Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Vaccination (0084–0117)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Among patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and their treating physicians, concerns prevail about the effectiveness and safety of vaccination against COVID-19, especially with respect to triggering RMD flares. The aim of our study was to collect safety data among RMD patients receiving COVID-19 vaccines.
Methods: The German COVID-19 vaccination registry is an observational longitudinal study launched February 8th, 2021. Data are entered voluntarily by RMD patients who have received at least 1 vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. The characteristics of all patients registered until May 29th, 2021 is presented here.
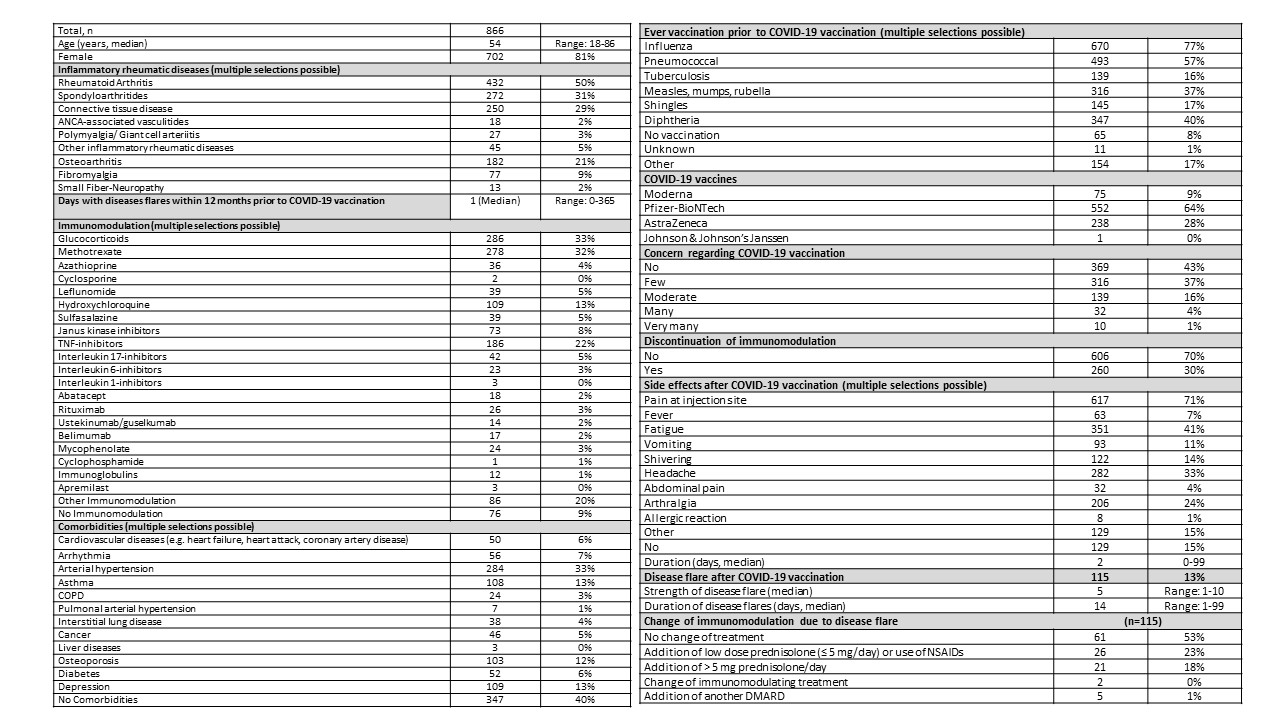
Results: So far, 866 patients reported their experience after the first COVID-19 vaccination. Median age was 54 years (range 18-86) and 81% of the participants were female (table 1). Most of the patients (50%) were diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, followed by spondyloarthritides (31%). At the time of vaccination, 33% were treated with glucocorticoids, 59% with conventional synthetic DMARDs, 23% with TNF-inhibitors, 9% with JAK-inhibitors, and 5% with IL17-inhibitors. No immunomodulatory therapy was reported from 9% of the patients. Within the last 12 months, 42% of the patients reported no disease activity and 40% did not state further comorbidities. The most common comorbidity was arterial hypertension (33%). Prior to COVID-19 vaccination, 77% of the patients had received ever influenza and 57% pneumococcal vaccinations. The majority of the patients were vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (67%), followed by AstraZeneca vaccine (28%). Most of the participants reported no or low concerns regarding COVID-19 vaccination (80%) and 70% did not change their immunomodulation around the vaccination period. The most common side effect was pain at the injection site (71%), followed by fatigue (41%), headache (33%), and arthralgia (24%). Only 1% of the patients reported allergic reactions. Side effects lasted in median for two days (range 0-99 days) and 15% reported no relevant side effects. Disease flares after first COVID-19 vaccination as reported by patients on a 1-10 scale was indicated in 13% of the patients. In these patients, 6% needed a change of their immunomodulation treatment. In 41% of the cases with disease flares, increasing the GC dose was sufficient to cope with the flares.
Conclusion: The first COVID-19 vaccination was well tolerated by the majority of RMD patients. Adverse events were similar to those observed in the general population. Only in 13% of the patients, self-reported disease flare was indicated and in these patients, only 6% needed changes in their immunomodulatory therapy. These preliminary results support the recommendation for COVID-19 vaccination in RMD patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hasseli R, Hoyer B, Lorenz H, Pfeil A, Richter J, Regierer A, Schmeiser T, Strangfeld A, Voll R, Krause A, Schulze-Koops H, Müller-Ladner U, Specker C. Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines After First Vaccination in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases in a Patient Reported Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-of-covid-19-vaccines-after-first-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-in-a-patient-reported-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-of-covid-19-vaccines-after-first-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-in-a-patient-reported-survey/