Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Lupus Nephritis (1512–1516)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: The SLE thrombosis risk equation contains three components: lupus anticoagulant (dRVVT), low C3 and C4d bound to platelets (platelet C4d). We examined the role of platelet C4d in association with thrombosis and proteinuria.
Methods: A total of 150 patients, consented to the study, were enrolled with a maximum of 3 visits per patient (424 visits): baseline, 6 month follow up, and 12 month follow up. Platelet C4d was measured by flow cytometry and expressed as net mean Fluorescence intensity (MFI). An abnormal platelet C4d was defined as a net MFI >20. GEE models were used to assess the relationship between disease activity measures and platelet C4d, accounting for within patient correlations. Linear mixed effects model was used to evaluate the within-patient associations.
Results: This analysis included 150 patients: 86% were female; 34.7% were African-American; and 55.3% were Caucasian. The mean age at diagnosis was 30.7 years (SD=14.1 years). 206 visits had a platelet C4d net MFI< 5, 77 visits had a net MFI between 5 and 10, 59 visits were 10-< 20, 27 were 20-< 30, and 54 were 30 or above. Adjusting for age at visit, race, and sex, platelet C4d was associated with low complement (OR 3.65 (2.11, 6.32), p< 0.0001) and increased anti-dsDNA (OR 1.77 (1.16, 2.72), p=0.0083). In a comparison of intermittent or persistently positive vs normal platelet C4d, positive platelet C4d was associated with deep vein thrombosis (OR 6.14 (1.43, 26.31), p=0.0144), any venous thrombosis (OR 12.3 (2.48,61.53), p=0.0022), and any venous or arterial thrombosis (OR 5.54 (1.84, 16.66), p=0.0023). A “within patient” analysis was also done (Table 1), showing a significant increase in urine protein/cr (p=0.0005). The percentage of patient visits with urine protein/cr ≥ 0.5 g at each platelet C4d level is shown in Table 2.
Conclusion: Platelet C4d represents the importance of immunothrombosis in SLE: that thrombosis reflects cross-talk between coagulation, complement and platelets. In our between patient analyses, platelet C4d was associated with serologies (low complement and anti-dsDNA) and both arterial and venous thrombosis. In our within patient analyses, it was associated with proteinuria. The association with proteinuria is novel and may be one of the ways that serologies – which are more common in lupus nephritis – act to effect thrombosis risk and organ damage.
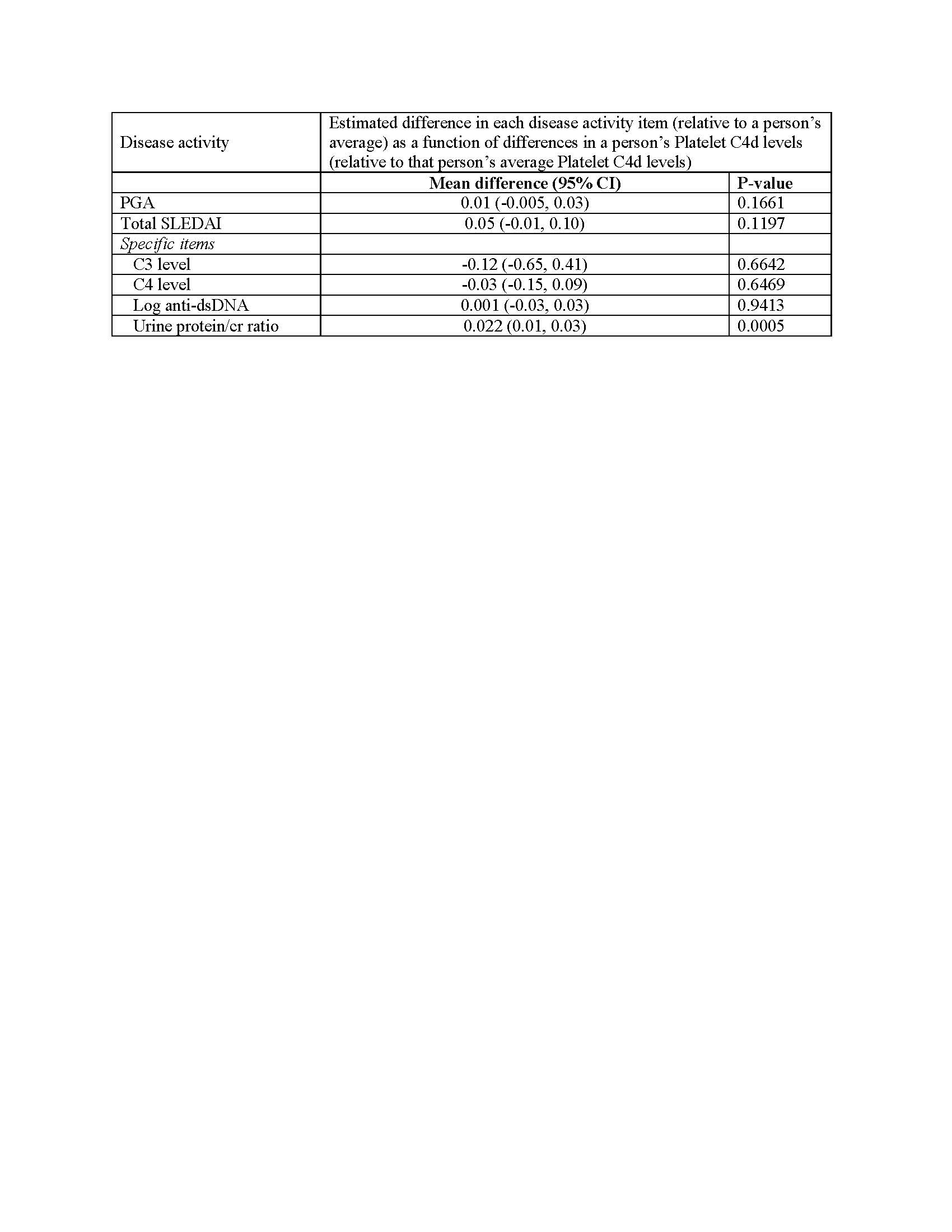 Estimated difference in disease activity variables at each visit per 10 unit difference in between the patient’s Platelet C4d at that visit and the person’s average Platelet C4d.
Estimated difference in disease activity variables at each visit per 10 unit difference in between the patient’s Platelet C4d at that visit and the person’s average Platelet C4d.
 Percentage of patient visits with urine protein/cr ≥ 0.5 g at each platelet C4d level.
Percentage of patient visits with urine protein/cr ≥ 0.5 g at each platelet C4d level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Petri M, Li J, Conklin J, O'Malley T, Ligayon J, Wolover L, Dervieux T. Role of Platelet C4d in Thrombosis and Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-platelet-c4d-in-thrombosis-and-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-platelet-c4d-in-thrombosis-and-lupus-nephritis/
