Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Long-term drug-free remission is an unmet need for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which might be achieved by restoring antigen-specific immune tolerance. Autoantigenic peptide therapy targeted to antigen-induced T cell activation has been proven to offer a potential approach to re-establish immune balance in RA. Here, we conducted a first-in-human phase 1b dose escalation trial of FNS007, a non-T cell receptor (TCR) contacting peptide derived from Collagen II, to determine its safety and efficacy in RA patients.
Methods: This multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of FNS007 enrolled patients 18-70 years of age with active RA who had an inadequate response to csDMARDs (methotrexate or leflunomide). Thirty eligible patients were assigned to each of three cohorts defined by the dose level of FNS007 (20, 40, and 60 mg, respectively). For each cohort, patients were randomized to the FNS007 or placebo group (8:2), receiving intravenous administration twice a week for a total of 8 treatments, followed by a 4-week (20 and 40 mg groups) and a 12-week (60 mg group) follow-up. The primary endpoint was the safety and tolerability of FNS007. The secondary endpoints included American College of Rheumatology (ACR) responses, Health Assessment Questionnaire disability index (HAQ-DI), and disease activity score-28 joints (DAS28).
Results: The study showed that FNS007 was tolerated with no serious adverse events (SAEs). No differences were found in the rates of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) with FNS007 compared to placebo.
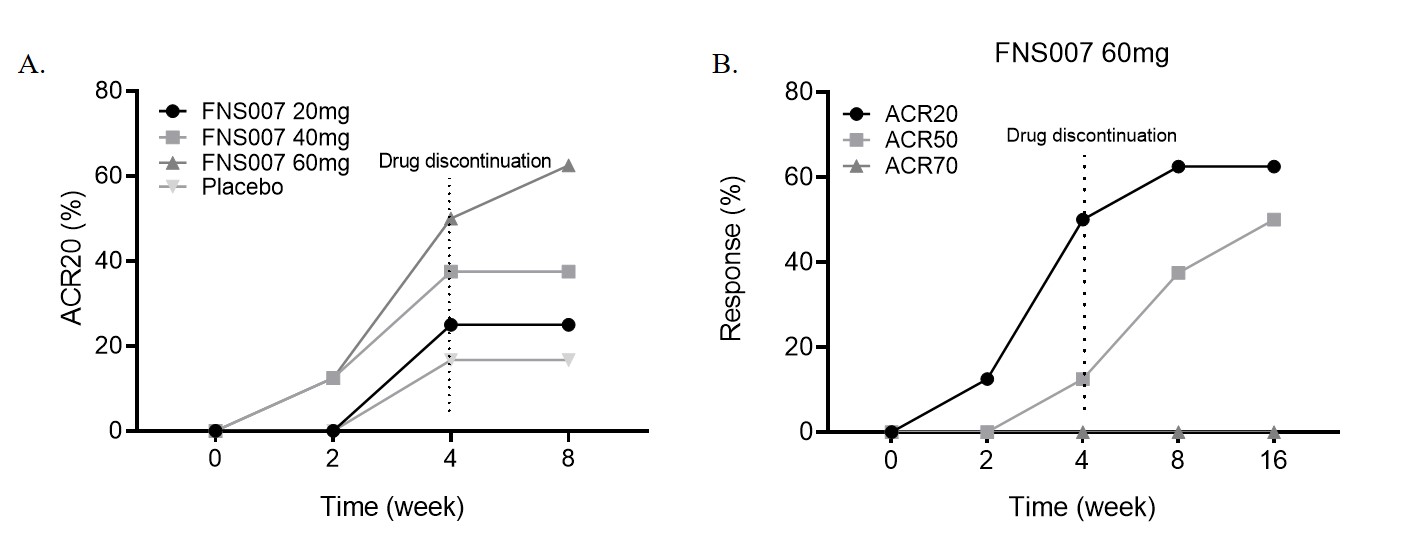
At week 4, FNS007 indicated a dose-dependent improvement, with ACR20 response rates of 25.0%, 37.5%, and 50.0% for the 20, 40, and 60 mg groups, respectively, compared to 16.7% for the placebo group. The proportion of patients achieving ACR50 were 12.5%, 25.0%, and 12.5% for FNS007 at 20, 40, and 60 mg, respectively, while no patients in the placebo group achieved this response. The changes of TGF-β increased in the 20, 40, and 60 mg groups (1.3±2.1, 0.1±6.7, and 4.5±12.7 ng/ml, respectively) and decreased in the placebo group (-1.54±2.0 ng/ml). The changes of the relative number of CD45RA+CD62L– Teff in CD4+ T cells showed a decrease (-1.03%±0.13%, and -3.29%±0.55%) for the 40, 60 mg groups, compared to the placebo group (0.53%±1.19%).
At week 8, ACR50 response rates increased to 25.0%, 25.0%, and 37.5% for the 20, 40, and 60 mg groups, respectively, but still 0% in the placebo group, after discontinuing FNS007 for 4 weeks. Patients who met the remission status (DAS28-ESR ≤ 2.6) were 0%, 37.5%, and 50.0% for the 20, 40, and 60 mg groups, respectively, compared to 0% in the placebo group. A downward trend in HAQ-DI was shown in the FNS007 groups at weeks 4 and 8.
Patients in the FNS007 60 mg group were followed up for 12 weeks after drug discontinuation at week 4. The results showed that ACR20 and ACR50 responses were 62.5% and 50%, respectively, showing an increased improvement during the 12 weeks of follow up.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that FNS007 was tolerated and effective in a dose-dependent manner. It indicated that FNS007 might eliminate Teff cells and increase TGF-β to induce immune tolerance. The results support a future phase 2 clinical trial.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li R, Sun X, Niu S, Sun X, Zheng G, Liu M, Lv J, Zhou G, Yuan G, Ye Y, Wang S, Fang P, Tang Q, Kang J, Li X, Sun C, Zhang S, Mei Y, Wang J, Su H, Huang L, Li C, Liu C, Zhang F, Wang Q, Yang N, Li F, Chen L, Fang Y, Li Z. Safety and Efficacy of FNS007, a Non-T Cell Receptor Contacting Peptide, for Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Proof-of-concept Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-fns007-a-non-t-cell-receptor-contacting-peptide-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-proof-of-concept-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-fns007-a-non-t-cell-receptor-contacting-peptide-for-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-proof-of-concept-trial/