Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and inducible costimulator ligand (ICOSL) are implicated in autoimmune disease pathogenesis, and clinical findings support their utility as drug targets in autoimmune disease (Navarra SV Lancet 2011; Cheng LE Arthritis Rheumatol 2018). Rozibafusp alfa is a first-in-class bispecific antibody-peptide conjugate that inhibits BAFF and ICOSL and is currently in phase 2 clinical development for the treatment of SLE. This final analysis of a phase 1b study (NCT03156023) reports the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD), immunogenicity, and effect of rozibafusp alfa on disease control in subjects with RA.
Methods: A total of 34 subjects (age 42–75 years; 82.4% female) with active RA, defined as a disease activity score (DAS28-CRP) >2.6, were randomized 3:1 to receive rozibafusp alfa (N=26, divided into 4 multiple ascending dose cohorts of 70, 140, 210, and 420 mg) or placebo (N=8) subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 10 weeks (6 doses), with 24 weeks of follow-up. All subjects were maintained on a stable dose of MTX. The primary endpoint was the subject incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). Additional assessments included serum PK profiles, PD (eg, ICOSL receptor occupancy (RO), changes in peripheral blood B-cells), incidence of anti-rozibafusp alfa antibodies (ADA), and Patient and Physician Global Assessments (PtGA and PhGA) of disease activity.
Results: TEAEs occurred in 96.2% and 87.5% of subjects receiving rozibafusp alfa and placebo, respectively. Two rozibafusp alfa-treated subjects (7.7%) reported serious adverse events; none were considered related to treatment by the study investigator. Rozibafusp alfa demonstrated nonlinear PK and a mean terminal half-life of 4.6–9.5 days, with longer half-lives at higher doses. ICOSL RO on circulating B-cells was dose-related and reversible; >90% mean RO was observed for the 210 and 420 mg dose cohorts (Figure). Treatment with rozibafusp alfa reduced the percentage of naïve B-cells and increased the percentage of memory B-cells in all cohorts (Figure). Five (20%) subjects developed ADA with no associated AEs, but 1 subject had lower PK and reduced ICOSL RO at day 57. RA disease activity showed greater numerical improvement from baseline in PtGA and PhGA with rozibafusp alfa vs. placebo in the 210 and 420 mg cohorts; maximum score reduction for PtGA and PhGA was achieved after 10 and 6 weeks of rozibafusp alfa treatment, respectively, in both cohorts and persisted through day 183 in the 420 mg cohort.
Conclusion: Multiple ascending doses of rozibafusp alfa were safe and generally well tolerated, with exploratory efficacy results observed in the highest dose cohorts. PK/PD analysis demonstrated nonlinear, target-mediated disposition consistent with cell surface target interaction and PD activity consistent with dual ICOSL/BAFF neutralization. These findings informed the design and dose selection of an ongoing phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and safety of rozibafusp alfa in subjects with active SLE and inadequate responses to standard of care therapy.
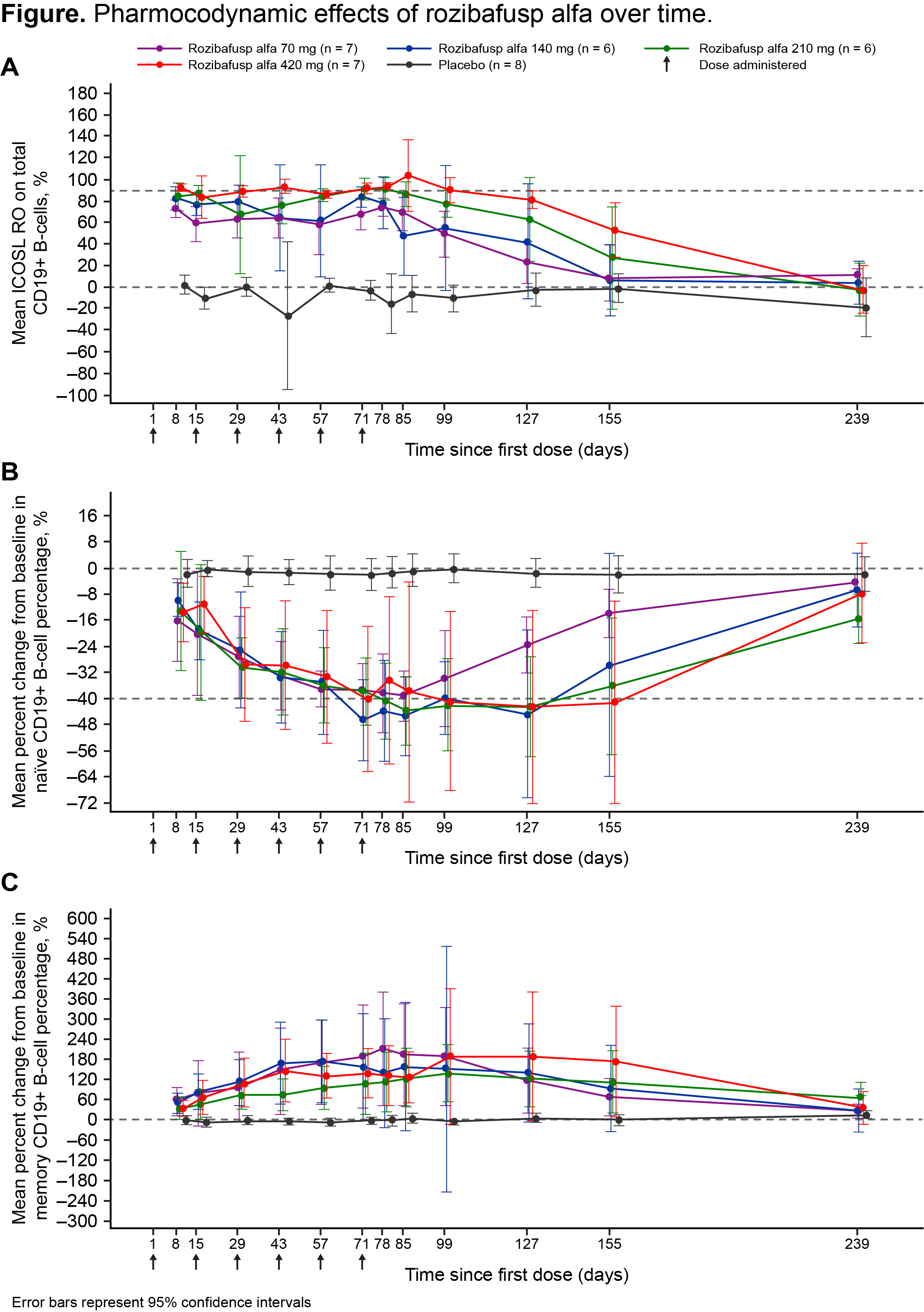 Figure. Pharmacodynamic effects of rozibafusp alfa over time
Figure. Pharmacodynamic effects of rozibafusp alfa over time
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abuqayyas L, Cheng L, Park K, Teixeira dos Santos M, Sullivan B, Wang H, Zhou Y, Chindalore V, Cohen S, Kivitz A, Posch M, Parnes J. Safety and Biological Activity of Rozibafusp Alfa in Subjects with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Final Results of a Phase 1b Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multiple Ascending Dose Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-biological-activity-of-rozibafusp-alfa-in-subjects-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-final-results-of-a-phase-1b-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-multiple-ascending-dose-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-biological-activity-of-rozibafusp-alfa-in-subjects-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-final-results-of-a-phase-1b-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-multiple-ascending-dose-study/
