Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) is a very effective treatment for autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRD). However, treatment increases risk of infections and impairs responses to vaccines. Prior studies from our group and others showed that many patients receiving RTX have absent or numerically low antibody titers of IgG anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike after vaccination with 2 doses of the BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 vaccines or 1 dose of Ad26.COV2.SCovid-19 vaccine. In August 2021, the CDC recommended that immunocompromised individuals receive a supplemental dose. Here, we evaluate the response to that dose.
Methods: We conducted an observational cohort study on adult patients with AIRD treated with RTX since January 2020 at our institution. Details regarding disease treatment, Covid-19 infection and vaccinations, and immunologic parameters were abstracted through chart review and telephone calls. The anti-spike protein antibodies were measured using ELISA (Attelica IM COV2G or ADVIA Centaur COV2G, Siemens, Healthineers). For statistical analysis, we used the Mann Whitney test to compare continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables.
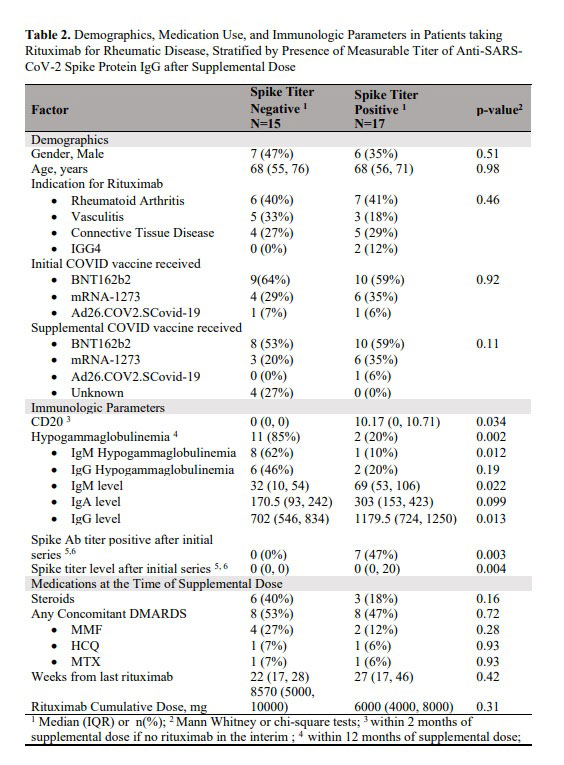
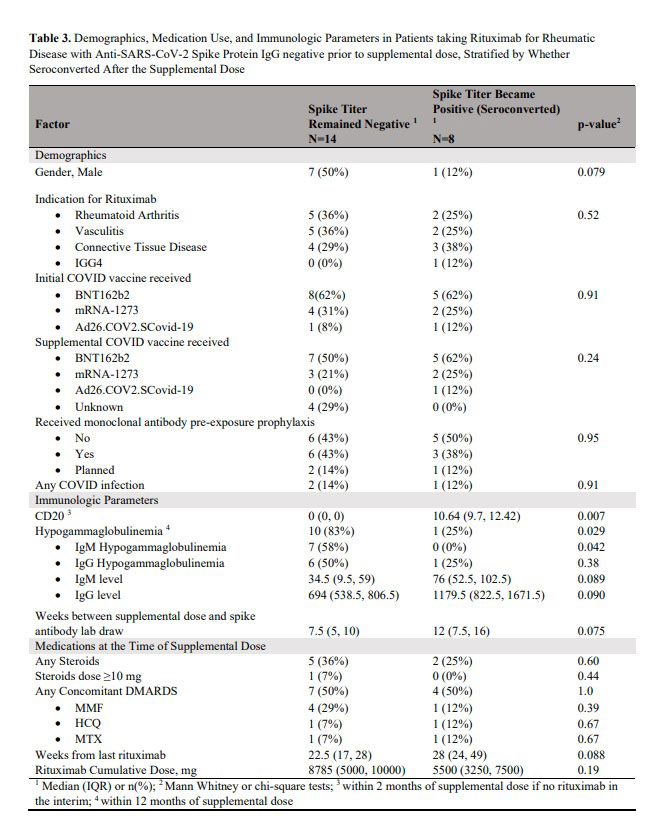
Results: Among 72 patients (median [IQR] age, 63 [54.8, 71] years), 52 (72.2%) received a supplemental Covid-19 vaccine from August 2021 to May 2022. The median (IQR) time from pre-vaccination RTX infusion to vaccination was 24 (18.5, 31) weeks. Of the 32 patients who had spike protein antibodies measured after the supplemental dose, 17 (53.1%) had detectable antibody titers. Compared to patients who had positive titers, those who were negative had lower levels of CD20 and more severe hypogammaglobinemia with lower IgM and IgG levels. Of the 22 patients who did not mount an antibody response after the original vaccine series, 8 patients (36%) had positive antibodies (seroconverted) after the supplemental dose. Patients were 15.2 times less likely to seroconvert if they had been hypergammaglobulinemic in the 12 months preceding the vaccination. There have been 21 infections in 19 patients since the beginning of the pandemic, including 11 infections after the supplemental dose. Of the 7 patients with spike antibody measurements who had Covid-19 infection at any point during the pandemic, 5 (71.4%) had positive spike antibodies. Five patients (26%) required hospitalization for their covid-19 infection, including 2 after receiving the supplemental dose. Three patients (60%) were treated in an ICU. 20 (28.6%) patients have received monoclonal antibodies pre-exposure prophylaxis, and none have had covid-19 after the prophylaxis.
Conclusion: In this single-institution study of patients receiving RTX for autoimmune rheumatic diseases, approximately 1/3 of the patients who did not initially mount an antibody response to Covid-19 vaccination, were positive after the supplemental dose. We found that hypogammaglobulinemia was a strong negative predictor of seroconversion. Breakthrough infections occurred despite vaccination. Even after infection and vaccination, some patients did not seroconvert. Approximately a quarter of RTX treated patients have received monoclonal antibodies pre-exposure prophylaxis which to date has been highly efficacious in preventing infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Magliulo D, Kyttaris V, Rose E. Rituximab Treated Patients with Hypogammaglobulinemia Are Less Likely to Seroconvert Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Supplemental Dose [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treated-patients-with-hypogammaglobulinemia-are-less-likely-to-seroconvert-following-sars-cov-2-vaccine-supplemental-dose/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-treated-patients-with-hypogammaglobulinemia-are-less-likely-to-seroconvert-following-sars-cov-2-vaccine-supplemental-dose/