Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Impact (0225–0240)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: SF-36 and its components, as well as other PROs have been shown to predict various disease outcomes. We hypothesized that positive responses to questions (Q) 11A “I seem to get sick a little easier than other people“, and 11C “I expect my health to get worse“ from the general health (GH) domain of the SF-36 v1 questionnaire may correspond to a more fragile self-perceived GH status, and thus serve as possible predictors of future disease outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We aimed to investigate whether these 2 questions could predict therapeutic response in patients with RA starting their first anti-TNF therapy.
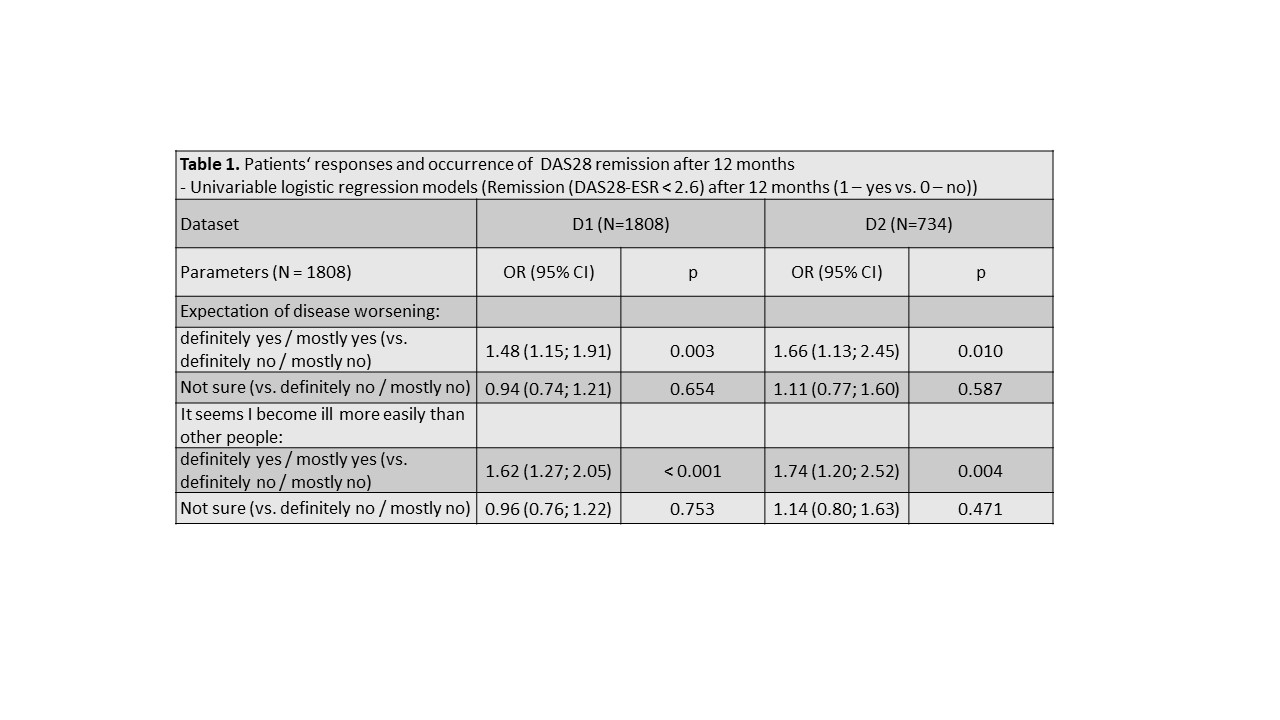
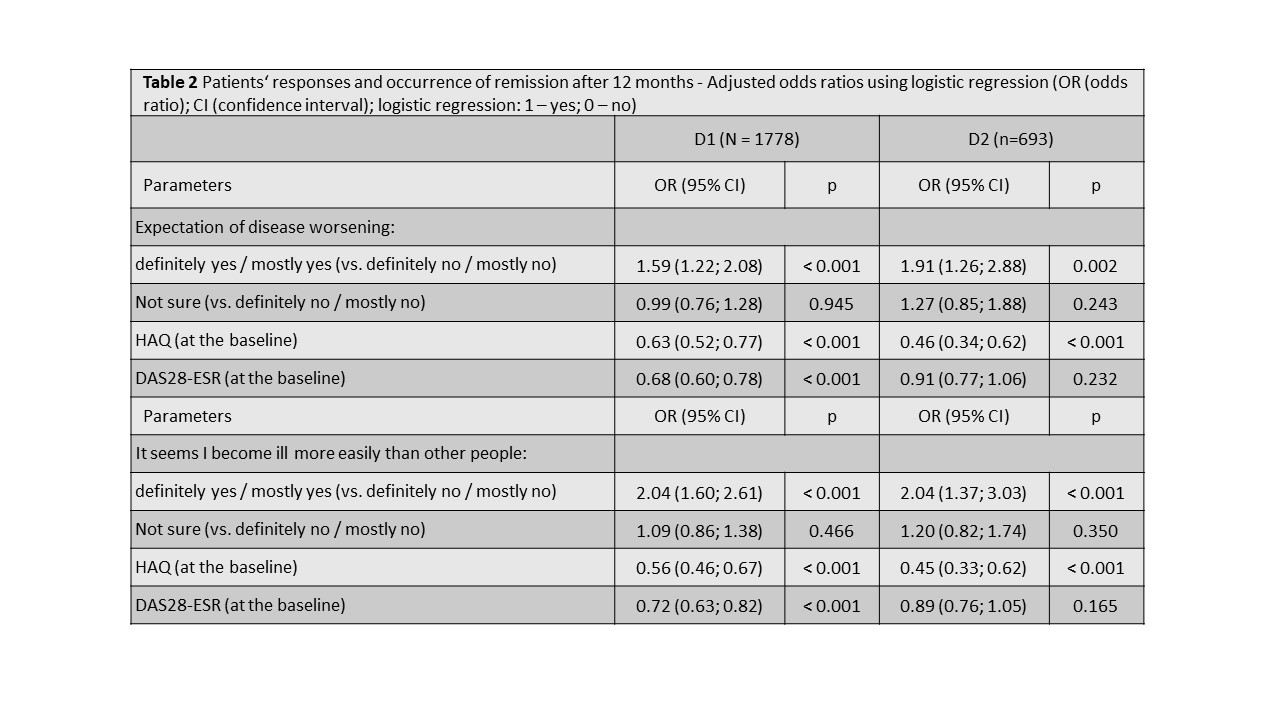
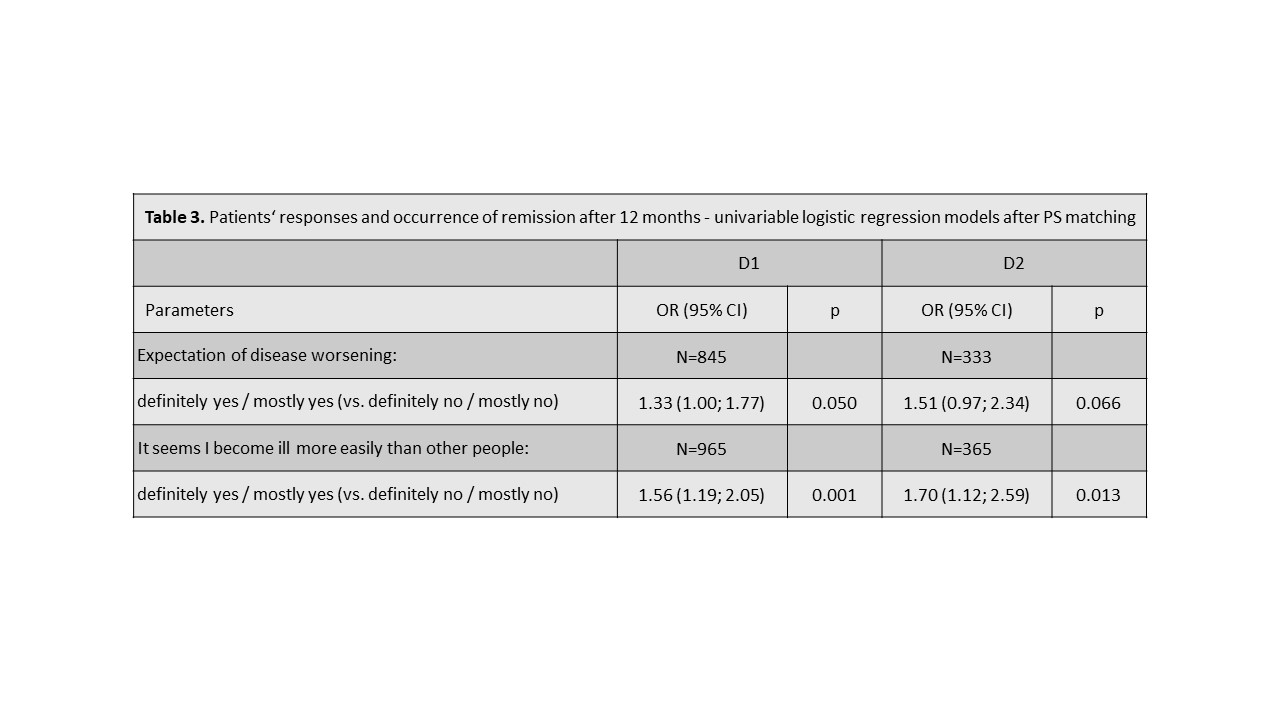
Methods: We have used two separate datasets from the Czech biologics registry ATTRA to validate our hypothesis. Dataset D1 included RA patients with at least 1 year follow-up and all relevant data available starting their first-line anti-TNF treatment within period 01/01/2012-31/12/2017 (N=1808), and dataset D2 pts starting in in 01/01/2018–01/01/2020 (N=734). Our primary outcome was DAS28-ESR remission (REM) at 12 months. REM was defined as DAS28< 2.6. Patients were grouped according their response (definitely/mostly yes vs. definitely/mostly no) to Q11A and Q11C at baseline. REM rates after 12 months of 1st-line anti-TNF treatment were compared across patients‘ groups with Pearson chi-squared test. Firstly, odds ratios (ORs) using logistic regression (univariate, and then adjusted to baseline DAS28 and HAQ) were calculated to predict REM at 12M. Secondly, ORs were calculated after matching pts with positive or negative responses by a propensity score (PS) using sex, age, disease duration, baseline DAS28, calendar year and co-medication to balance baseline differences.
Results: At baseline, 79% and 80% pts were female, mean (SD) age was 52(12) and 54(13) years, DAS28 6.3 (0.9) and 6.2 (1.1), HAQ 1.5(0.6) and 1.5(0.6) , 74% and 68% were RF+ , 70% and 69% ACPA+ in D1 and D2 resp. In D1 34% and 31% pts, and in D2 32% and 30% responded positively to Q11A and 11C resp. Patients with positive responses to Q11A and 11C tended to have slightly (but statistically significantly) higher DAS28, HAQ, CRP or ESR, and patient- and physician global activity assessment at baseline. At 12 months, 40% (49%), 31% (37%), and 30% (40%) patients with positive, negative and neutral response to Q 11A reached REM; p< 0.001 (p=0.018) in D1 (D2) resp. At 12 months, 42% (51%), 31% (37%), and 30% (40%) patients with positive, negative and neutral response to Q 11C reached REM; p< 0.001 (p=0.04) in D1 (D2) resp. Crude and adjusted ORs for reaching REM according to responses to Q11A and Q11C are shown in tables 1-3.
Conclusion: We provide a robust evidence that self-perceived general health at start of anti-TNF therapy predicts reaching remission at 12 months in pts with RA.
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the project (Ministry of Health, Czech Republic) for consensual development of research organization 023728
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zavada J, Nekvindova L. Self-perceived General Health at Start of Anti-TNF Therapy Predicts Therapeutic Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analysis from the Czech Biologics Registry ATTRA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-perceived-general-health-at-start-of-anti-tnf-therapy-predicts-therapeutic-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-analysis-from-the-czech-biologics-registry-attra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-perceived-general-health-at-start-of-anti-tnf-therapy-predicts-therapeutic-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-analysis-from-the-czech-biologics-registry-attra/