Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1155–1182) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Muscle weakness in inflammatory myopathies (IIM) is due to muscle-edema, atrophy and fatty-infiltration among which edema is the predominant cause at baseline. Some IIM pateints do not achieve full muscle power even with immunosupressive treatment which mainly targets edema. Serial changes occuring in skeletal muscles visualized on thigh MRI can help understand the failure of complete recovery. Role of Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) assessed skeletal muscle compositon as outcome measure in IIM was not studied previously.
Objectives:To see the changes in skeletal muscle composition over 6 months in IIM patients using imaging and to assess the agreement of MRI and DXA scores with each other and with clinical outcome measures
Methods: Patients satisfying 2017 ACR-EULAR classification criteria for IIM were prospectively enrolled. All patients underwent thigh MRI(t-MRI) STIR and T1 weighted sequences (axial and coronal) at baseline, 3 and 6 months and DXA scan at baseline and 6 months. Manual muscle testing-8(MMT-8), Functional index-3(FI-3), 2-minute walk distance (2MWD) were assessed at baseline, 3 and 6 months. t-MRI was scored using a semi-quantitative score for muscle edema, fascial edema, muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration. Friedman test was used to compare variables at baseline, 3 and 6 months and Spearman correlation was done for agreement of MRI and DXA scores with each other and clinical outcome measures.
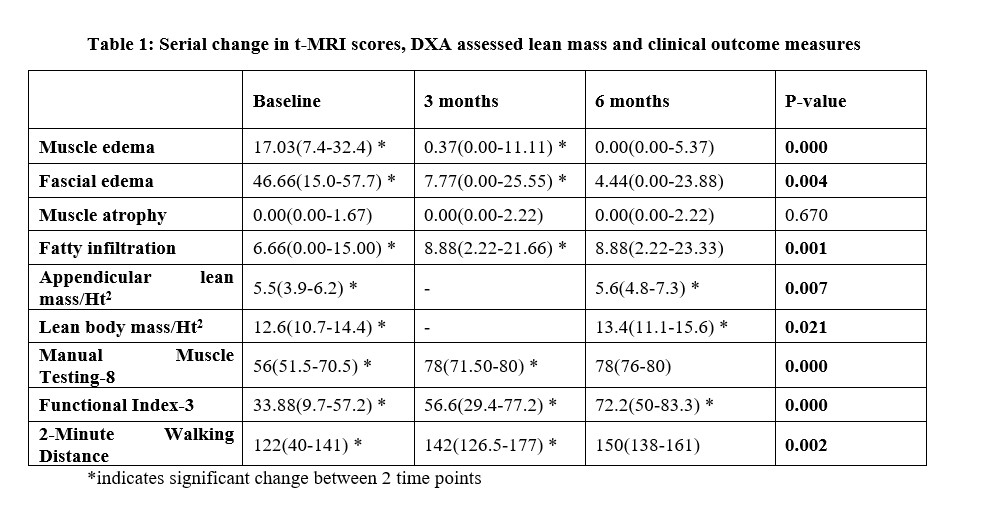
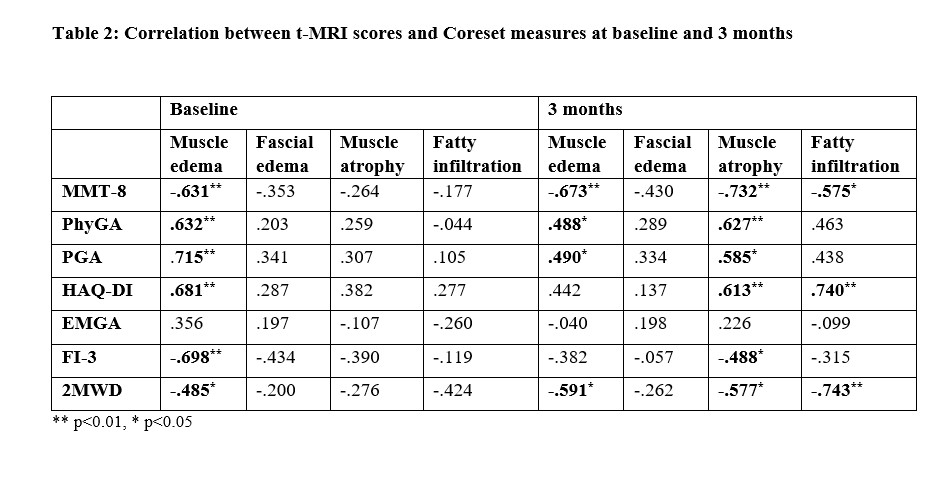
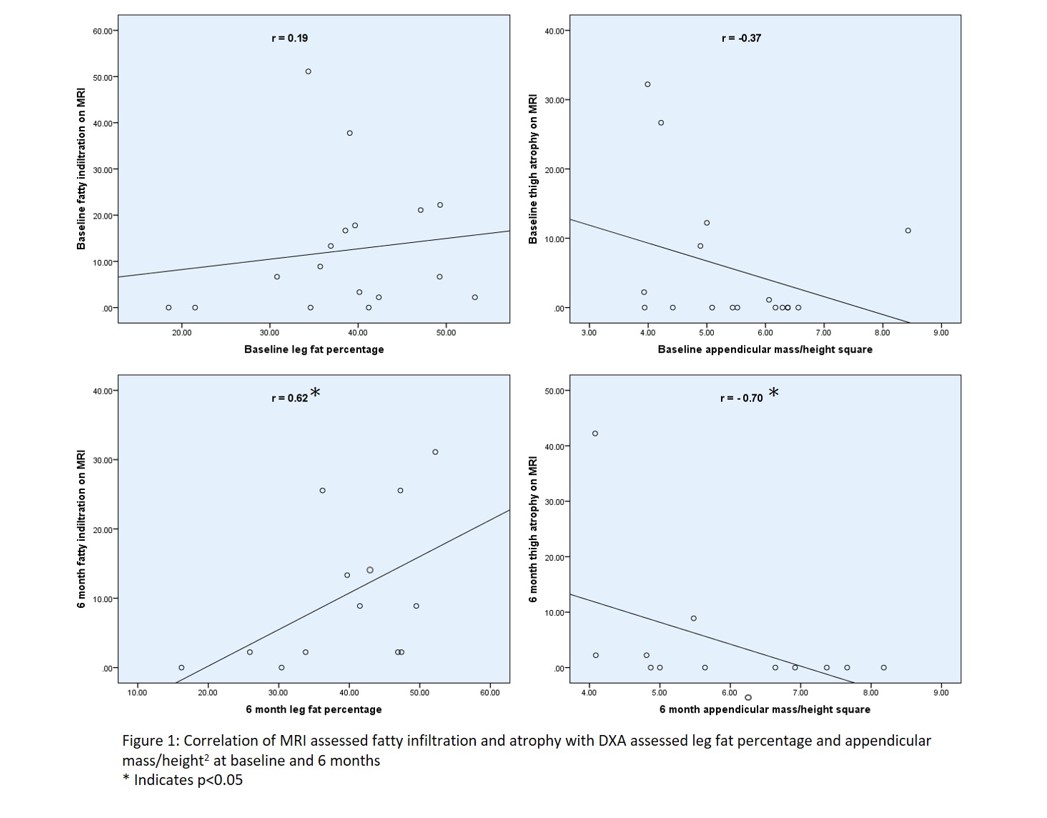
Results: 17 patients (12 females) were enrolled and all of them completed 3-months follow-up while only 13 completed 6-months follow-up. Median (IQR) age was 38 (27-46) years, disease duration was 6 (2-24). The study group comprised of 10 dermatomyositis, 5 antisynthetase syndrome and 3 immune mediated necrotizing myopathy patients MRI assessed muscle-edema and fascial-edema decreased significantly and fatty-infiltration increased significantly (p < 0.01) from baseline to 3-months. Muscle atrophy showed no change. Improvement in MMT-8 and 2MWD was significant between baseline and 3-months(p< 0.001) whereas FI-3 continued to improve till 6-months(p< 0.001) (Table 1). At baseline MMT-8(r=-0.631; p< 0.01), FI-3(r=-0.698; p< 0.01) and 2MWD (R=-0.485; p< 0.05) negatively correlated with only muscle edema. At 3-months MMT-8 and 2MWD negatively correlated with muscle-edema (r=-0.673, r=-0.591), atrophy (r=-0.732, r=-0.577) and fatty-infiltration (r=-0.575, r=-0.743) (p< 0.05) respectively (table 2). MRI fatty-infiltration score and atrophy score did not correlate with DXA assessed leg fat percentage and appendicular mass/ht2 respectively at baseline but had significant correlation (p< 0.05) at 6- months (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In IIM, edema decreased but fatty infiltration increased significantly in first 3-months. DXA assessment of fat and lean mass did not agree with MRI atrophy and fatty infiltration at baseline probably due to concomitant muscle edema.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gorijavolu M, Kavadichanda C, Ananthakrishnan R, Mariaselvam C, Thabah M, Negi V. Serial Imaging Changes in Skeletal Muscle Composition and Their Association with Clinical Outcomes in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serial-imaging-changes-in-skeletal-muscle-composition-and-their-association-with-clinical-outcomes-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serial-imaging-changes-in-skeletal-muscle-composition-and-their-association-with-clinical-outcomes-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/