Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Enthesitis can be a debilitating spondyloarthritis (SpA) manifestation and the cause of pain, reduced quality of life and impaired physical function.1,2 Herein, we evaluated the effect of secukinumab on axial and peripheral enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients with baseline enthesitis (BLE) across all Maastricht AS EnthesiS (MASES) sites (N=13), axial sites [N=11; 13 MASES minus Achilles tendons (AT); AxS] and peripheral sites (N=6; AT + lateral condyles of humerus/femur; PS) and the AT (N=2) at Weeks 16 and 52.
Methods: This post hoc analysis pooled data across 4 secukinumab studies in AS (MEASURE 1-4) from patients originally randomized to secukinumab 150mg (approved dose in AS), 300mg (MEASURE 3 only), or placebo (PBO) with BLE (MASES >0). Study designs have been reported previously.3-5 Evaluations include mean change from BL in MASES, complete resolution (CR; MASES=0) and improvement from BL in MASES score of ≥5 counts. Mixed-effect model repeat measurement (MMRM) analysis was done on change from BL in MASES score and non-responder imputation for resolution of enthesitis at Week 16; data are reported as observed at Week 52.
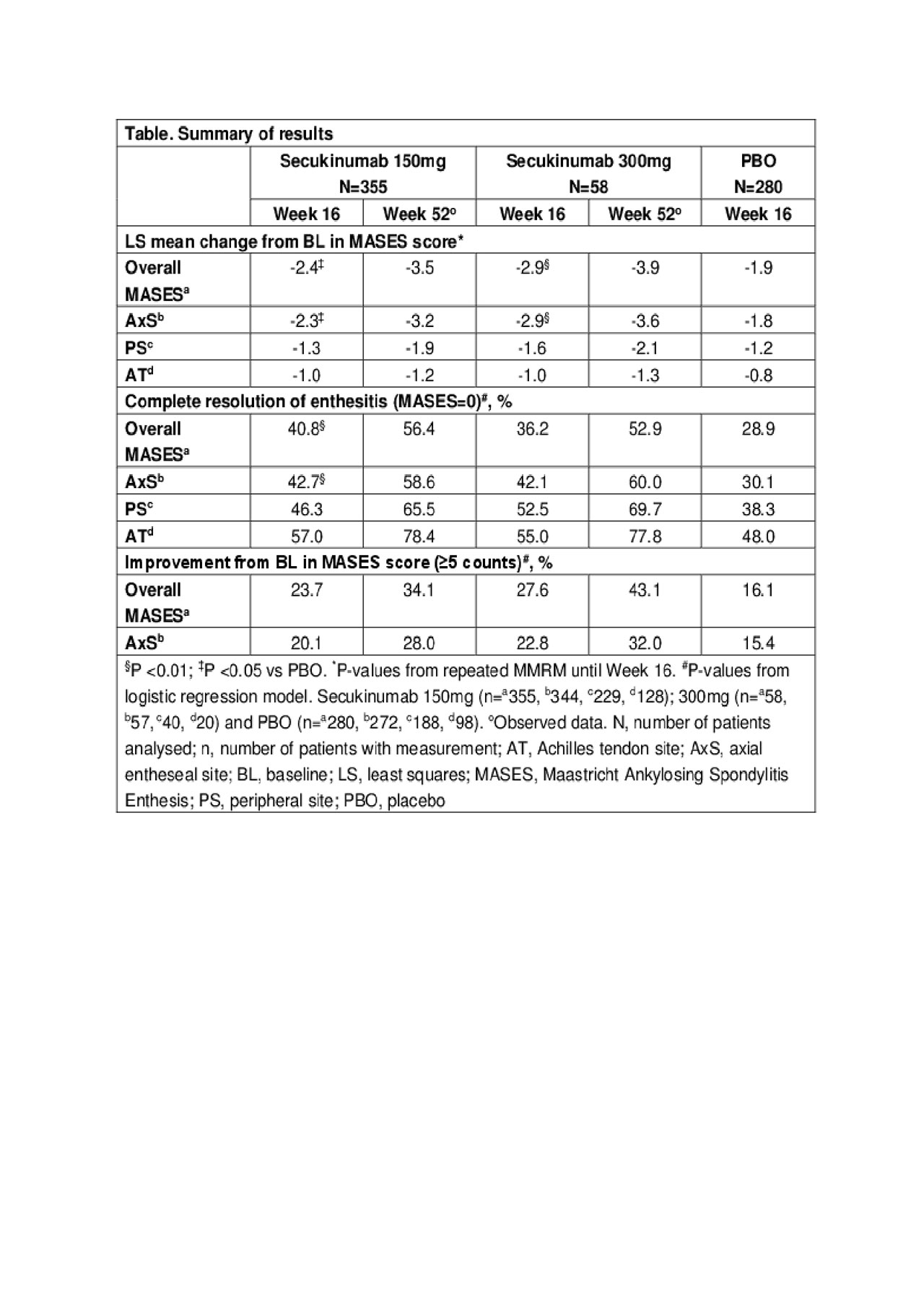
Results: A total of 355 (70.4%), 58 (76.3%), and 280 (72%) patients had BLE in 150mg, 300mg and PBO groups, respectively. BL characteristics were generally comparable across groups. At Week 16, mean change from BL for overall MASES and AxS was greater for secukinumab 150mg (-2.4 and -2.3; both p< 0.05) and 300mg (-2.9 and -2.9; both p< 0.01) vs PBO (-1.9 and -1.8). At Week 16, patients treated with secukinumab 150mg (40.8% and 42.7%) and 300mg (36.2% and 42.1%) vs PBO (28.9% and 30.1%) achieved CR of enthesitis based on overall MASES and at AxS, respectively. A higher proportion of patients treated with secukinumab 150/300mg vs PBO achieved a higher threshold of improvement (≥5 counts) in overall MASES at Week 16. Further improvements were observed for all endpoints at Week 52 (Table).
Conclusion: Secukinumab 150mg and 300mg were associated with higher mean change in MASES and complete resolution of enthesitis at overall MASES and axial sites compared to placebo in AS patients at Week 16, which further increased through Week 52.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schett G, Baraliakos X, Van den Bosch F, Deodhar A, Gensler L, Østergaard M, Agawane S, Das Gupta A, Mpofu S, Fox T, Winseck A, Porter B, Shete A. Secukinumab Provides Sustained Improvement of Enthesitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients: A Pooled Analysis of Four Pivotal Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvement-of-enthesitis-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-a-pooled-analysis-of-four-pivotal-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-provides-sustained-improvement-of-enthesitis-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-a-pooled-analysis-of-four-pivotal-phase-3-trials/