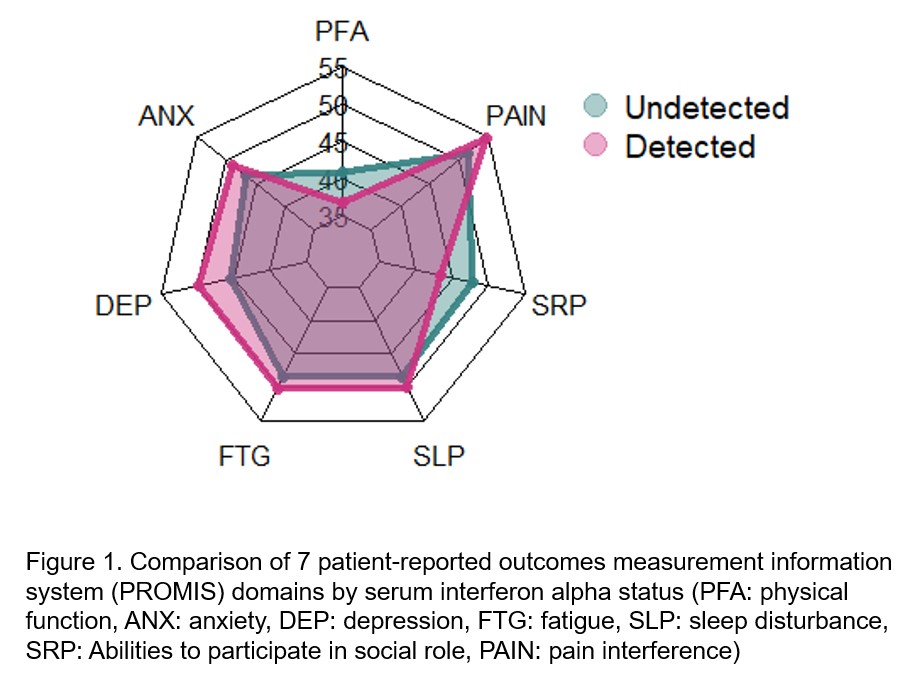
Results: Among those patients (N=18) who had detectable IFN-alpha, there were significant differences observed for physician global assessment, physical function, depression, and abilities to participate in social roles, compared with patients who did not have IFN-alpha detected. (Table 1) Those who had detectable IFN-alpha had a poorer physical function and impaired abilities to participate in social roles. (Figure 1) Although there was no statistically significant difference, those who have detectable IFN-α tend to have a higher number of swollen joints, higher seropositivity, and higher pain interference. Interestingly, inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 beta, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP), pain levels, and RA disease activity scores such as disease activity score 28-CRP and clinical disease activity index were not different between the patients with detectable IFN-alpha and without. (Table 1)
Conclusion: This study highlights the potential roles of serum IFN alpha as a biomarker in identifying a distinct subgroup of patients among those who have similar RA disease activity scores.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hwang Y, Zhu L, Wu D, Moreland L. Serum Interferon-Alpha Levels Could Help Identify a Subgroup of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Poorer Physical Function and Higher Physician Global Assessment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-interferon-alpha-levels-could-help-identify-a-subgroup-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-poorer-physical-function-and-higher-physician-global-assessment/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-interferon-alpha-levels-could-help-identify-a-subgroup-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-poorer-physical-function-and-higher-physician-global-assessment/