Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: ORAL Surveillance (NCT02092467; a post-authorization safety study of tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily [BID] vs TNF inhibitors [TNFi]) found higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (MACE) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) with tofacitinib vs TNFi.1 A post hoc analysis of ORAL Surveillance found higher risk of MACE with tofacitinib vs TNFi in patients (pts) with history of atherosclerotic CV disease (ASCVD); risk did not appear different with tofacitinib 5 mg BID vs TNFi in pts without history of ASCVD.2 This post hoc analysis expands on 3-point MACE (MACE-3; a composite of CV death, and non-fatal MI and stroke) by evaluating risk of all adjudicated CV events as part of extended MACE endpoints in ORAL Surveillance with tofacitinib vs TNFi.
Methods: Pts with RA aged ≥50 years and with ≥1 additional CV risk factor received tofacitinib 5 mg (N=1,455) or 10 mg (N=1,456) BID, or TNFi (N=1,451). Extended MACE endpoints were based on MACE-3 and sequentially added adjudicated ischemic CV events (ie hospitalization for unstable angina [MACE-4], coronary revascularization procedures [MACE-5], transient ischemic attack [MACE-6], and peripheral vascular disease [MACE-7]), hospitalization for heart failure (HF; MACE-8), and VTE (MACE-8 plus VTE). Hazard ratios (HRs; time to first event analysis) were evaluated with tofacitinib vs TNFi for extended MACE endpoints (risk period up to first event of aggregated CV events) and for individual component endpoints (risk period up to first event of individual CV events), separately. Subgroup analyses by history of ASCVD were performed.
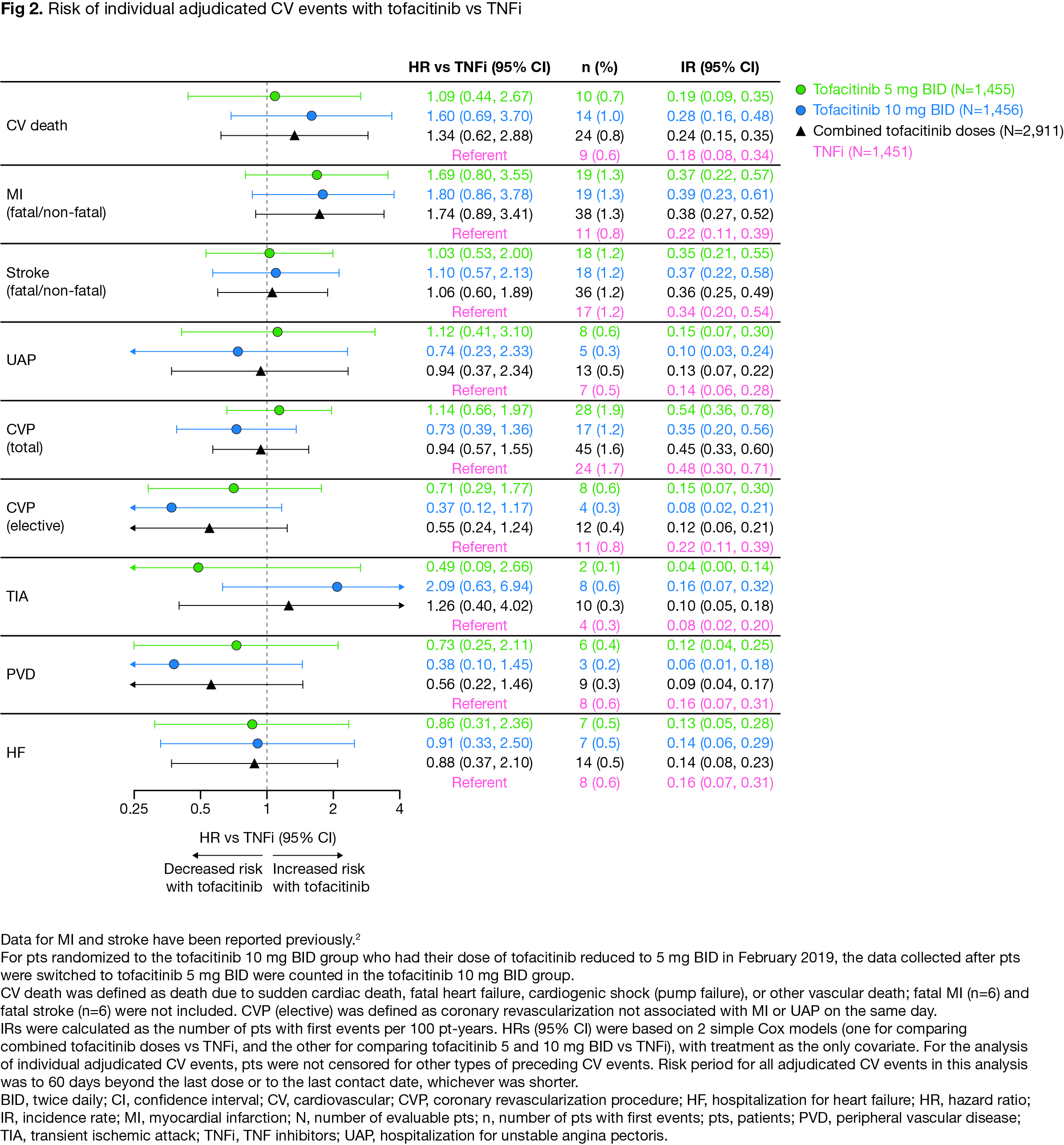
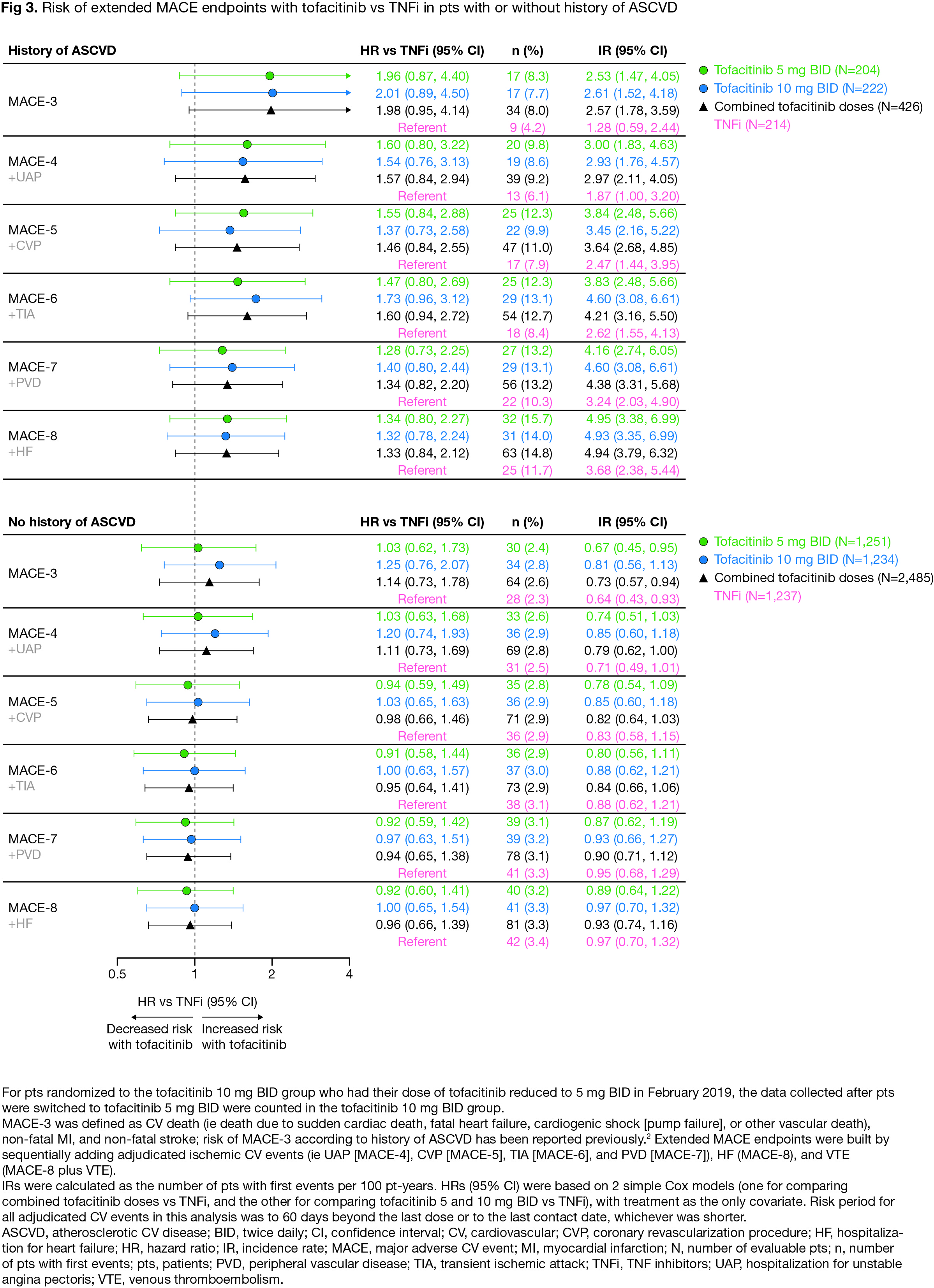
Results: For extended endpoints of adjudicated ischemic CV events (ie MACE-4 to -7), HRs with tofacitinib vs TNFi were similar to HRs for MACE-3 (Fig 1). Risk of MACE-8 was similar with combined tofacitinib doses vs TNFi (HR [95% confidence intervals (CI)] 1.08 [0.81, 1.44]). Risk of MACE-8 plus VTE was similar with tofacitinib 5 mg BID vs TNFi (HR 1.12 [0.82, 1.52]), but higher with tofacitinib 10 mg BID vs TNFi (HR 1.38 [1.02, 1.85]) (Fig 1). Risk of MI appeared higher with tofacitinib vs TNFi (HR 1.74 [0.89, 3.41], combined doses), but risk of other individual adjudicated CV events was generally similar (Fig 2). Across extended MACE definitions (ie up to MACE-8), risk appeared higher with tofacitinib vs TNFi in pts with history of ASCVD (Fig 3).
Conclusion: In ORAL Surveillance, risk of a composite of all ischemic CV events and HF (ie MACE-8) did not appear different with tofacitinib vs TNFi. However, across extended MACE endpoints risk was numerically higher with tofacitinib vs TNFi in pts with a history of ASCVD. The totality of CV risk (ie MACE-8 plus VTE) was higher with tofacitinib 10 mg BID vs TNFi, driven by an increase in VTE events. Limitations include low numbers of individual CV events and not considering severity/frequency of multiple events. These data highlight the need for a better understanding of risk of individual CV events in pts with RA.
Ytterberg et al. N Engl J Med 2022; 386: 316–26
Charles-Schoeman et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022: ard-2022-222259. Epub ahead of print
Study sponsored by Pfizer. Medical writing support was provided by L Hogarth, CMC Connect, and funded by Pfizer.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buch M, Bhatt D, Charles-Schoeman C, Giles J, Mikuls T, Koch G, Ytterberg S, Nagy E, Jo H, Kwok K, Connell C, Masri K, Yndestad A. Risk of Extended Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event Endpoints with Tofacitinib vs TNF Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase 3b/4 Randomized Safety Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-extended-major-adverse-cardiovascular-event-endpoints-with-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-extended-major-adverse-cardiovascular-event-endpoints-with-tofacitinib-vs-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3b-4-randomized-safety-study/