Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : The treatment of active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) remains problematic because the current treatment regimen based on corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents have significant side effects. Rituximab (RTX), a chimeric monoclonal antibody that selectively targets CD20-positive B cells, has proven optimistic results in a number of open-label trials, despite the fact that two randomized controlled trials in SLE did not meet the primary end points. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of RTX as a steroid sparing drug in patients with moderate to severe SLE.
Methods : All patients satisfied the American College of Rheumatology 1997 revised criteria for SLE. Forty-six patients who were treated with immunosuppressive regimen including RTX (RTX group) were enrolled in this retrospective study. To compare the outcomes, SLE patients who were treated with immunosuppressive regimen that did not include RTX were matched for SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) score in 2:1 ratio compared to RTX group. Data of the disease activity, infection rate and mortality, treatment modalities, and cumulative dosages of corticosteroid and cyclophosphamide were collected at baseline and at 1-, 6-, and 12-month, then every 12 months up to 36 months of follow-up.
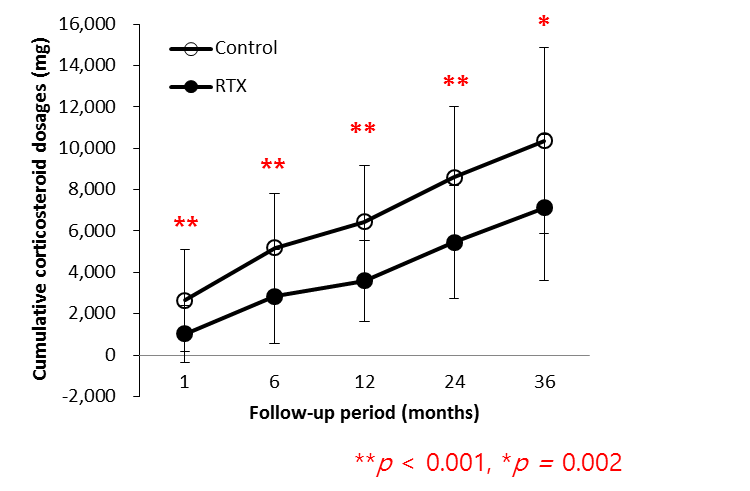
Results : Disease activity was similar in the RTX and control groups with mean SLEDAI scores of 22.3 ¡¾ 12.0 and 22.2 ¡¾ 12.0, respectively at baseline and 4.5 ¡¾ 6.2 and 3.5 ¡¾ 3.1, respectively at 36 months of follow-up. The cumulative corticosteroid doses at month 1 and 36 in the RTX group (1020.5 ¡¾ 1379.2 and 7130.1 ¡¾ 3548.7 mg, respectively) were significantly lower that those of the control group (2640.9 ¡¾ 2450.8 and 10371.7 ¡¾ 4489.7 mg, respectively). The difference in cumulative corticosteroid dosages at each visit, remained significant at all follow-up time points.
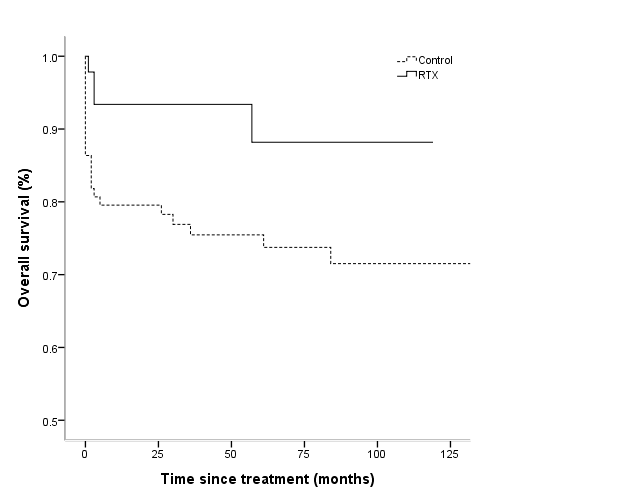
The mean cumulative dose of cyclophosphamide was lower in the RTX group compared with that in control group (2639.2 ¡¾ 3085.5 mg vs. 4169.5 ¡¾ 2464.0 mg, p = 0.028). Frequency of infection was significantly lower in RTX group (1.3 ¡¾ 1.5 vs. 1.9 ¡¾ 1.7 in control group, p = 0.040). The survival rate was significantly higher in RTX group compared with that in control group (91.3% vs. 73.9%, p = 0.022).
Conclusion : These data indicate that addition of RTX in standard immunosuppressive regimen revealed steroid-sparing effects for the treatment of moderate to severe SLE while it significantly improved the mortality and morbidity. Further studies with larger number of patients are needed to confirm the value of RTX.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim NR, Eun JS, Kang JW, Nam EJ, Kang YM. Rituximab As a Corticosteroid-Sparing Agent in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-as-a-corticosteroid-sparing-agent-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rituximab-as-a-corticosteroid-sparing-agent-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/