Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) is often determined on the basis of objective signs of inflammation (elevated C-reactive protein [CRP] and/or evidence of sacroiliitis on MRI).1 Secukinumab (SEC) significantly improved signs and symptoms in patients (pts) with nr-axSpA in the PREVENT study (NCT02696031).2 Here, we report a pre-planned exploratory analyses of the efficacy of SEC from PREVENT stratified by CRP and MRI status (positive and/or negative) at study entry.
Methods: Pts (555) fulfilling ASAS criteria for axSpA plus abnormal CRP and/or MRI, without evidence of radiographic changes in sacroiliac joints according to modified New York Criteria for AS were enrolled. All images were assessed centrally before inclusion. Pts were randomized (1:1:1) to subcutaneous SEC 150 mg with loading (LD), without loading (NL), or placebo (PBO) at baseline (BL), Weeks (Wks) 1, 2, 3, and 4, then every 4 wks (q4wk). NL pts received SEC 150 mg at BL and PBO at Wks 1, 2, 3, and 4, then 150 mg q4wk. Exploratory efficacy assessments by CRP and MRI status (positive and/or negative) at Wk 16 included ASAS40, BASDAI50, ASAS-partial remission (PR), and ASDAS-CRP inactive disease (ID) responses. Missing values were imputed as non-response.
Results: Response rates for ASAS40, BASDAI50, ASAS-PR, and ASDAS-CRP ID with SEC 150 mg LD or NL by CRP and MRI status are shown in the Table. Numerically higher response rates for SEC were observed vs PBO for all endpoints across subgroups with the most notable differences vs PBO observed for ASAS-PR and ASDAS-CRP ID.
Conclusion: SEC provided numerically higher response rates vs PBO in pts with nr-axSpA across CRP and/or MRI positive subgroups.
References:
- Lockwood MM and Gensler LS. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31:816−829.
- Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71 (suppl 10):L21.
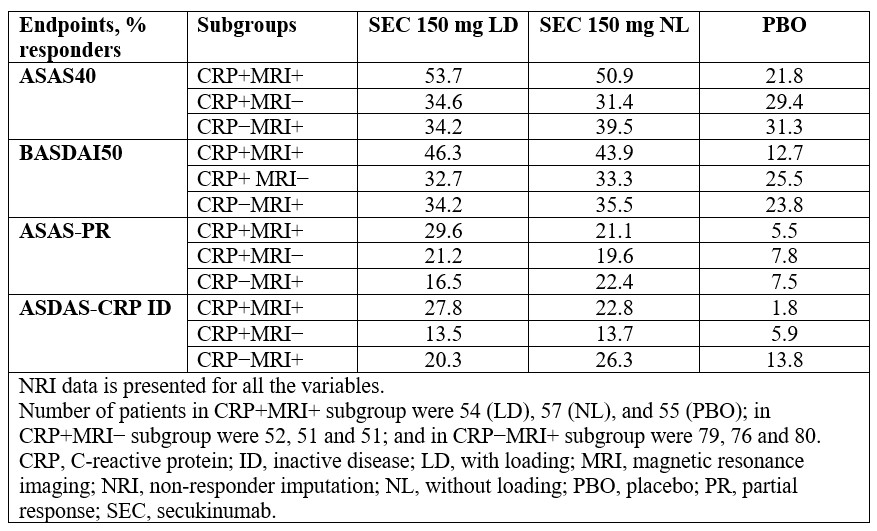 Summary of efficacy results at Week 16
Summary of efficacy results at Week 16
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Braun J, Blanco R, Marzo-Ortega H, Gensler L, Van den Bosch F, Kameda H, Poddubnyy D, van de Sande M, Wiksten A, Porter B, Moreno S, Shete A, Richards H, Haemmerle S, Deodhar A. Secukinumab Improved Signs and Symptoms in Patients with Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from a Randomized Controlled Phase III Study Stratified by Baseline Objective Signs of Inflammation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improved-signs-and-symptoms-in-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-phase-iii-study-stratified-by-baseline-objective-signs-of-inflam/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secukinumab-improved-signs-and-symptoms-in-patients-with-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-a-randomized-controlled-phase-iii-study-stratified-by-baseline-objective-signs-of-inflam/
