Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Plenary III (1424–1429)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) and juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA) are two conditions that represent pediatric correlates of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and adult psoriatic arthritis (PsA), respectively.1,2 Secukinumab (SEC) has demonstrated efficacy and safety in adult patients (pts) with PsA, ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axSpA.3-5 This study evaluated efficacy and safety of SEC using a randomized double-blind placebo controlled flare prevention design in pts with active ERA and JPsA.
Methods: Pts (aged 2 to < 18 years) classified as ERA or JPsA according to ILAR criteria of ≥ 6 months duration with active disease were included. The 2-year study consisted of open-label (OL) s.c. SEC (75/150 mg in pts < 50/ ≥ 50 kg) treatment at baseline (BL), and at Weeks (Wk) 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 and 12 in treatment-period (TP) 1. Responders who achieved at least JIA ACR 30 response at Wk 12 were randomized into the double-blinded TP2 to continue SEC or placebo (PBO) every four wks until a disease flare, or up to Wk 100. The primary endpoint was the time to flare in TP2; key secondary endpoints included JIA ACR 30/50/70/90/100, inactive disease, juvenile arthritis disease activity score (JADAS), enthesitis and active joint counts, and safety. Analysis of time to flare in TP2 included the proportion of pts with disease flare, Kaplan-Meier estimate of median days for time to flare, hazard ratio estimate, and stratified log-rank test P-value. Intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis using non-responder imputation (NRI) and as observed analysis were performed for JIA ACR 30/50/70/90/100 responses and inactive disease.
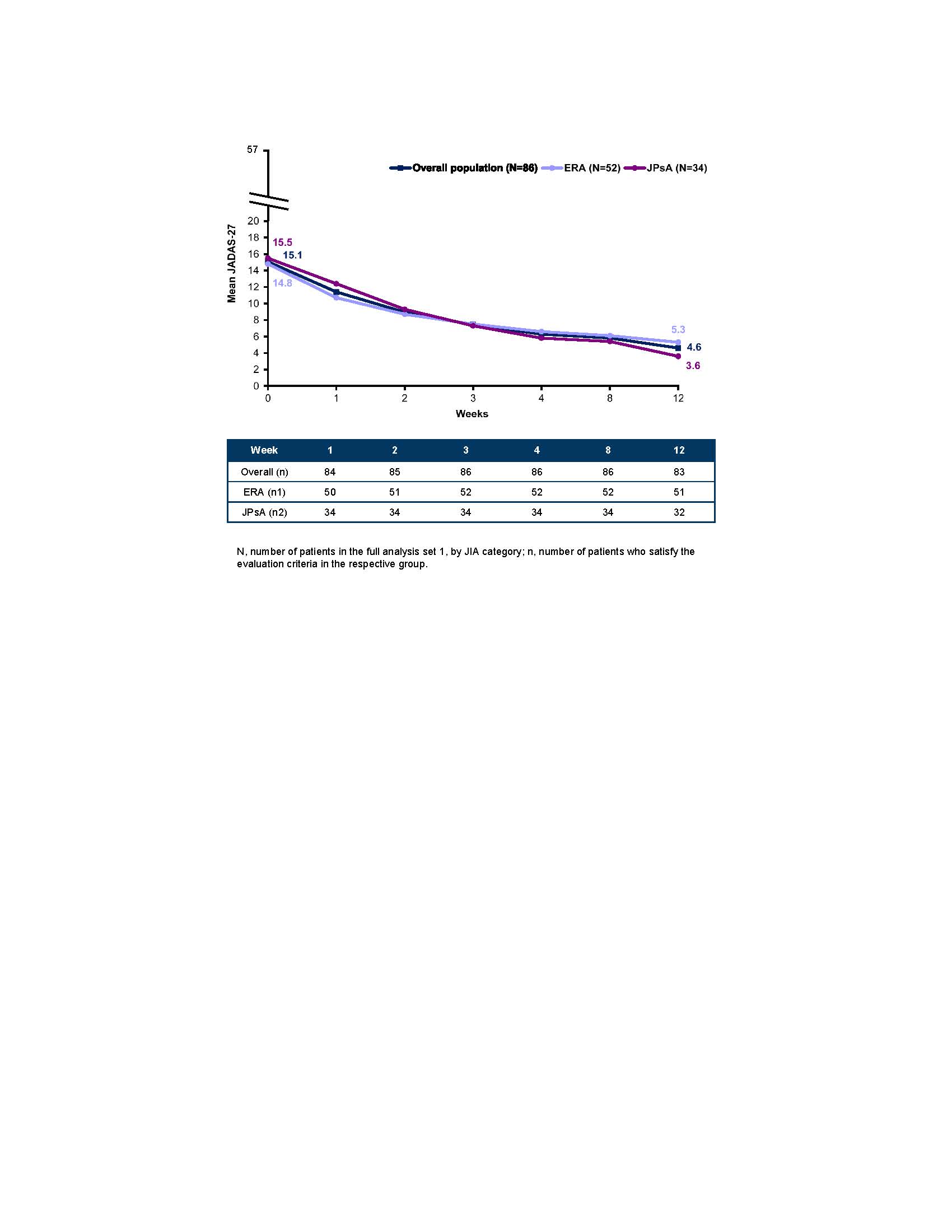
Results: 86/97 (88.7%) screened pts were enrolled in TP1 (mean age, 13.1 years; female, 33.7%; ERA, n=52; JPsA, n=34) with a mean JADAS-27 score of 15.1 and enthesitis count of 2.6 at BL. At Wk 12, 75/83 (90.4%) pts achieved JIA ACR 30 and entered TP2. There were 21 flares in PBO treated and 10 flares in SEC treated pts during TP2. The primary endpoint was met as, compared to PBO, SEC treated pts had a significantly longer time to flare, resulting in a 72% reduced flare risk (HR: 0.28; 95% CI: 0.13–0.63; P< 0.001). JIA ACR responses, disease activity, enthesitis count and joints with active arthritis are reported in the Table. There were minor differences between the ITT and as observed analysis in JIA ACR responses and inactive disease in TP1. Improvement in the JADAS-27 score was observed in pts in both the ERA and JPsA categories (Figure). Rates of adverse events (AEs; 91.7% vs 92.1%) and serious AEs (14.6% vs 10.5%) in the SEC and PBO groups were comparable in the entire TP. No new safety signals were observed in pts receiving SEC (injection site reaction, n=1; overall pt-years =141.5).
Conclusion: In children and adolescents with ERA and JPsA, efficacy of SEC was demonstrated with a significantly longer time to flare vs PBO with sustained improvement of signs and symptoms up to Wk 104. Efficacy was observed in both ERA and JPsA pts along with a favorable safety profile.
References:
1. Colbert RA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:477–85.
2. Martini A, et al. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:190–7.
3. McInnes IB, et al. Lancet. 2015;386:1137–46.
4. Baeten D, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2534–48.
5. Deodhar A, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73:110–20.
 Efficacy of secukinumab at the end of Treatment Periods 1 and 2 (Key secondary endpoints) as per ITT and NRI imputation for JIA ACR evaluation/inactive disease and as observed for continuous variables
Efficacy of secukinumab at the end of Treatment Periods 1 and 2 (Key secondary endpoints) as per ITT and NRI imputation for JIA ACR evaluation/inactive disease and as observed for continuous variables
 Improvement in JADAS_27 in the overall population, and ERA and JPsA categories in treatment period 1
Improvement in JADAS_27 in the overall population, and ERA and JPsA categories in treatment period 1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner H, Foeldvari I, Alexeeva E, Ayaz N, Calvo Penads I, Kasapcopur O, Chasnyk V, Hufnagel M, Zuber Z, Schulert G, Ozen S, Popov A, Ramanan A, Scott C, Sozeri B, Zholobova E, Zhu X, Whelan S, Pricop L, Ravelli A, Martini A, Lovell D, Ruperto N. Secukinumab Treatment in Children and Adolescents with Enthesitis-related Arthritis and Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis: Efficacy and Safety Results from a Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-treatment-in-children-and-adolescents-with-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-juvenile-psoriatic-arthritis-efficacy-and-safety-results-from-a-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-treatment-in-children-and-adolescents-with-enthesitis-related-arthritis-and-juvenile-psoriatic-arthritis-efficacy-and-safety-results-from-a-phase-3-study/
