Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Manifestations (0855–0896)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The American College of Rheumatology Neuropsychological Battery (ACR-NB) is the standard screening test for cognitive impairment (CI) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). While the ACR-NB is validated for classifying definite, indeterminate, or non-CI, it requires expensive administration by specialists that limits widespread use. Towards an accessible alternative, we developed a CI index with the Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics (ANAM) in a SLE population with definite or non-CI. Although our work provided evidence for the validity of the ANAM relative to the ACR-NB, one third of SLE patients are classified as indeterminate CI in practice. In this study, we further assessed the ANAM as a screener for CI in a population more reflective of clinical settings. Our objectives were to: (i) identify ANAM subtests predictive of CI, (ii) develop an initial approach for classifying definite, indeterminate, or non-CI, (iii) evaluate performance relative to the ACR-NB.
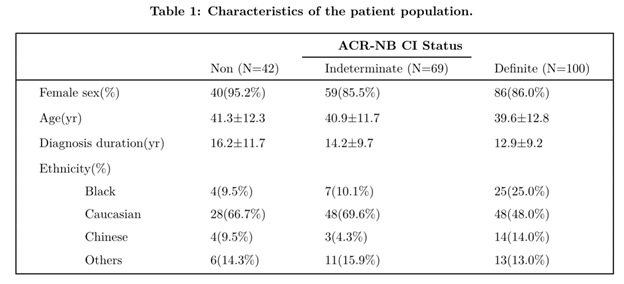
Methods: 211 adult SLE patients were given the ACR-NB and ANAM on the same day at a single center in 2016-2018 (Table 1). The ACR-NB scores across the 6 domains are standardized by age and gender to define CI as: definite: z-score ≤ -1.5 in ≥ 2 domains, indeterminate: z-score ≤ -1.5 in 1 domain, or non: z-scores in all domains > -1.5. The ANAM has 7 domains with 15 subtests scored with the mean reaction time (MR), percentage correct responses (PCT), the coefficient of variation of the MR (CV), and/or throughput (TH).
To classify ACR-NB CI status (definite/indeterminate/non-CI) with the ANAM subtests, we fit 6 models with all subtests and different score types: 4 with one score each, one with MR, CV, and PCT, and one with MR, CV, PCT, and TH. In each setting, we fit a proportional odds cumulative logit model with the adaptive elastic net penalty using the log transformed ANAM subtest scores. The penalized fitting identifies relevant subtests by shrinking coefficients of irrelevant subtests to zero. The initial estimates for penalization were obtained with ridge regression and the tuning parameter selected with cross-validation using the Akaike information criteria. Performance estimates relative to the ACR-NB were obtained with weighted 3-fold cross-validation.
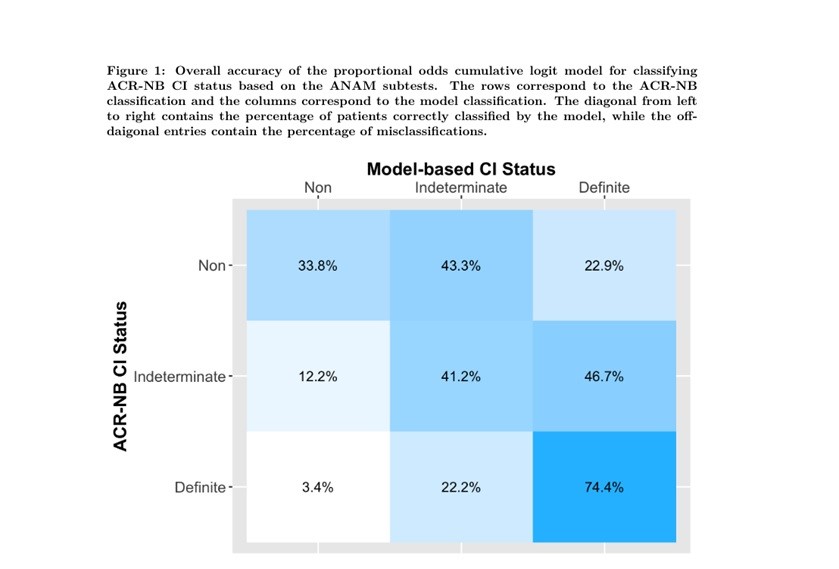
Results: The best performing model included the MR, CV, and PCT scores and selected 36 subtest scores across the 7 ANAM domains for classification of CI. The estimates of the nonzero coefficients are presented in Table 2. Figure 1 summarizes the overall classification accuracy of the model relative to the ACR-NB CI classifications. While the model tends to overcall the indeterminate group as definite CI and the non-CI group as indeterminate and definite CI, it performs well for definite CI compared to ACR-NB. Used as a screening test for CI relative to indeterminate or non-CI, the model has a sensitivity of 0.62 (95% confidence interval: 0.48, 0.76), specificity of 0.72 (0.60, 0.88), and area under the curve of 0.76 (0.69, 0.80).
Conclusion: This is the first study to evaluate the ANAM in discriminating definite, indeterminate, and non-CI in a real world SLE population. The ANAM holds promise as a CI screener and warrants further assessment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pan R, Diaz-Martinez J, Gronsbell J, Touma Z. Screening for Cognitive Impairment with the Automated Neuropsychological Assessment Metrics in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/screening-for-cognitive-impairment-with-the-automated-neuropsychological-assessment-metrics-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/screening-for-cognitive-impairment-with-the-automated-neuropsychological-assessment-metrics-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/