Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0460–0479) Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatic diseases, and specifically SLE, present with greater sexual dysfunction than other chronic diseases. Sexual dysfunction (SxD) is multifactorial and comprises disease-related factors, psychological factors, hormonal imbalance, and treatment. Self-esteem has an association with mental and physical health in SLE patients, however, its impact has not been studied as a determinant of SxD.
We aimed to assess the association between body self-esteem, global self-worth and sexual functioning in SLE patients.
Methods: We performed a transversal study in a tertiary care center in Mexico City. Patients ≥18 years old who fulfilled EULAR/ACR criteria for SLE were included. Body self-esteem was assessed by the Body Self-esteem Scale (BSS) and global self-worth by the Rosenberg´s Self-Esteem Scale (RSES). Sexual function was assessed by the CSFQ-14 questionnaire. Disease activity was measured by SLEDAI and disease-associated damage by SLICC index. Relevant demographic, clinical and serological characteristics were recorded. We used univariate and multivariate analysis to assess association between self-esteem and SxD. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS V.25.
Results: We included a total of 280 patients, in whom self-esteem was analyzed. Most patients were female (87%), the mean age was 41 (±12 years) and mean BMI was 25.6 (±4.9kg/m2). Mean SLEDAI and SLICC scores were 2.45 (±2.72) and 0.8 points (±1.04), respectively. A correlation between body self-esteem and SxD was found in both genders. Interestingly, the correlation was higher in men than in women (r=0.45, p=0.008 vs r=0.25, p=0.0001, respectively). In addition, a correlation was established between global self-worth and SxD for both men and women (r=0.4, p=0.006 vs r=0.18, p=0.004) respectively. Interestingly, both scales (BSS and RSES) showed a moderate correlation with SxD in men with SLE (r=0.45, p=0.008 and r=0.47, p=0.006, respectively). Although this correlation was also found in women (between BSS, RSES and SxD), it was weaker than in men (r=0.25, p=0.0001 and r=0.18, p=0.004)
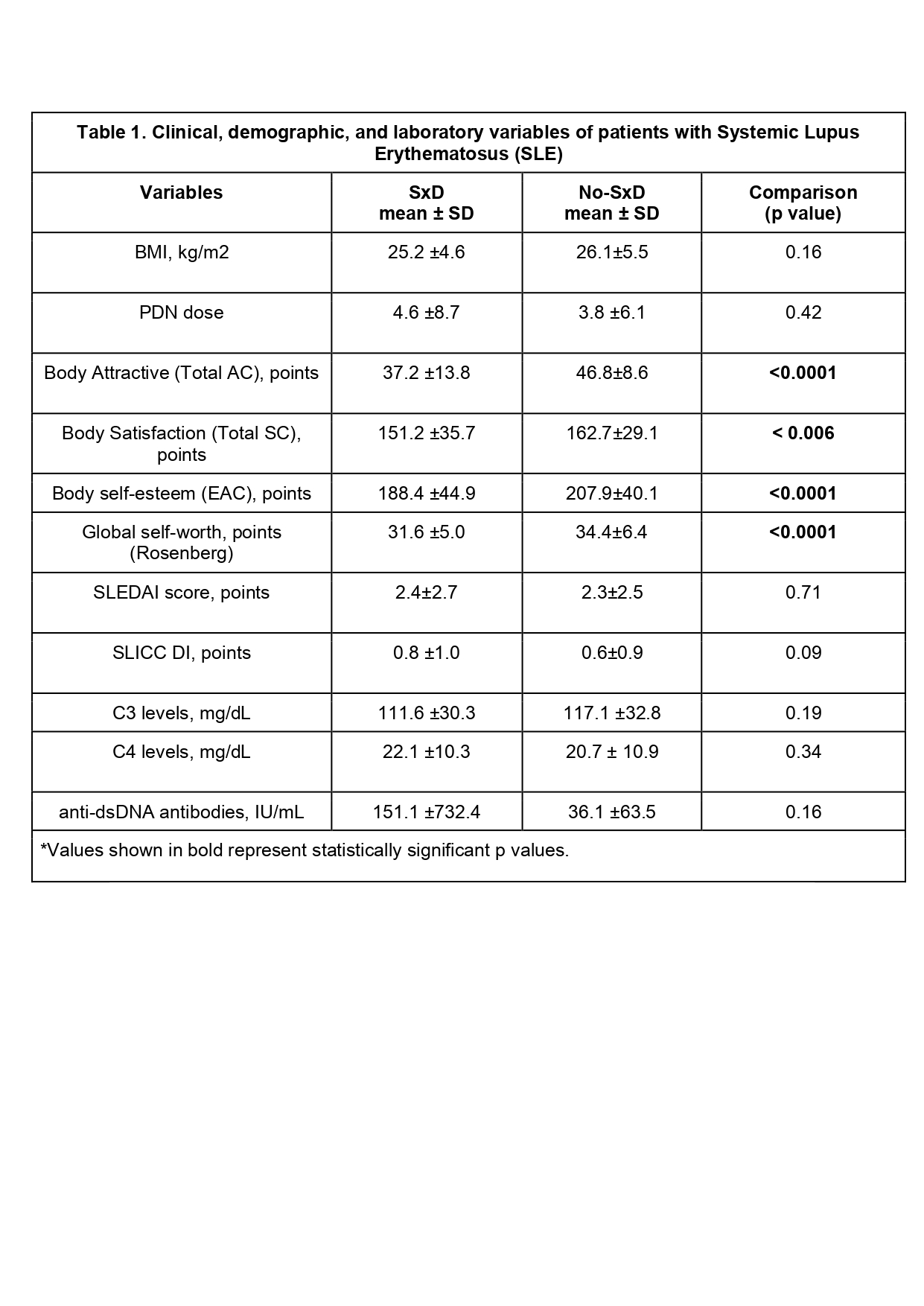
Other clinical and laboratory variables were studied, such as prednisone, cyclophosphamide, obesity, depression, body self-esteem, SLEDAI and SLICC damage index; however, no statistical significance was found (Table 1).
The multivariate analysis showed that age (0.96, 95% CI 0.94-0.98, p=0.003), lower RSES score (1.08, 95% CI 1-1.14, p=0.01) and leukocytes (1.19, 95% CI 1-1.40, p=0.02) were independently associated with SxD. Although there was a trend for an association with lower BSS, it did not reach statistical significance (1.00, 95% CI 1-1.15, p=0.055).
Conclusion: To our knowledge this is the first study to evaluate self-esteem (with two different scales) as a determinant of sexual function in SLE patients, showing a greater impact in male population. Given the complexity of sexual function in SLE patients and the various factors that can affect it, it is important to consider additional psychosocial aspects, such as self-esteem, to help us identify and address potential problems early on, leading to better quality of life through timely interventions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Espinosa-León M, Marengo-Rodríguez D, Ibarra-Velasco M, Barrera-Vargas A, Merayo-Chalico J. Self-esteem as a Determinant of Sexual Function in SLE Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-esteem-as-a-determinant-of-sexual-function-in-sle-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-esteem-as-a-determinant-of-sexual-function-in-sle-patients/