Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The subcutaneous (SC) formulation of CT-P13 received marketing authorization for RA from the EMA by demonstrating non-inferiority compared to CT-P13 intravenous for efficacy in RA patients1. CT-P13 SC can provide a clinically meaningful improvement in the quality of life, convenience in treatment and use, as well as enable patients to gain better control over their condition. To provide patients with more comfortable administration of CT-P13 SC, an AI was developed and this study is to investigate the usability and safety including localized injection site reactions (ISRs) of the AI versus PFS for SC delivery of CT-P13 in RA.
Methods: Usability assessment was conducted as a sub-study of the pivotal CT-P13 SC study in RA patients. Patients self-injected CT-P13 SC every 2 weeks via AI from Weeks 46 to 54 and via PFS from Weeks 56 to 64. The usability of both devices was determined by the observer (healthcare professional) rating of successful, hazard-free self-injection and patient reporting of device experience using the Self-Injection Assessment Questionnaire (SIAQ). Safety, including localized ISRs, was recorded during the usability assessment period.
Results: Patients (N=168) self-injected at least one dose of CT-P13 SC via AI or PFS and had at least one usability assessment performed. The results of usability for CT-P13 SC via AI and PFS were both high (Figure 1), as rated by the patients based on the mean scores ranging from 7.09 to 9.37 for AI and 7.03 to 9.41 for PFS on a scale of 0 (worst experience) to 10 (best experience) for all post SIAQ domains. Following the use of both devices, patients rated their self-confidence higher; 6.47 to 6.97 before using AI, but changed to 7.09 to 7.30 after using AI; 6.73 to 6.84 before using PFS but changed to 7.03 to 7.20 after using PFS. Except for 11 patients who missed assessment or discontinued from the study, all patients were able to successfully self-administer the injections and completed all instructions from the self-injection assessment checklist for both AI and PFS. The number of patients with the hazard (experiencing a needle stick in the non-critical area) was decreased from 9 patients at Week 46 to 3 patients at Week 54 with AI showing that AI improved in terms of safety by reducing the risk of injury and improper administration. Only 1 patient was with hazard at Weeks 56 and 64, and therefore there was no increase in potential hazard after switching from AI to PFS (Table 1). At least one treatment-emergent adverse event was reported in 67 (39.9%) patients during the usability assessment period. CT-P13 administered by either AI or PFS was generally safe, demonstrating consistency with the known safety profile of infliximab (Table 2).
Conclusion: Infliximab delivered by both AI and PFS was generally well-tolerated and the results demonstrated that there were no differences in usability between AI and PFS. The availability of both AI and PFS will allow patients to select a device based on their own preferences and experiences and will lead to increased adherence during long-term therapy.
References:
1. Westhovens R, et al. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019;78:1158-1159.
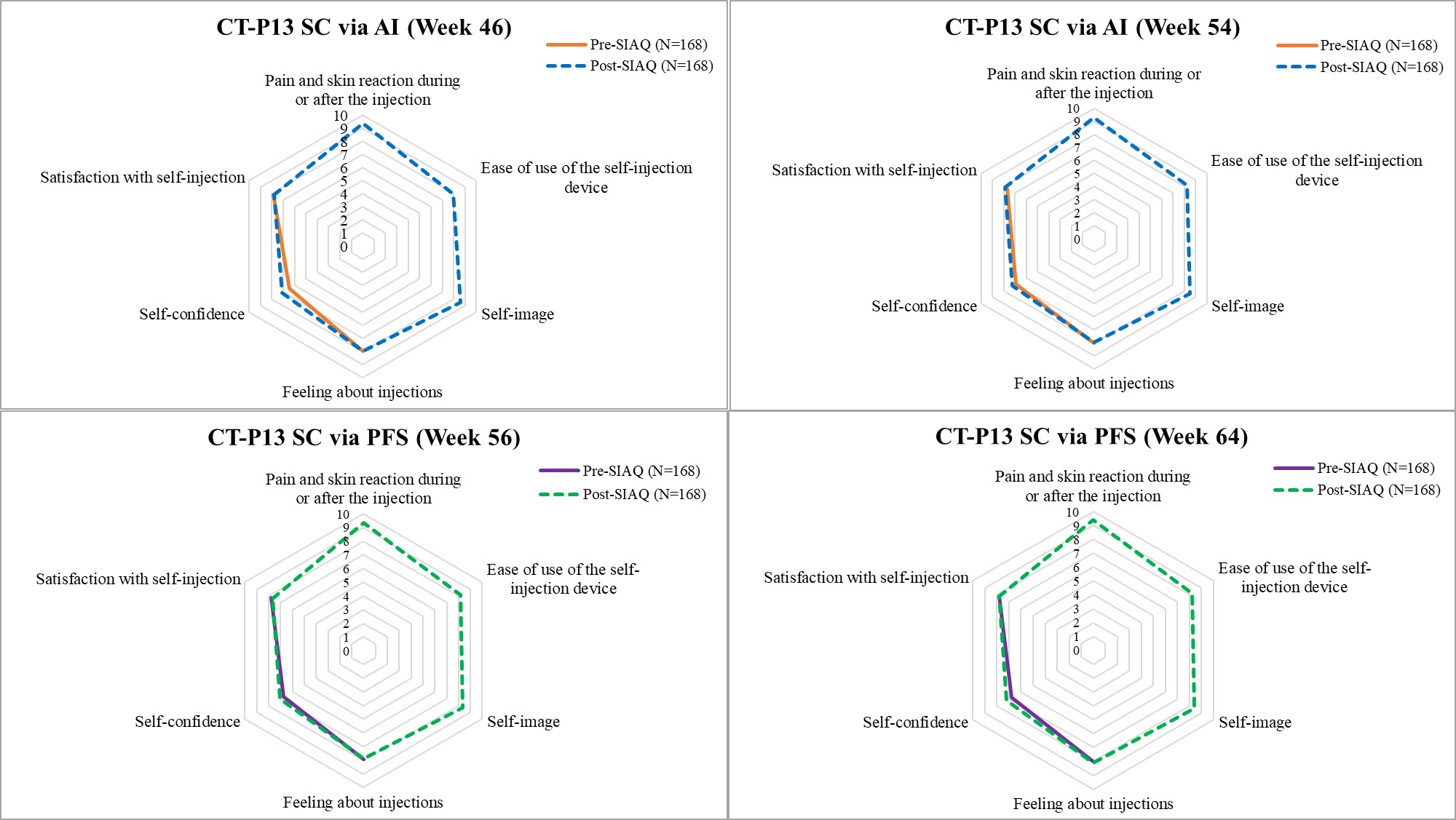 Figure 1. Spidergram of Pre- and Post-Self Injection Assessment Questionnaire
Figure 1. Spidergram of Pre- and Post-Self Injection Assessment Questionnaire
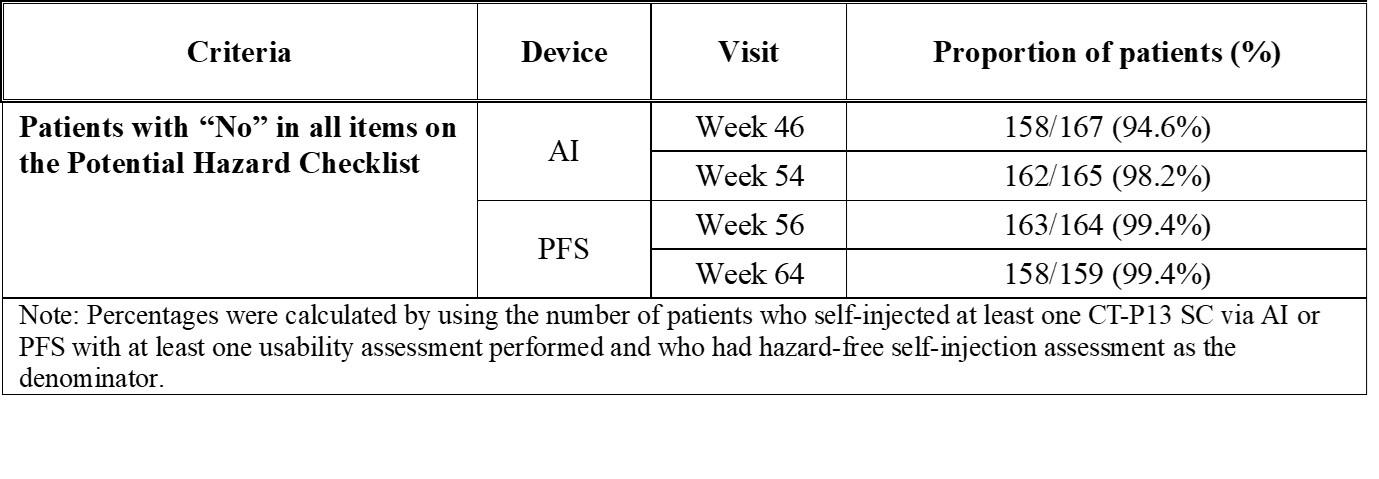 Table 1. Summary of Proportion in Hazard-free Self-Injection
Table 1. Summary of Proportion in Hazard-free Self-Injection
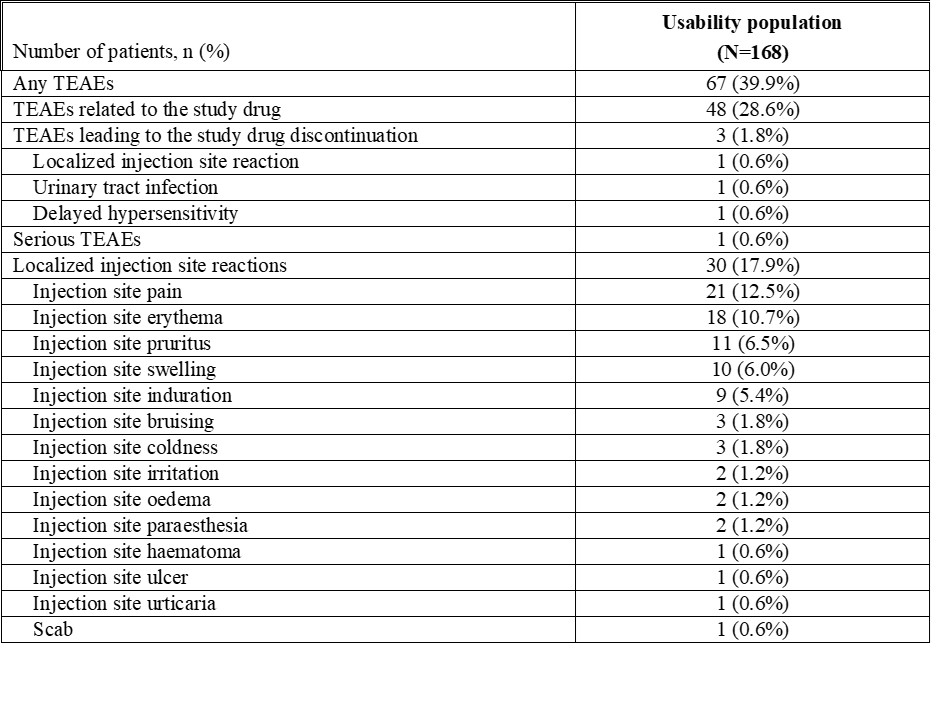 Table 2. Summary of Adverse Events during the Usability Assessment
Table 2. Summary of Adverse Events during the Usability Assessment
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Westhovens R, Yoo D, Wiland P, Zawadzki M, Ivanova D, Berrocal Kasay A, Chalouhi E, Balázs E, Lee S, Kim S, Suh J, Han N, Lee H. Safety and Usability of Infliximab Administration by Auto-injector (AI) and Pre-filled Syringe (PFS) in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Patient-reported Experience from a Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Pivotal Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-usability-of-infliximab-administration-by-auto-injector-ai-and-pre-filled-syringe-pfs-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patient-reported-experience-from-a-multicenter/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-usability-of-infliximab-administration-by-auto-injector-ai-and-pre-filled-syringe-pfs-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patient-reported-experience-from-a-multicenter/
