Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
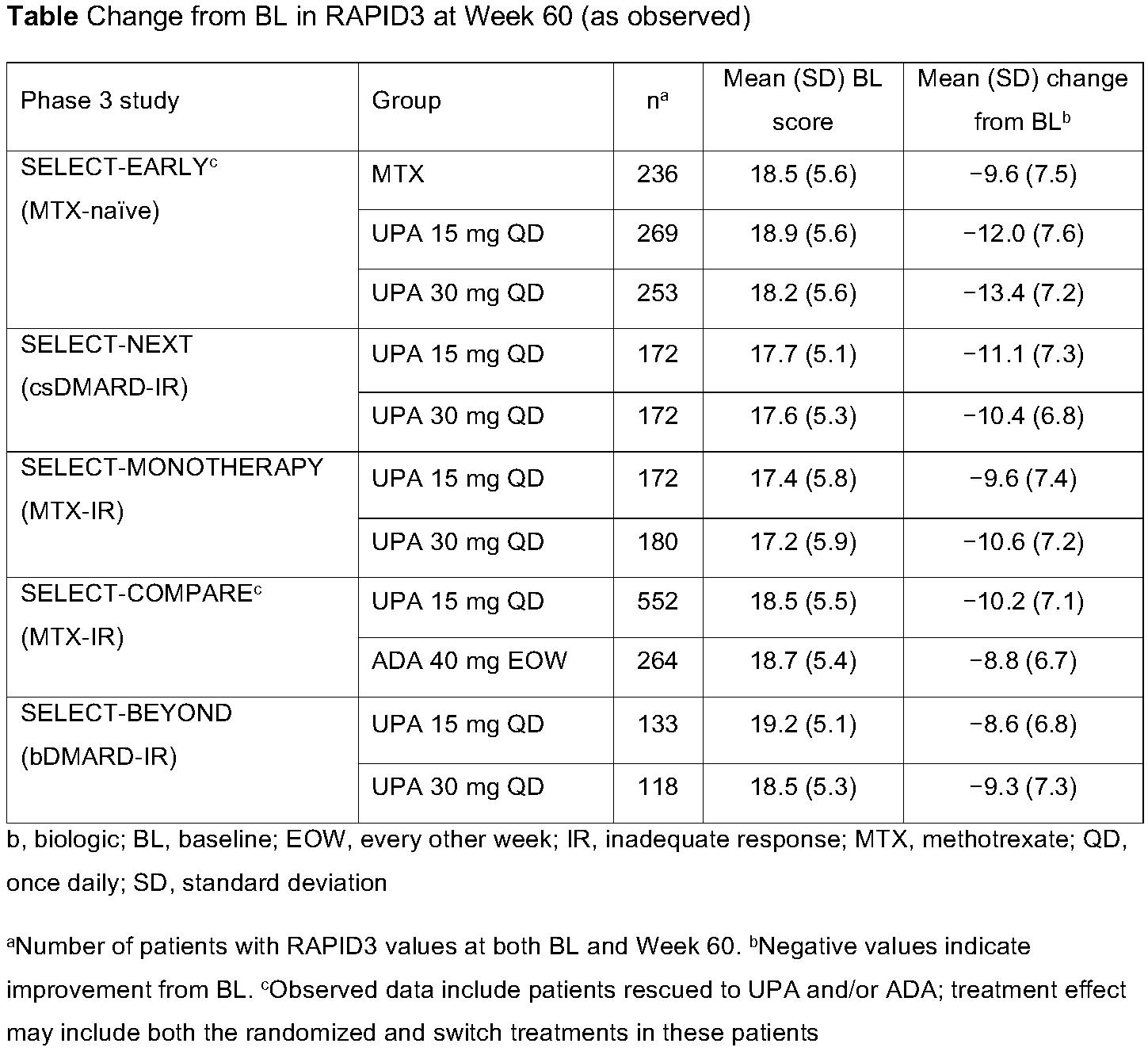
Background/Purpose: Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) is a pooled index of 3 patient-reported measures: patient global assessment, pain, and physical function. RAPID3 was shown to correlate with other composite measures of disease activity1 and is recommended by the American College of Rheumatology for use in clinical practice.2 The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the impact of upadacitinib (UPA) versus comparators on RAPID3 over 60 weeks, as well as the correlation of RAPID3 scores with other disease measures in the UPA phase 3 SELECT clinical program.
Methods: This post hoc analysis included placebo-controlled (SELECT-NEXT, -BEYOND, and -COMPARE) and active comparator-controlled (SELECT-EARLY, -MONOTHERAPY, and -COMPARE) trials. Patients received UPA as monotherapy or in combination with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs). Mean change from baseline in RAPID3 and the proportion of patients reporting RAPID3 remission (≤3), low (LDA, >3 to ≤6), moderate (MDA, >6 to ≤12), and high disease activity (HDA, >12) were assessed. Correlations between absolute scores for RAPID3 and Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI), and 28-joint Disease Activity Score with C-reactive protein (DAS28[CRP]) were assessed using Spearman correlation coefficients. All data are as observed.
Results: A total of 661, 498, 648, 1629, and 945 patients were included from SELECT-NEXT, -BEYOND, -MONOTHERAPY, -COMPARE, and -EARLY. At baseline, the majority of patients across all studies were in RAPID3 HDA (mean baseline RAPID3 [across all studies], 17.2–19.2) (Table and Figure). Improvements from baseline in RAPID3 were observed with UPA 15 mg and 30 mg through Week 60, with numerically greater improvements observed with UPA compared with active comparators (Table). Across studies, mean improvements in RAPID3 exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID) with UPA and adalimumab (ADA) treatment (MCID=3.83). By Week 60, approximately one-half of UPA-treated patients were in RAPID3 remission or LDA, with only 10–25% remaining in HDA, except for the more refractory population in SELECT-BEYOND, in which ~38% of patients remained in HDA (Figure). RAPID3 scores moderately to strongly correlated with CDAI (ρ=0.69–0.83), SDAI (ρ=0.69–0.82), and DAS28(CRP) (ρ=0.58–0.77), across all studies, at Week 60 (all p< 0.001).
Conclusion: UPA, as monotherapy or in combination with csDMARDs, was associated with improvements in patient-reported disease activity, pain, and physical function, as assessed by RAPID3 over 60 weeks in the phase 3 SELECT clinical program. RAPID3 continues to be an important tool in clinical practice to assess disease activity, as it was shown to correlate to other disease activity measures and allows for rapid scoring.
References:
1. Pincus T, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:181–9.
2. England BR, et al. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2019;71:1540–55.
3. Ward MM, et al. J Rheumatol 2019;46:27–30.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bergman M, Buch M, Tanaka Y, Citera G, Bahlas S, Wong E, Song Y, Tundia N, Suboticki J, Strand V. Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Long-Term Upadacitinib Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/routine-assessment-of-patient-index-data-3-rapid3-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-long-term-upadacitinib-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/routine-assessment-of-patient-index-data-3-rapid3-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-long-term-upadacitinib-therapy/