Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To understand the role of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress biomarkers in the renal disease in people with gout. We hypothesized that higher gout severity, the lack of urate-lowering treatment (ULT) use and elevated inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers will be associated with the presence of advanced renal disease in people with gout.
Methods: We prospectively enrolled patients with clinically diagnosed gout in the UAB Rheumatology Arthritis Database and Repository (RADAR) from January 2018 to December 2019. All except one patient (score of 7; the threshold of >=8) met ACR-EULAR gout classification criteria. Demographic and clinical data including gout severity and allopurinol use were collected. Serum and plasma were assayed for key inflammatory markers and oxidative stress pathway metabolites, and renal function tests and other clinical end points were assessed. Gout severity was assessed on the basis of: (1) High disease activity defined as treating physician’s impression or ≥ one gout flare in the last 3-6 month, or serum urate level above target (6 mg/dl) necessitating escalation of ULT; (2) presence of tophi (yes/no); and (3) the current serum urate. We used analysis of variance (continuous) and chi-square (categorical) to examine association of gout severity, ULT use and cytokines and oxidative stress markers with advanced renal disease, defined as glomerular filtration rate (GFR) ≤ 60 ml/min.
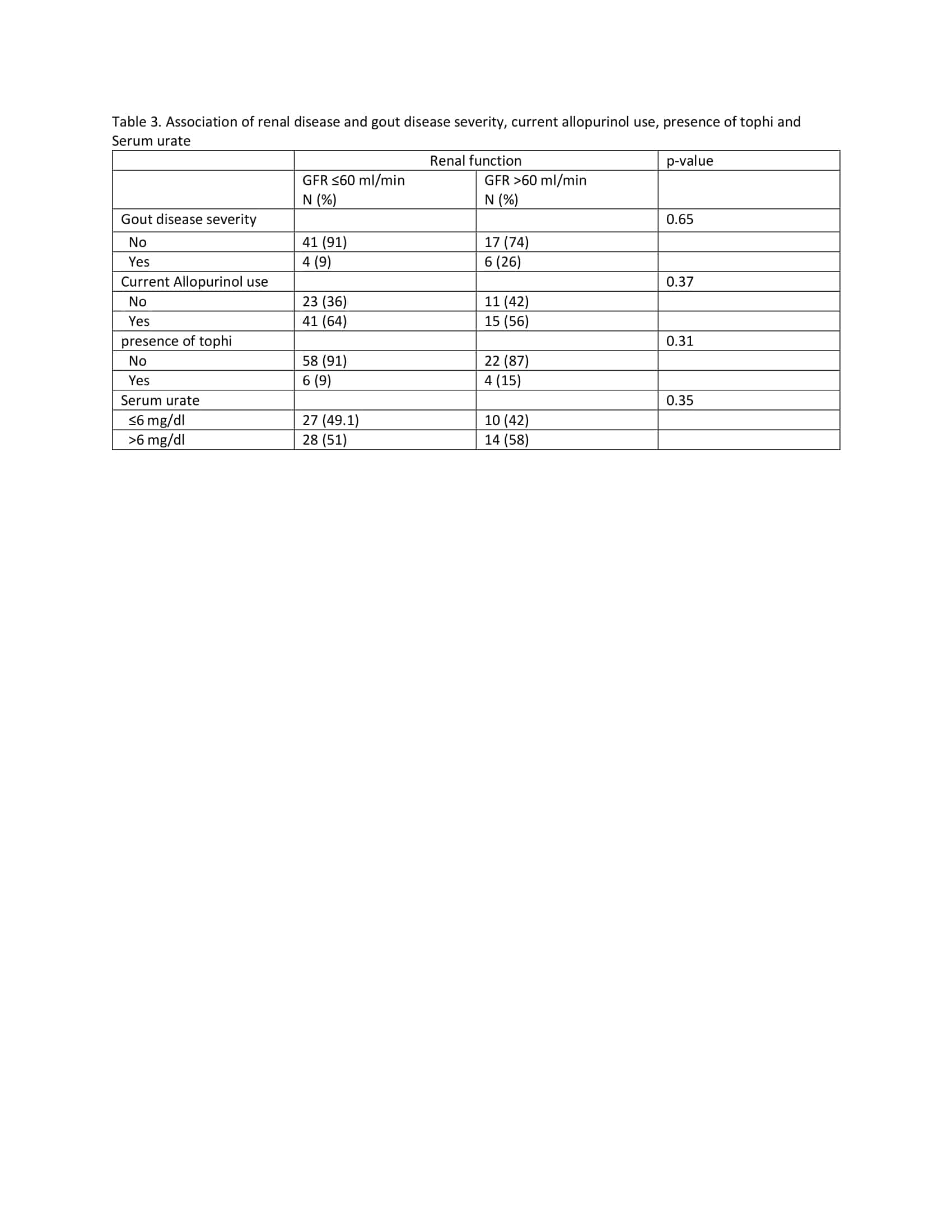
Results: Our study included a total of 90 patients with gout, 73% males, 48% African American, 48% Caucasian and 11% active smokers. Of these, 54% (N=49) hadat least one gout attack in this period, 89% had non-tophaceous gout and 74% had hypertension (Table 1). The mean serum urate level, serum creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) were 6.48 mg/dl (2.21), 1.83 mg/dl (3.34), 38.6 ml/min (16.4) respectively. Four inflammatory markers were increased in patients with advanced renal disease (GFR ≤60 ml/min) versus non-renal disease (GFR >60 ml/min); IL-1beta, PDGF-AA, A PDGF-BB and TNF- alpha, which statistically significant (P=0.03, 0,02, 0,03, 0.02; Table 2). 8-Isoprostane levels were low in people with advanced renal disease with no significant differences in other oxidative stress pathway markers including nitrotyrosine, carbonyl content, oxyHb, MetHb, nitrite or nitrates. Severity of gout disease, the presence of tophi, current allopurinol use and serum urate < 6 mg/dl were not associated with the presence of advanced renal disease (Table 3).
Conclusion:
High level of oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine markers were associated with the presence of advanced renal disease in patients with gout. These associations need further study in larger samples.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alduraibi F, Ricart K, Patel R, Szalai A, Melnick J, Singh J. Role of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Pathway Biomarkers in Renal Disease in Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-inflammatory-and-oxidative-stress-pathway-biomarkers-in-renal-disease-in-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-inflammatory-and-oxidative-stress-pathway-biomarkers-in-renal-disease-in-gout/