Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Breathe: RA-ILD
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Adipokines are metabolic cytokines shown to be dysregulated in RA and prognostic of RA-related complications such as cardiovascular disease. Similarly, aberrations in adipokines have been demonstrated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a disease closely related to RA-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD); however, they are not yet well studied in RA-ILD. We investigated whether serum adipokines were associated with RA-ILD risk and prognosis in a multicenter, prospective RA cohort with well-phenotyped RA-ILD.
Methods: We conducted both a cross-sectional study of prevalent ILD and a cohort study of incident ILD through the Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis (VARA) registry. Adiponectin, leptin, and fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF-21) were measured from banked serum samples, log-transformed and standardized, and analyzed as both continuous values and dichotomized by the median (high/low). All RA-ILD diagnoses were validated through systematic medical record review by a rheumatologist specializing in RA-ILD. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to evaluate associations between adipokines and prevalent ILD, and multivariable Cox regression models were used for incident ILD, adjusting for potential confounders, including body mass index (BMI) categories. Associations of adipokines with all-cause mortality risk were determined among those with prevalent ILD using multivariable Cox regression.
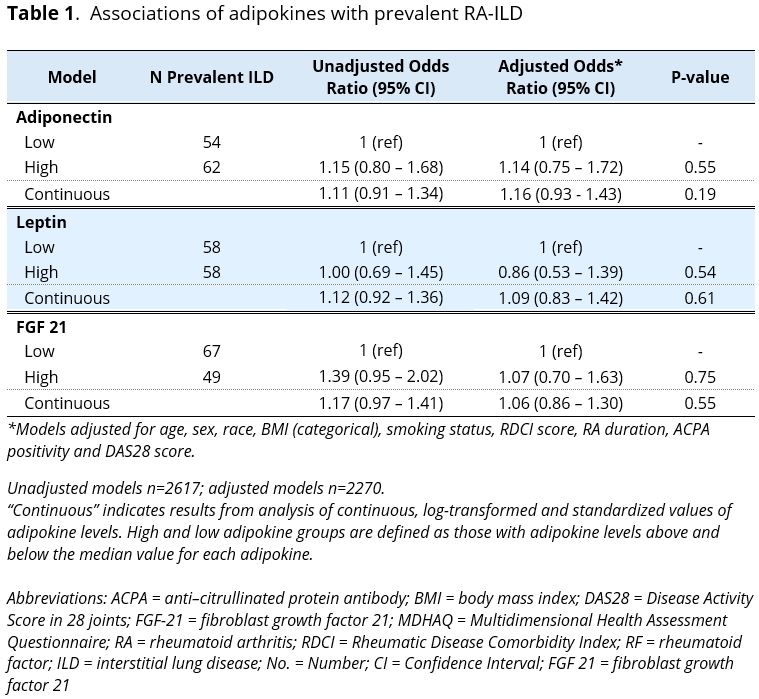
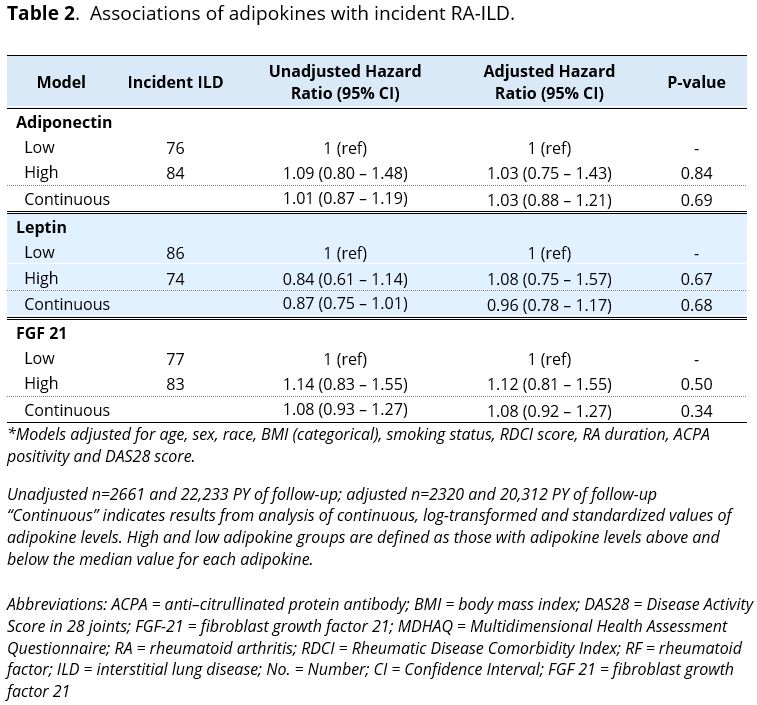
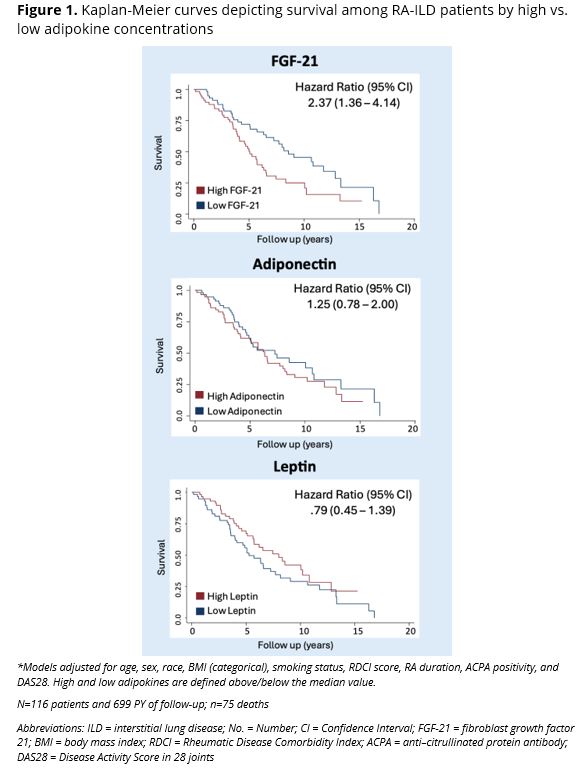
Results: Among 2,777 total participants (88% male, mean age 64 years), 116 (4%) had prevalent ILD. Among 2,661 participants without prevalent ILD, 160 (6%) developed incident ILD over 22,233 patient-years of follow-up. There were no significant associations between the adipokines and prevalent (aOR range: 1.06 to 1.16, p >0.19; Table 1) or incident (aHR per 1 SD increase: range 0.96 to 1.08; p >0.34; Table 2) ILD. Among those with prevalent ILD, higher FGF-21 concentrations were significantly associated with increased all-cause mortality risk (high vs. low, aHR: 2.37 [95% CI 1.36 – 4.14], p < 0.002; Figure 1). Leptin (aHR 0.79) and adiponectin (aHR 1.25) were not significantly associated with survival. Forced vital capacity was not correlated with adipokine concentrations (Pearson r: -0.06 to -0.15).
Conclusion: While serum adipokine concentrations were not significantly associated with prevalent or incident RA-ILD, FGF-21 concentrations were predictive of survival among those with RA-ILD. These findings suggest that metabolic dysregulation in RA-ILD is indicative of poor prognosis. This finding can be used to guide further research into the role of metabolic changes in RA-ILD disease progression and prognostication.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Haggart A, Baker J, Johnson T, Yang Y, Roul P, Wysham K, Cannon g, Kunkel G, Ascherman D, Monach P, Kerr G, Reimold A, Duryee M, Thiele G, Mikuls T, England B. Serum Adipokines and Interstitial Lung Disease in a Prospective Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-adipokines-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-a-prospective-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-adipokines-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-a-prospective-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/