Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic inflammation is an integral part of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Despite substantial inflammation in the affected tissues such as skin, entheses and joints, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels are not elevated in PsA. Based on this situation, acute phase reactants such as CRP are not highly reliable in measuring inflammation in PsA, especially also in early PsA, when CRP is frequently negative.
The aim of this study was to investigate whether alternative inflammation markers can detect systemic inflammation in early PsA patients with better precision than CRP.
Methods: Adult patients with early (median disease duration: 6 months) DMARD-naïve PsA were compared to sex- and age matched controls (HC) and early (disease duration: 5 months) DMARD-naïve RA patients. CRP, serum amyloid A (SAA), serum calprotectin (S100A8/9), complement C3, thrombocytes, ferritin were measured in the serum. The markers were compared in PsA, RA patients and HC having normal CRP (≤5 mg/L) (Kruskal-Wallis). Same markers were compared in RA, PsA and HC having BMI ≥30. Sensitivity and specificity analysis (ROC) was conducted.
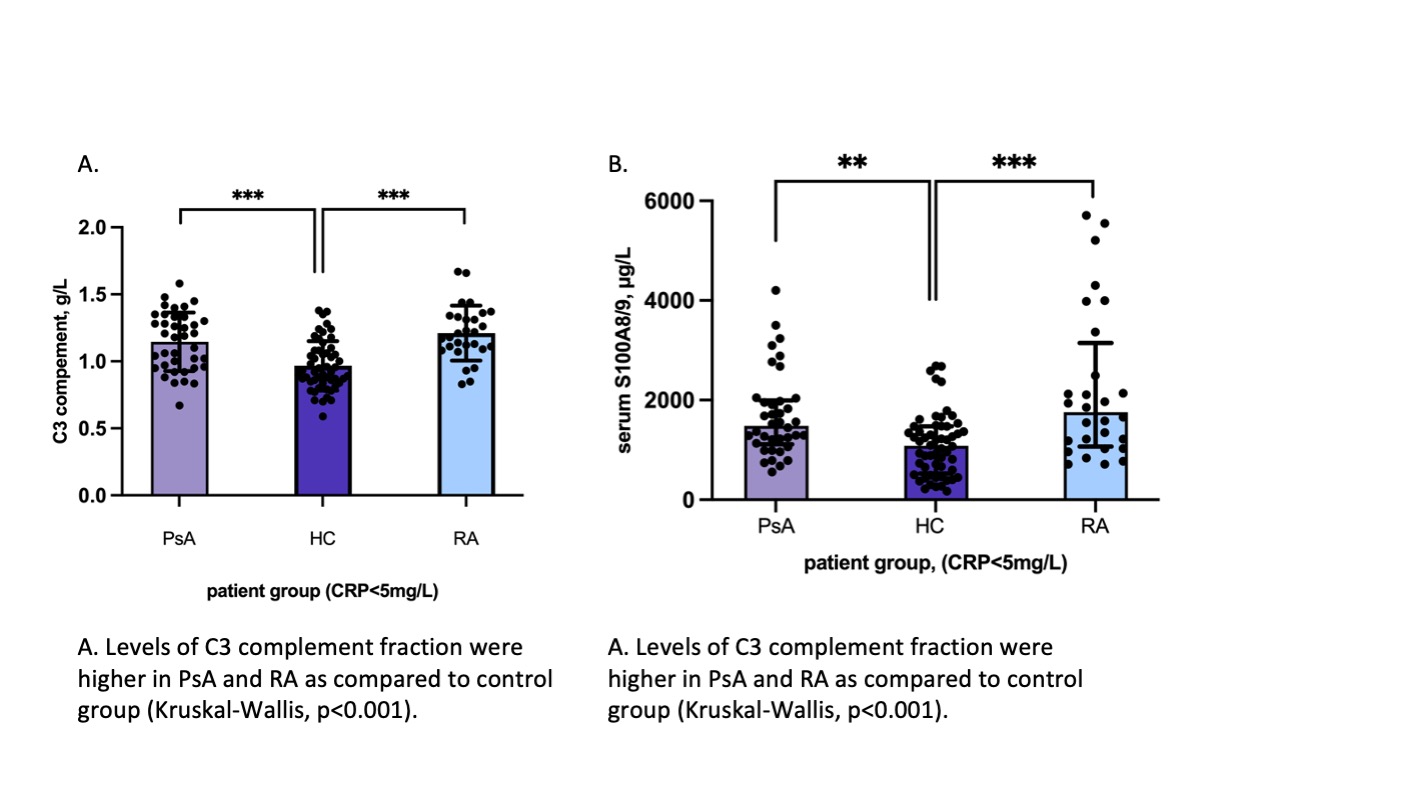
Results: Thirty nine of 67 (58%) PsA, 29/50 (56%) RA patients and 57/61 (93%) HC had normal CRP. Demographic, clinical and disease activity characteristics of PsA patients having CRP≤5mg/L and CRP >5mg/L were comparable. The median[IQR] levels of C3 (g/L) and S100A8/9 (hg/ml) were higher in “CRP-negative” PsA (1.19[0.38] and 1523[840] accordingly) than in HC (0.92[0.24] and 1071[978]) (p< 0.0001 and p=0.002). No difference between PsA and RA patients was observed (Figure 1). The levels of SAA, thrombocytes, ferritin were comparable in “CRP-negative” PsA, RA and HC. When analysing the total cohort (CRP-positive and CRP-negative PsA, RA and HC) we found similar results, with higher calprotectin, C3 and SAA levels in PsA and RA than in HC (p< 0.001 for all comparisons).
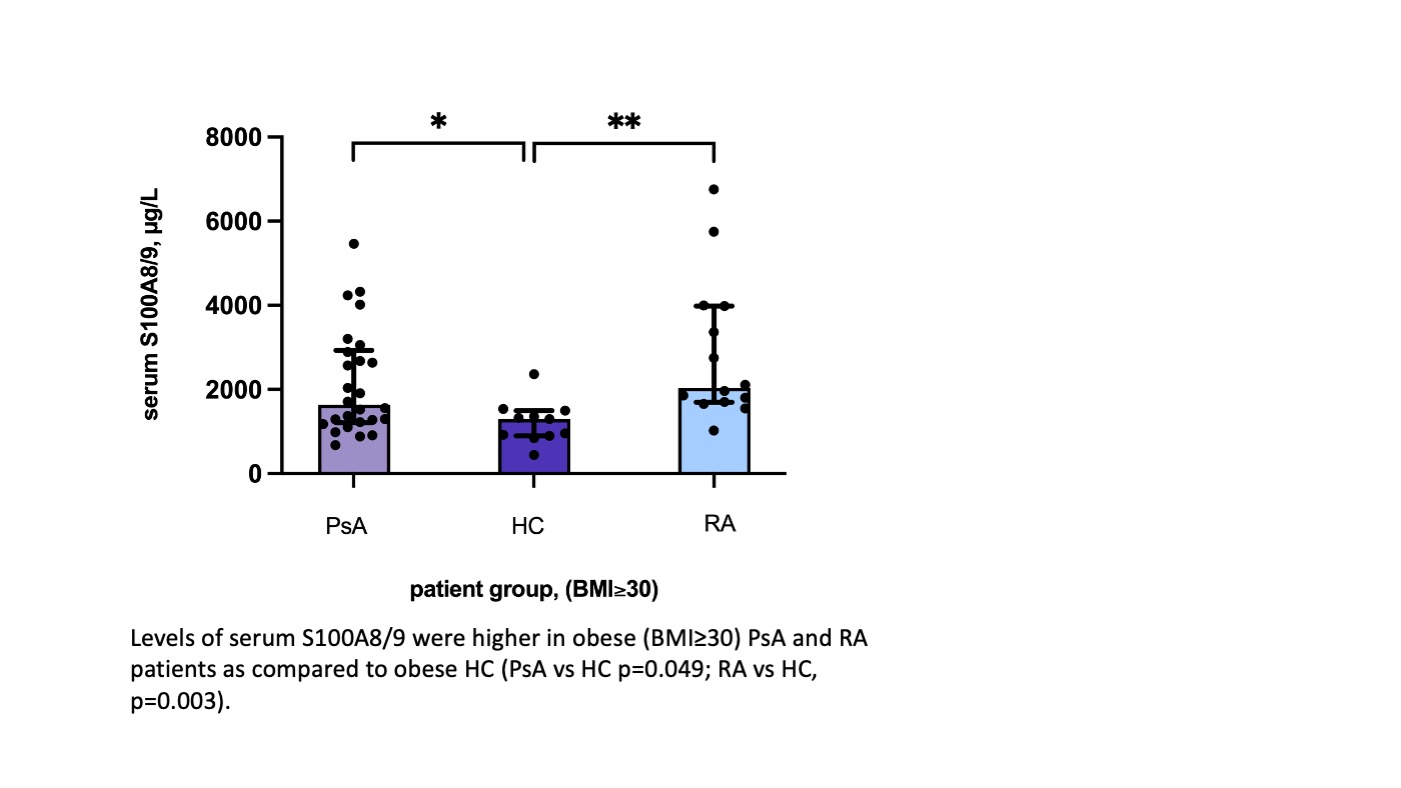
In the obese PsA (27/67, 40.3%) and RA patients (14/50, 28%) the levels of S100A8/9 were significantly higher as compared to obese HC (11/61, 18.3%) (p=0.004) (Figure 2). The levels of CRP, C3, SAA, thrombocytes, ferritin were comparable in the three groups.
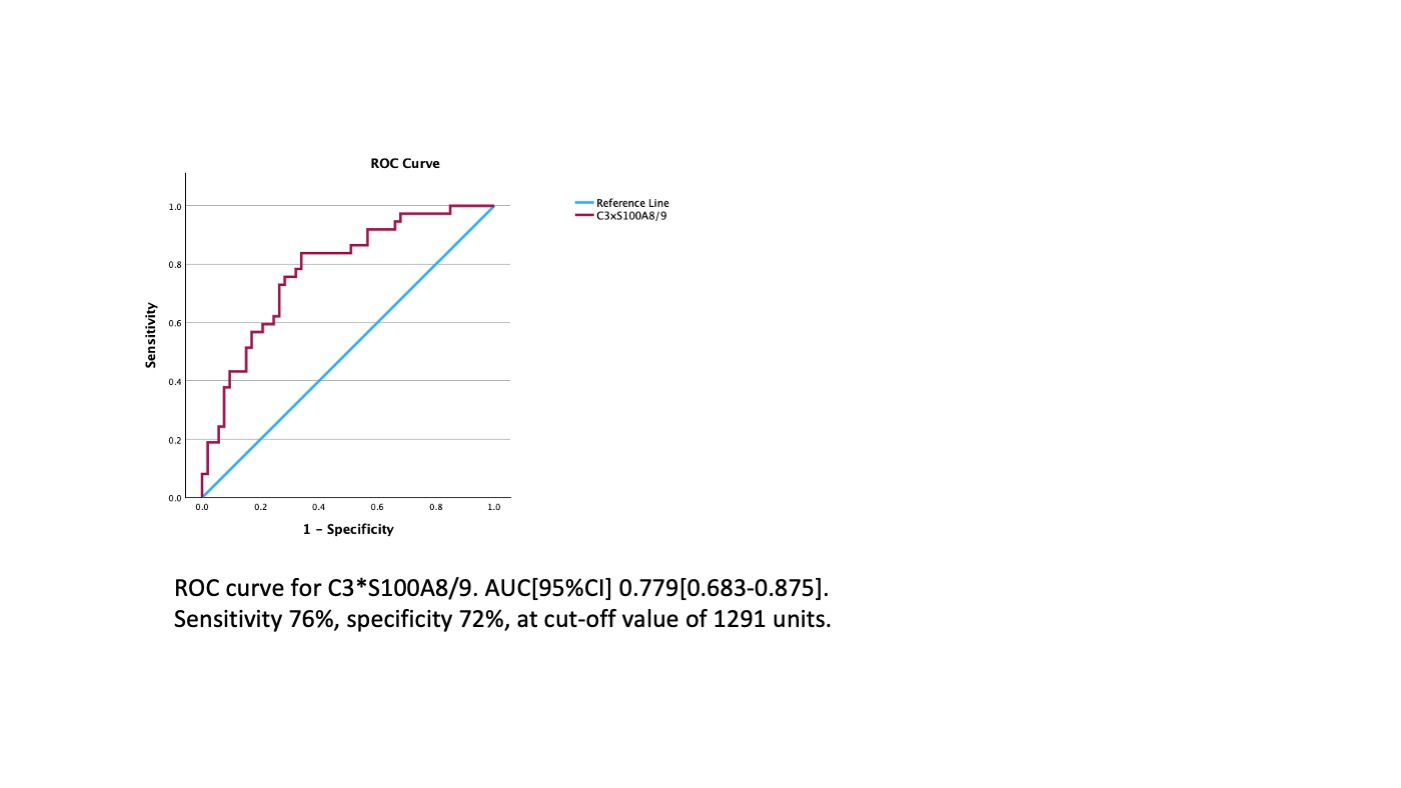
We have then conducted the ROC analysis in “CRP negative” PsA and HC subgroup with PsA being positive classifier. The C3*S100A8/9 multiplication product had the highest predictive value with AUC[95%CI] 0.779[0.683-0.875] specificity of 76% and sensitivity of 72% at an optimal cut off value of 1291 units (Figure 3).
Furthermore, the observation that calprotectin and C3 levels correlated with TJC68 and SJC66 and C3 levels with PASI and SPARCC scores in PsA patients, suggests that these markers indeed associated with inflammation in PSA.
Conclusion: Complement C3 and serum calprotectin levels are significantly higher in “CRP-negative” PsA patients than in HC. In obese PsA patients, serum calprotectin levels are increased as compared to HC, while the CRP level is comparable in both groups. In conclusion, complement C3 and serum calprotectin could be used in a selected population of early PsA patients for measuring systemic inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ishchenko A, Van Mechelen M, Pazmino S, Storms L, Verschueren P, Lories R, de Vlam K. Serum Calprotectin (S100A8/9) and Complement Factor C3 as Potential Inflammatory Markers in Obese and “CRP Negative” Early PsA Patients: Data from a Multicenter METAPSA Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-calprotectin-s100a8-9-and-complement-factor-c3-as-potential-inflammatory-markers-in-obese-and-crp-negative-early-psa-patients-data-from-a-multicenter-metapsa-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-calprotectin-s100a8-9-and-complement-factor-c3-as-potential-inflammatory-markers-in-obese-and-crp-negative-early-psa-patients-data-from-a-multicenter-metapsa-cohort/