Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The DISSOLVE Phase 3 study program investigated the efficacy and safety of SEL-212, a novel, once-monthly, two-component infusion therapy consisting of pegadricase (SEL-037, a pegylated uricase) and immune-tolerizing nanoparticles containing sirolimus (SEL-110), in United States (US) and Eastern European patients with chronic gout refractory to conventional therapy. Since standard of care may differ between the US and Eastern Europe, here we compare the pooled data and outcomes from US participants and all other participants (ex-US) enrolled across the DISSOLVE studies.
Methods: DISSOLVE I (NCT04513366) included only patients from the US, while DISSOLVE II (NCT04596540) also included patients from Eastern Europe. In both double-blind studies, participants were randomized 1:1:1 between two doses of SEL-212 (high-dose [HD]: sequential infusions of 0.15 mg/kg SEL-110 and 0.2 mg/kg SEL-037; low-dose [LD]: sequential infusions of 0.10 mg/kg SEL-110 and 0.2 mg/kg SEL-037) and placebo. During the main study period, treatments were administered every 28 days for up to 6 treatment periods (TPs). For the analysis of the pre-specified US and ex-US subgroups, pooled data from TP1–6 was evaluated for primary and secondary endpoints and safety outcomes.
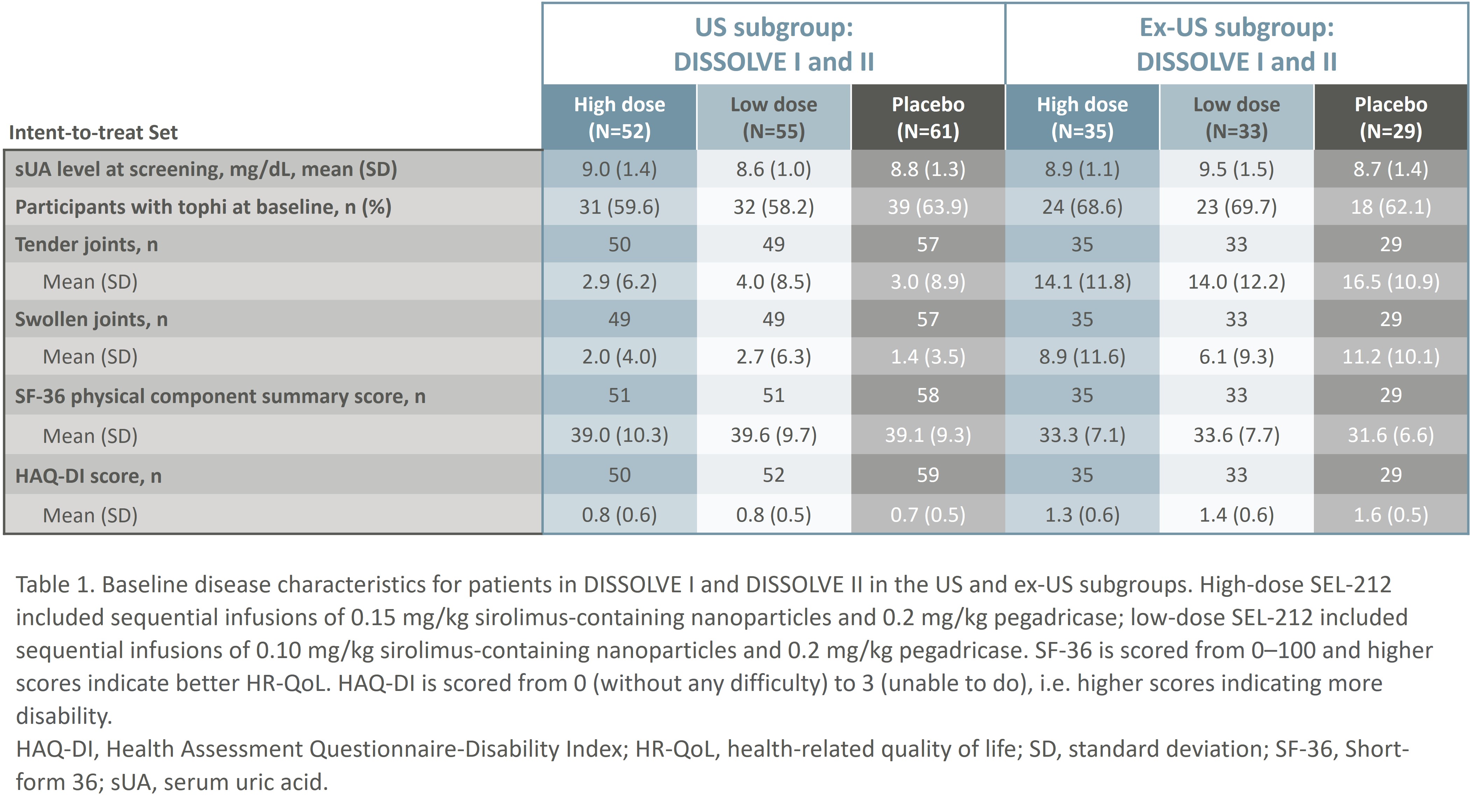
Results: Among 265 patients in DISSOLVE I and II, 168 patients were from the US, including 52, 55, and 61 patients in the HD, LD and placebo arms, respectively. The ex-US group included 97 patients, including 35, 33, and 29 patients in the HD, LD and placebo arms, respectively. The proportion of non-white patients was higher in the US group. Age, proportion of male patients, levels of serum uric acid (sUA) and percentage of participants with tophi were similar between the two subgroups at enrollment. However, patients in the ex-US subgroup had more tender and swollen joints, and subpar quality of life as measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and the Short-form 36 (SF-36) physical component summary (PCS) score, suggesting that ex-US patients may have had more severe gout upon study entry.
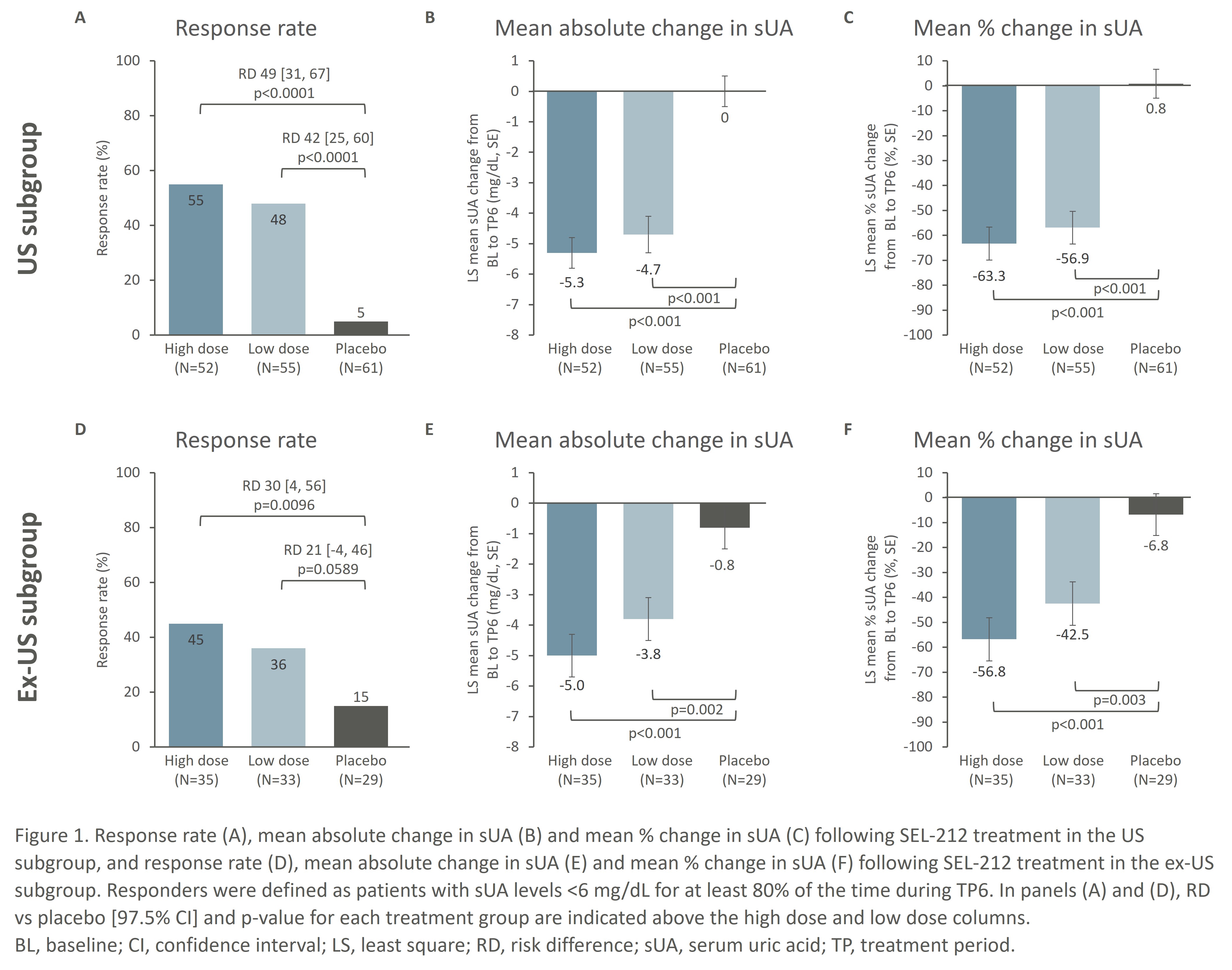
Response rates, defined as sUA levels < 6 mg/dL for ≥80% of the time during TP6, were numerically higher in US patients: 55% vs 45% in HD, 48% vs 36% in LD, and 5% vs 15% in the placebo arm for patients in the US and ex-US populations, respectively (Fig. 1A, 1D). Mean absolute (mean %) sUA changes from baseline showed a similar trend of slightly higher improvements in the US compared to ex-US subgroup: -5.3 mg/dL vs -5.0 mg/dL (-63.3% vs -56.8%) for HD, -4.7 mg/dL vs -3.8 mg/dL (-56.9% vs -42.5%) for LD, and 0 mg/dL vs -0.3 mg/dL (0.8% vs -6.8%) for placebo in the US and ex-US subgroups, respectively (Fig. 1B, 1C, 1E, 1F). No new safety signals were detected and infusion reactions were low in all patient groups.
Conclusion: This post hoc analysis of the DISSOLVE studies suggests that SEL-212 is safe and effective at lowering sUA in patients in both regions, including in those patients with a higher disease burden at baseline, as demonstrated by the number of swollen and tender joints, HAQ-DI and SF-36 PCS scores. The findings support SEL-212 as a potential novel once-monthly treatment option that can alleviate the disease burden of chronic gout refractory to conventional therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pillinger M, Kivitz A, Singhal A, Patel A, Azeem R, Falk A, Desai B, Santin-Janin H, Baraf H. Safety and Efficacy of SEL-212 in the US and ex-US Subgroups: Results from the Phase 3 DISSOLVE Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-sel-212-in-the-us-and-ex-us-subgroups-results-from-the-phase-3-dissolve-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-sel-212-in-the-us-and-ex-us-subgroups-results-from-the-phase-3-dissolve-studies/