Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Alarmins are proteins found in the nuclei of epithelial, endothelial, and immune cells that are released following cell damage and act as stress signals. Facilitating tissue homeostasis and repair, alarmins have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of both rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and tissue fibrosis in other conditions including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (Lee JU et al. BMC Pulm Med 2017). The objective of the current study was to quantify associations of serum alarmins with risk of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
Methods: Three alarmins (IL-33, thymic stromal lymphopoietin [TSLP], and IL-25) were measured using serum collected at enrollment from the multicenter prospective Veterans Affairs RA registry. RA-ILD was classified using systematic medical record review and based on a provider diagnosis of ILD, plus either consistent findings from chest CT or histopathological abnormalities. Given their distributions, IL-33 and TSLP concentrations were log-transformed and standardized (per 1 SD), while detectable IL-25 was categorized into tertiles (undetectable as referent). Cross-sectional associations of alarmin values with RA-ILD at enrollment (prevalent RA-ILD) were examined using separate logistic regression models. Associations of alarmins with incident RA-ILD were examined using Cox proportional hazards regression. Covariates in multivariate models included age, sex, race, smoking status, RA disease activity score, and anti-CCP antibody positivity. For analytes associated with incident RA-ILD, the cumulative incidence of ILD was summarized graphically by alarmin quartile.
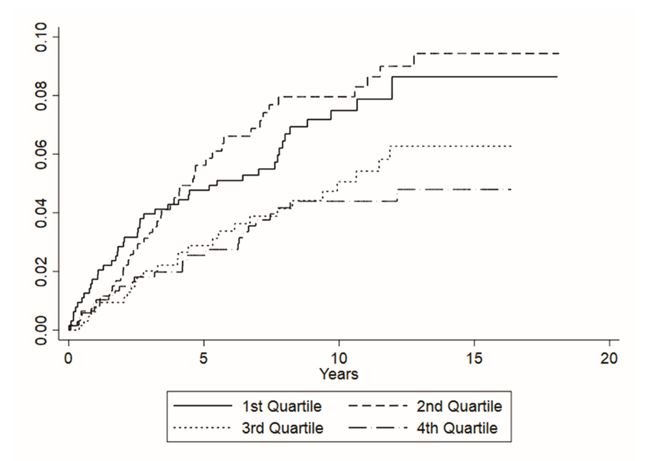
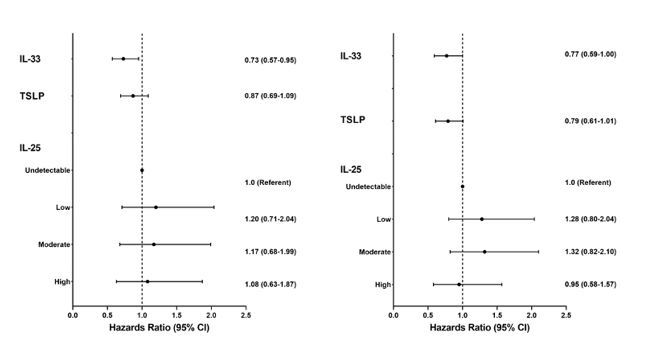
Results: Of 2,835 study participants (88% male, mean age 65 ± 11 years, 77% White, 76% current or former smoker), 115 participants (4.1%) had prevalent RA-ILD at baseline. An additional 146 (5.1%) developed incident ILD over a median follow-up of 3.0 years (IQR 1.2-6.3 years). There were no associations between serum alarmins and prevalent ILD in unadjusted or adjusted logistic regression models (not shown). Likewise, no significant associations of TSLP or IL-25 with incident ILD were observed. The cumulative incidence of RA-ILD development by IL-33 quartile among those without ILD at enrollment is shown in Figure 1. After 10 years of follow-up, approximately 8% of uncensored patients with RA in the lower two IL-33 quartiles had developed ILD compared to approximately 4% in the upper two quartiles. There was a significant inverse association between IL-33 concentration and risk of developing incident RA-ILD in unadjusted (HR 0.73 per log-fold increase; 95% CI 0.57-0.95; p=0.018) and adjusted (HR 0.77; 95% CI 0.59-1.00, p=0.047) models (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In contrast to our a priori hypothesis, we observed a significant inverse association between serum IL-33 concentration and the risk of developing incident RA-ILD. These results suggest that by promoting tissue homeostasis and repair, circulating IL-33 could play a protective role in the ‘pre-clinical’ stages of RA-ILD and its measurement could improve risk stratification efforts in addition to informing future strategies of treatment and prevention.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mikuls T, England B, Sayles H, Johnson T, Duryee M, Hunter C, Baker J, Kerr G, Kunkel G, Cannon G, Sauer B, Wysham K, Joseph A, Wallace B, Thiele G, Poole J. Serum Alarmins and the Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-alarmins-and-the-risk-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-alarmins-and-the-risk-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/