Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Cardiopulmonary Aspects
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
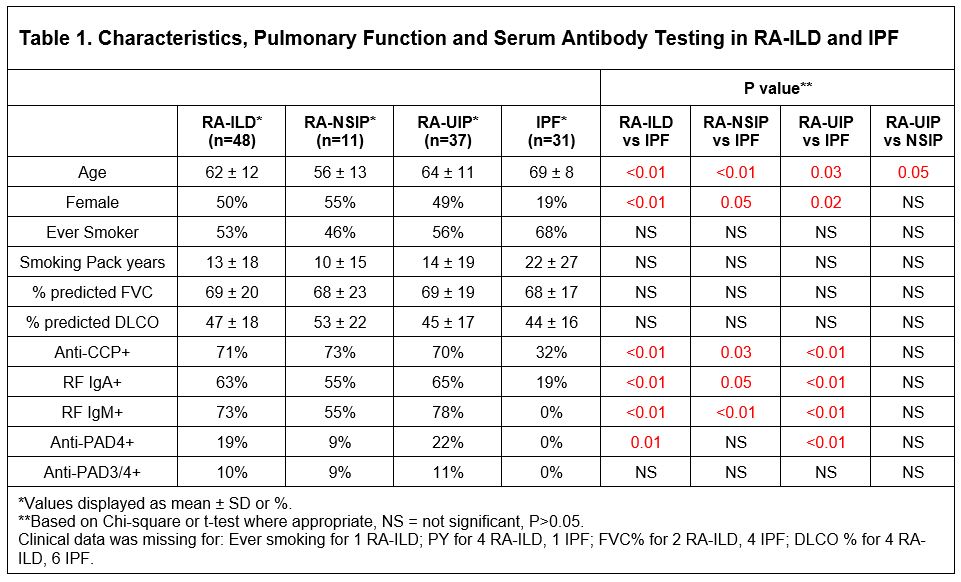
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) associated-interstitial lung disease (ILD) affects approximately 10% of RA patients. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, which is more severe in the fibrotic subtype RA-usual interstitial pneumonia (RA-UIP). Serum antibodies to peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 (anti-PAD4), particularly a subset that cross-react with PAD3 (PAD3/4XR), have been associated with imaging evidence of ILD. However, whether anti-PAD4 and anti-PAD3/4XR antibodies are associated with a particular phenotype of RA-ILD is unknown. Importantly, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) shares similar risk factors and clinical features with RA-ILD, and a recently published study by our group found that anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies were present in 25% of IPF patients. As such, in this study, we sought to identify the specificity and lung disease characteristics of anti-PAD4 and anti-PAD3/4XR antibodies in RA-ILD and IPF.
Methods: Our cohort included 48 patients with RA-ILD (confirmed by chest imaging and assessment of a pulmonologist specializing in ILD) and 32 patients with IPF (meeting 2018 diagnostic criteria) who had stored serum in the National Jewish Health Biobank. Forty-six patients with RA-ILD and 28 with IPF performed pulmonary function tests within 3 months of serum collection. Subgroups of RA-ILD were defined by imaging pattern on high-resolution chest computed tomography (HRCT) scan (nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, RA-NSIP; usual interstitial pneumonia, RA-UIP) as determined via consensus reads by a trained radiologist and pulmonologist. Serum was tested for anti-CCP (CCP3.1 IgG/IgA, Inova) and rheumatoid factor (RF-IgA and IgM) by ELISA. Serum anti-PAD4 and anti-PAD3/4XR antibodies were quantified using immunoprecipitation of radiolabeled target protein and gel electrophoresis. Clinical characteristics, measures of lung function (% predicted forced vital capacity, FVC; % predicted diffusion capacity carbon monoxide, DLCO) and prevalence of serum antibodies were compared using Chi-square and t-tests as appropriate.
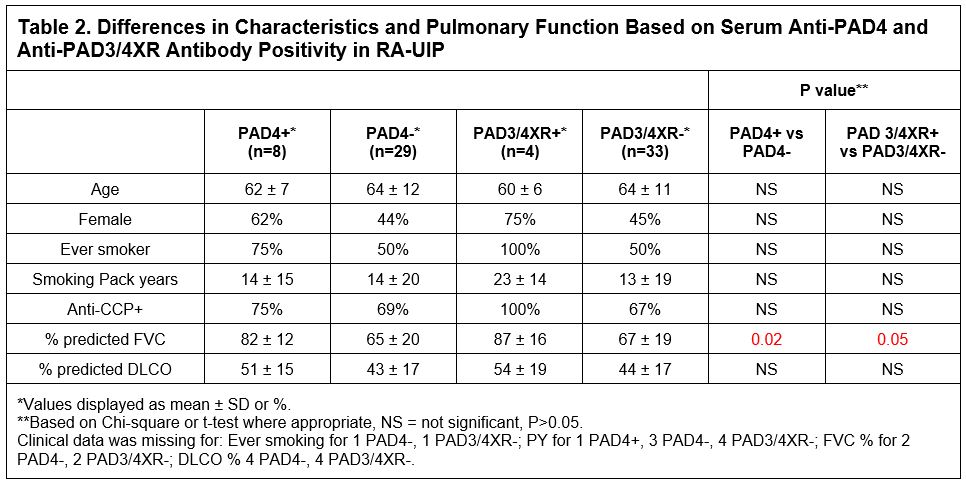
Results: Compared to IPF, subjects with RA-ILD were younger and more often female, but there were no differences in smoking history or baseline lung function (Table 1). Anti-PAD4 and anti-PAD3/4XR antibodies were present in 9/48 (19%) and 5/48 (10%) subjects with RA-ILD, respectively, and no subjects with IPF (Table 1). Within the RA-ILD group, anti-PAD4 antibodies were associated with better lung function. In particular, within RA-UIP subjects, the % predicted FVC was higher in anti-PAD4(+) and anti-PAD3/4XR(+) RA-UIP subjects (Table 2 and Figure 1).
Conclusion: We demonstrate that serum anti-PAD4 and anti-PAD3/4XR antibodies are highly specific for RA-ILD and associated with better lung function in RA-UIP patients. Because patients with RA-UIP can often have a worse prognosis compared to RA-NSIP patients, the identification of a biomarker that is associated with better lung function could provide new insights into RA-ILD pathogenesis and may identify a new prognostic biomarker for RA-ILD, although future longitudinal studies are needed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wilson T, Solomon J, Swigris J, Darrah E, Demoruelle M. Serum Anti-PAD4 and Anti-PAD3/4XR Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated-Interstitial Lung Disease Are Associated with Better Lung Function [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-anti-pad4-and-anti-pad3-4xr-antibodies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-are-associated-with-better-lung-function/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-anti-pad4-and-anti-pad3-4xr-antibodies-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-are-associated-with-better-lung-function/