Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and cartilage destruction. RA has been recognized as a systemic disease associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Current CV risk screening and management strategies underestimate the actual CV risk in RA.Thus, an adequate CV risk stratification has special relevance in RA to identify patients at risk of CV disease.
To evaluate the cardiovascular risk profile in patients with RA by assessing both traditional CVD risk factors, carotid ultrasound finding and risk estimation using SCORE and SCORE2.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed including adult moderate to severe RA patients who had initiated treatment with JAK inhibitors or anti TNF. Traditional risk factors were evaluated. The Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) and its updated version, SCORE2, were employed to estimate the global cardiovascular risk in this population. Furthermore, carotid ultrasound examinations were conducted to investigate subclinical atherosclerosis in RA patients. Measurements of carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) were obtained as a surrogate marker of early vascular damage. Additionally, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, a hallmark of advanced vascular disease, was documented. This study was performed from September-2022 to April-2023 and was approved by the Ethics Committee. Statistical analysis was performed using R.
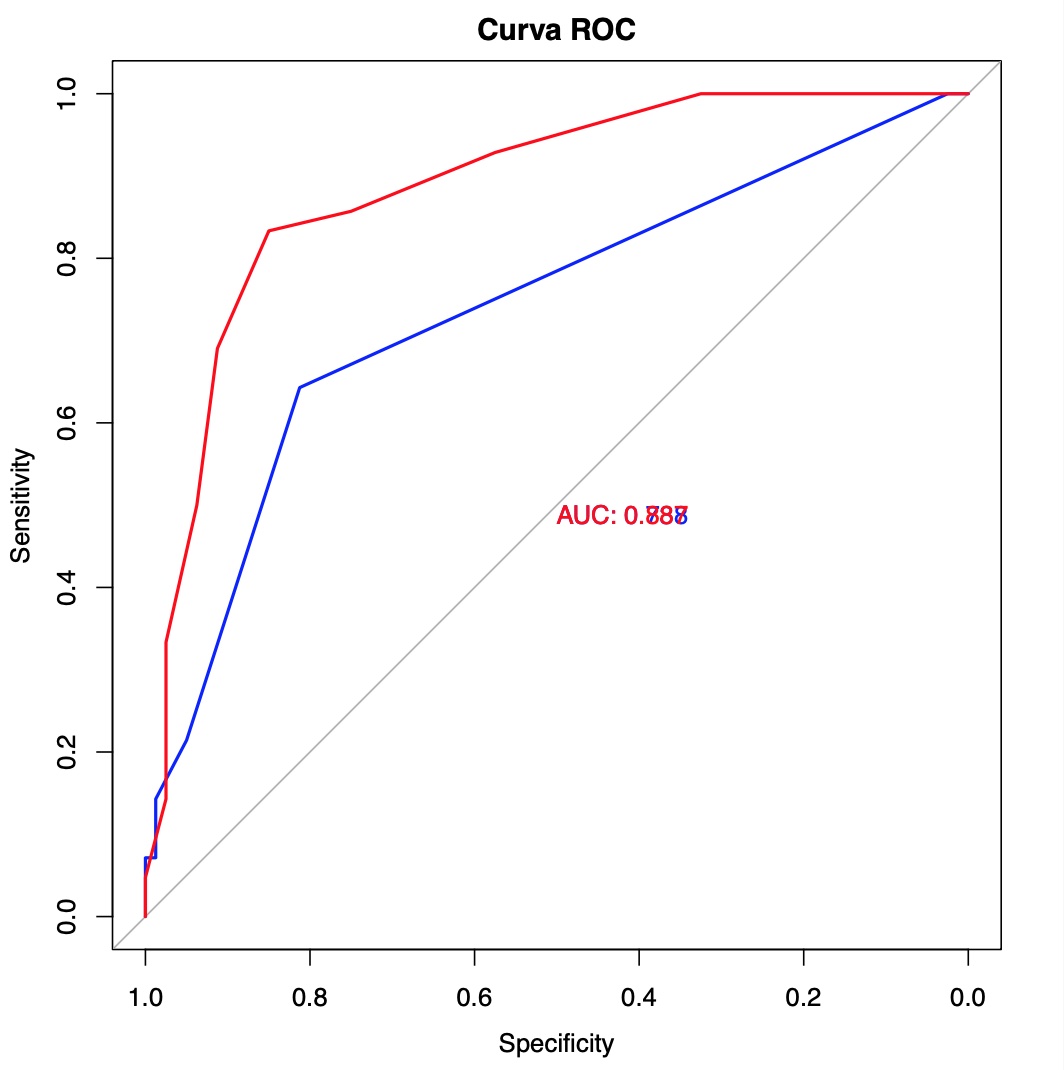
Results: A total of 123 patients were included in the study. Demographical and clinical variables are shown in table 1. Among the RA patients, a high prevalence of CVD risk factors was observed. The mean values of SCORE and SCORE2 indicated a moderate to high estimated 10-year risk of fatal CVD events in this population (mean SCORE: 2.77%, mean SCORE2: 4.07%). Carotid ultrasound measurements revealed an increased mean IMT in RA patients (mean right carotid cIMT: 0.64 [0.12]; mean left carotid cIMT 0.69 [0.11]). Furthermore, a substantial proportion of patients (34.1%) displayed the presence of atherosclerotic plaques. The concordance correlation coefficient between SCORE and SCORE2 demonstrated a significant moderate positive relationship (estimate 0.32 [0.19-0.43] IC 95%). ROC curves were calculated for SCORE and SCORE2 regarding their predictive capacity for plaques, showing a significant difference between them (p< 0.001) indicating a superior predictive capacity of SCORE2. A linear regression model, adjusted for confounding factors, was used to assess the relationship between SCORE and SCORE2 with IMT. Both SCORE (estimate 1.41 p=0.02, R2=0.045) and SCORE2 (estimate 1.55 p< 0.01, R2=0.015) were positively associated with IMT.
Conclusion: The relationship between SCORE and SCORE2 was found to be satisfactory, indicating their adequacy for prediction plaque development. However, the predictive capacity of both scores may be further enhanced by incorporating multiplication factors. Additionally, both SCORE and SCORE2 were positively associated with IMT, but SCORE2 demonstrated a greater predictive capacity in this regard. Furthermore, the SCORE2 explained a higher proportion of the IMT variation compared with SCORE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Campos Fernández C, Martínez Calabuig P, Fragío Gil J, González Mazarío R, Roman Ivorra J. SCORE and SCORE2 Comparison in Cardiovascular Risk Estimation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Cross-sectional Study Including Carotid Ultrasound [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/score-and-score2-comparison-in-cardiovascular-risk-estimation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-cross-sectional-study-including-carotid-ultrasound/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/score-and-score2-comparison-in-cardiovascular-risk-estimation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-cross-sectional-study-including-carotid-ultrasound/