Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Osteoarthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Clinical Trials and Interventions
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Animal studies suggested that inhibiting IL-1α/β with ABT-981 may reduce pain and slow structural progression in OA. This study (NCT02087904; ILLUSTRATE-K) assessed the safety and efficacy of ABT-981 in subjects with knee OA.
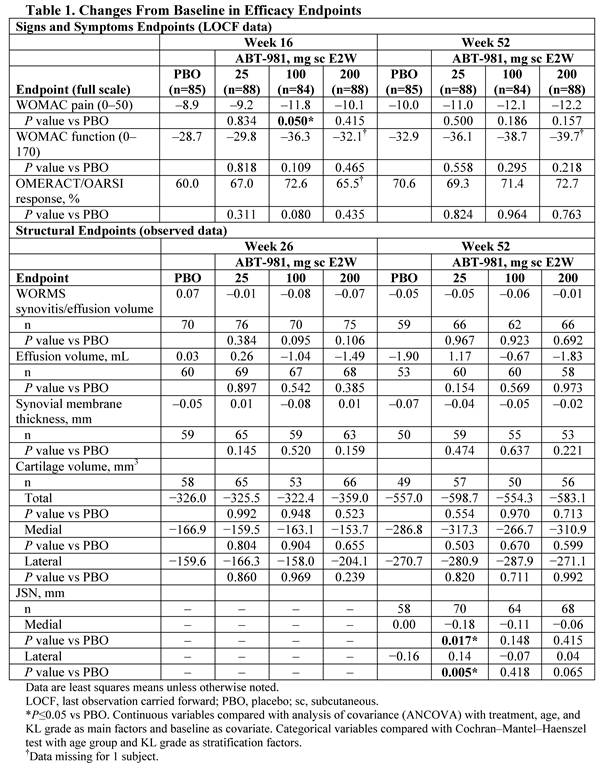
Methods: Subjects (N=350; 347 analyzed) with Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade 2–3 knee OA, synovitis on MRI or US, and visual analog scale knee pain score 4–8 (range, 0–10) were randomized to placebo (PBO) or ABT-981 25, 100, or 200 mg subcutaneously (sc) every 2 wk (E2W) for 50 wk. The primary endpoints were change from baseline (BL) in WOMAC pain at wk 16 and change from BL in MRI synovitis at wk 26. Other endpoints included WOMAC function and OMERACT/OARSI response (wk 16, 26, and 52) MRI cartilage volume (wk 26 and 52), and x-ray joint space narrowing (JSN) (wk 52). Continuous efficacy assessments used ANCOVA (main factors: treatment, age group, KL grade; covariates: BL values).
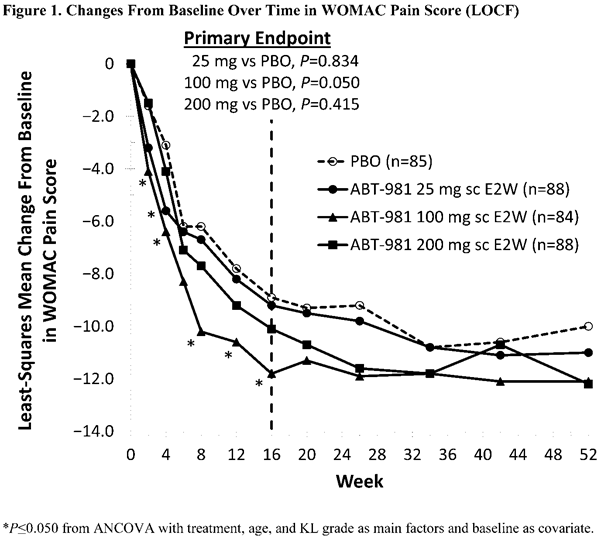
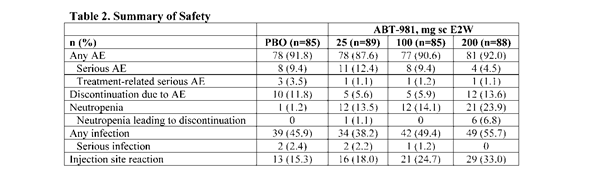
Results: BL demographics and disease characteristics were balanced (KL grade 3, 36.0%–38.8%; mean WOMAC pain (scale 0–50), 26.2–28.4). The primary endpoint of WOMAC pain at wk 16 improved significantly, compared with PBO, with ABT-981 100 mg (P=0.050; Figure 1), but not 25 mg (P=0.834) or 200 mg (P=0.415). WOMAC pain reduction in all ABT-981 groups was sustained from wk 16 to 52, but differences between ABT-981 and PBO for WOMAC pain and other key signs and symptoms were not significant (Table 1). Synovitis-related imaging, cartilage volume endpoints, and JSN were similar between ABT-981 and PBO groups at wk 26 and 52. ABT-981 was well tolerated; serious adverse events (SAEs), treatment-related SAEs, and infections and serious infections were similar with ABT-981 vs PBO (Table 2). Injection site reactions, grade 2/3 neutropenia, and discontinuations due to neutropenia were more frequent with ABT-981 vs PBO. ABT-981 exposures reached steady state after wk 6 and were stable through wk 52. Pharmacodynamic responses (neutrophil and high-sensitivity CRP levels) plateaued at the 100 mg dose and data were similar at 200 mg. The low immunogenicity to ABT-981 did not meaningfully affect outcomes.
Conclusion: ABT-981 was generally well tolerated and met the primary endpoint of reduction in WOMAC pain at wk 16 compared with placebo at a dose of 100 mg, but not at 25 mg or 200 mg; cartilage thickness, synovitis, and other structural endpoints were similar between ABT-981 and PBO.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Bliddal H, Blanco FJ, Schnitzer TJ, Peterfy C, Chen S, Wang L, Conaghan PG, Berenbaum F, Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J, Vaeterlein O, Liu W, Levy G, Zhang L, Medema JK, Levesque MC. Safety and Efficacy of ABT-981, an Anti–Interleukin-1α/β Dual Variable Domain (DVD) Immunoglobulin, in Subjects with Knee Osteoarthritis: Results from the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Phase 2 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-abt-981-an-anti-interleukin-1%ce%b1%ce%b2-dual-variable-domain-dvd-immunoglobulin-in-subjects-with-knee-osteoarthritis-results-from-the-randomized-double-blind-p/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-abt-981-an-anti-interleukin-1%ce%b1%ce%b2-dual-variable-domain-dvd-immunoglobulin-in-subjects-with-knee-osteoarthritis-results-from-the-randomized-double-blind-p/