Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical scenarios in which clinicians initiate cTT, as well as the safety and effectiveness of cTT in patients with IMIDs.
Methods: The COMBATT registry is an academic, observational, nationwide registry aiming at enrolling at least 1000 IMID patients treated with cTT over 7 years. Inclusion criteria include age > 18, IMID diagnosis, and cTT treatment. Safety was assessed by serious adverse effects and cTT discontinuation due to tolerance issues. Efficacy was evaluated by cTT maintenance, clinician evaluation, and corticosteroid-sparing effects.
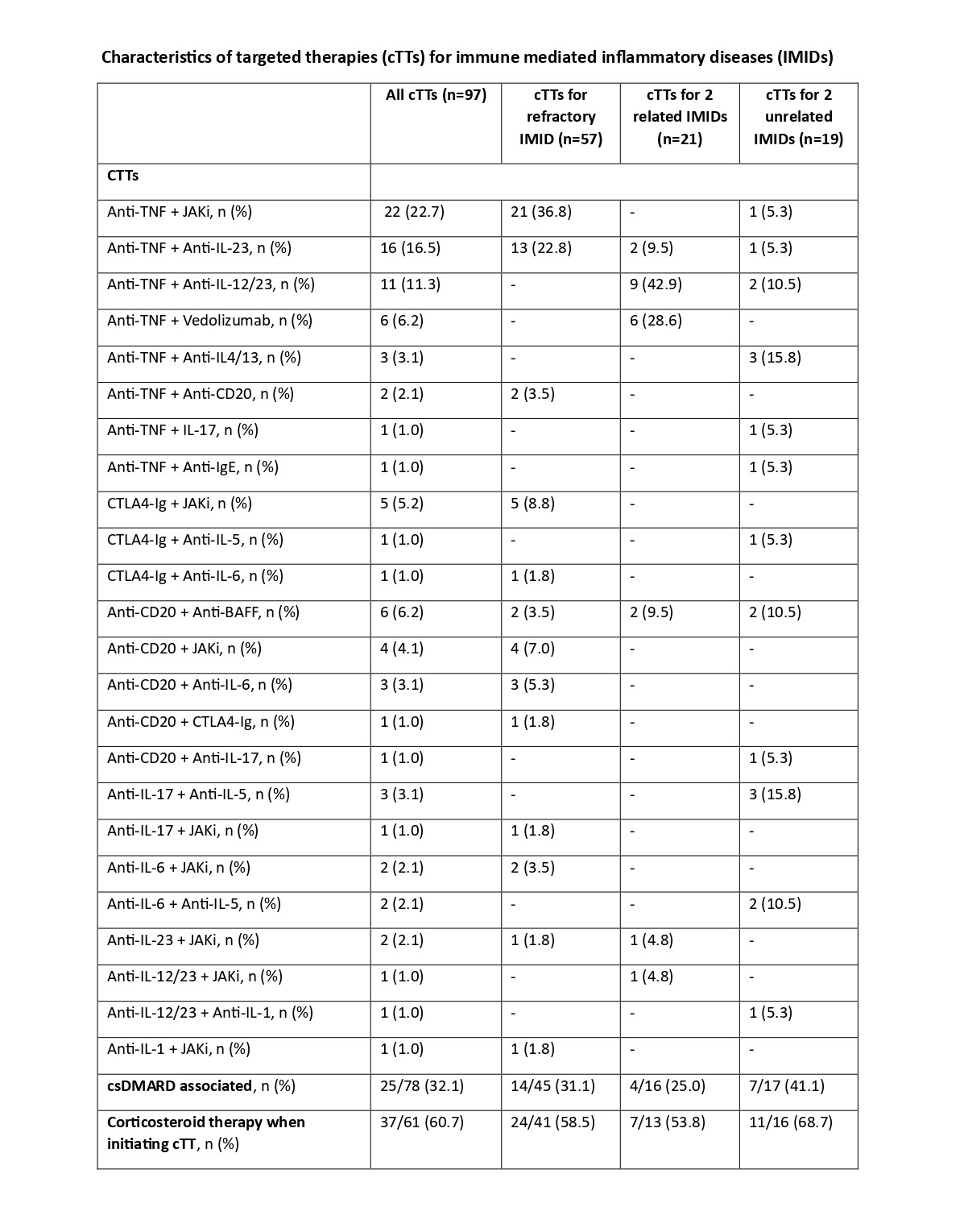
Results: The study included 79 patients (65.8% female, median age 53 years [IQR: 44-67]), with 13 patients treated with more than one cTT. In total, 97 cTTs were analyzed. cTT was initiated for one refractory IMID in 46 patients (58.2%, 57 cTTs), two related IMIDs in 16 patients (20.3%, 21 cTTs), and two unrelated IMIDs in 17 patients (21.5%, 19 cTTs). Refractory IMIDs were mostly rheumatoid arthritis (43.5%), spondylarthritis (SpA) (19.6%), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (10.8%), with a median of 6 (IQR: 3.5-8) targeted therapy lines before cTT initiation. Related IMIDs were mainly SpA or PsA and inflammatory bowel diseases (93.7%). Most patients with two unrelated IMIDs had asthma (29.5%).
The most frequent cTTs were anti-TNF + JAK inhibitors (22.7%), anti-TNF + anti-IL-23 (16.5%), anti-TNF + anti-IL-12/23 (11.3%), anti-TNF + Vedolizumab (3.2%), and anti-CD20 + anti-BAFF (6.2%). Follow-up is already available for 64 patients with a median follow-up of 11.5 months (IQR: 4-24), equivalent to 61.3 person-years.
A total of 12 serious adverse events occurred (19.6/100 p-yrs): 9 severe infections (14.7/100 p-yrs; 4 under anti-TNF + JAKi, 2 under anti-TNF + anti-IL-23, 1 under CTLA4-Ig + JAKi, 1 under anti-IL-23 + JAKi, 1 under anti-CD20 + anti-BAFF), 2 cytopenias (3.26/100 p-yrs; 2 under anti-IL-6 + anti-IL-5), and 1 thromboembolic event (1.63/100 p-yrs; under CTLA4-Ig + JAKi).
Of the 80 cTTs with at least 1 follow-up visit, 41 (51.3%) were discontinued due to 20 primary failures (48.8%), 9 secondary loss of efficacy (22.0%), 6 remissions (14.6%), 5 tolerance issues (12.2%), and 1 missing data. Among the 46 cTTs for 36 patients with one refractory IMID and at least 1 follow-up visit (median follow-up of 6 months [IQR: 3.5-12]), 20 were effective (43.5%), 6 were partially effective (13.0%), 2 were initially effective with subsequent loss of effectiveness (4.3%), 16 were ineffective (34.8%), and 2 were not evaluable (4.3%). Corticosteroid therapy was discontinued in 27.6% of cases after cTT initiation.
Conclusion: Initial results from the COMBATT registry indicate that cTTs are commonly used to target different inflammatory pathways in patients with refractory IMID or multiple IMIDs. Preliminary findings suggest cTTs have an acceptable short-term safety profile and may reduce disease activity in some refractory IMID patients. The COMBATT registry will provide valuable data on long-term safety in a larger population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kawka L, Gottenberg J, Avouac J, BROCQ O, HAYEM G, Mariette X, Meyer A, FLACHAIRE B, FOGEL O, GANDIOLLE A, LESTURGIE M, KLEINMANN J, Ahmed Yahia S, Pham T. Safety and Effectiveness of 97 Combinations of Targeted Therapies in Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases : Preliminary Data from the COMBATT Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-97-combinations-of-targeted-therapies-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-preliminary-data-from-the-combatt-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-effectiveness-of-97-combinations-of-targeted-therapies-in-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-preliminary-data-from-the-combatt-registry/