Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: There is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and remission rates vary greatly 10-60%; thus, there is an unmet need for safe adjunctive therapeutic agents to decrease inflammation and improve RA outcomes. The use of cannabidiol (CBD) in preclinical RA models have shown reductions in pain, disease severity, and inflammatory infiltrates. The objective of this pilot randomized controlled trial (RCT) was to examine the dose-dependent safety and efficacy CBD relative to placebo (PBO) in RA patients with moderate to severe disease activity.
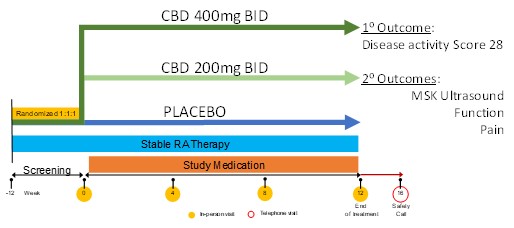
Methods: We conducted a 12-week randomized, double-blind, PBO-controlled RCT of oral CBD (200mg bid and 400mg bid), vs PBO (1:1:1) in patients with moderate to severe RA disease activity defined as disease activity score (DAS28) > 3.2 and power doppler ultrasound score (PDUS) > 5. The primary endpoint was change in DAS28 over 12 weeks and secondary endpoints included pain visual analogue scale (VAS), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ-DI), Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3), PDUS, and grey scale (GSUS) over 12 weeks. During the 12-week trial, detailed accounts of adverse and serious adverse events were captured. Linear regression models were used to compare primary and secondary outcomes for each CBD arm versus placebo. Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to compare the changes in MSUS measures over time between each CBD arm and placebo.
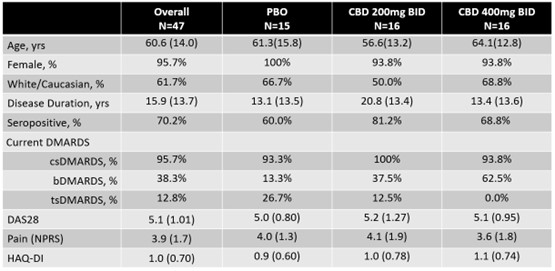
Results: RA patients were randomized as follows: 15 to PBO, 16 to CBD 200mg bid, and 16 to CBD 400mg bid (Figure 1). Participants were 60.6 years (SD 14.0), 96% female, disease duration 15.9 years (SD 13.7), 62% Caucasian, and 70.2% seropositive (Table 1). After 12 weeks of treatment, DAS28 was not significantly different between CBD arms and PBO (p >0.05). For secondary outcomes PDUS, GSUS, HAQ, RAPID3, and pain VAS, there were no significant differences between CBD arms and PBO. A numerically higher reduction in pain VAS was noted in the CBD 200mg bid versus PBO (-0.95 vs -0.31, p=0.08), but not seen for CBD 400mg bid. More patients withdrew from the CBD 400mg bid group (N=5) than CBD 200mg bid (N=2) and PBO (N=0) due to adverse effects, though this was not significant (p >0.05). GI side effects were reported in the CBD 400 mg bid at 63%, CBD 200mg bid 43.8%, and PBO 33.3%.
Conclusion: This is the first RCT study examining the safety and efficacy of CBD in RA patients. Findings indicate that high doses of CBD may not be well tolerated in RA patients with moderate to severe disease activity. Overall, CBD was not effective in reducing RA disease activity as measured by clinical or imaging outcomes. However, numerical improvement in subjective pain ratings between CBD 200mg bid and PBO groups suggests future research is warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ranganath V, Wilhalme H, Morris N, Brook J, Taylor M, Yang H, Kermani T, Aung T, Skaggs B, Elashoff D, Cooper z. Safety and Efficacy of Cannabidiol in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Phase 1B Pilot Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-cannabidiol-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-phase-1b-pilot-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-cannabidiol-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-a-phase-1b-pilot-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/