Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:15PM
Background/Purpose: Recent reports from a post-marketing safety trial, “ORAL Surveillance”, indicated an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) outcomes in RA patients treated with tofacitinib. Thus, the aim of this study was to examine the risk of CV outcomes associated with tofacitinib, compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFI), in patients with RA.
Methods: Using U.S. claims data from ‘Optum’ Clinformatics (2012-2020), IBM ‘MarketScan’ (2012-2018), and Medicare (parts A, B, and D, 2012-2017) databases, we created two study cohorts of RA patients initiating treatment with tofacitinib or TNFI: 1) A restrictive “RCT-duplicate cohort” mimicking inclusion/exclusion criteria of the ORAL Surveillance trial to calibrate our findings against trial results, 2) a broader “real-world evidence (RWE) cohort” including representative population from routine care. Patients were followed from treatment initiation for study outcomes until treatment discontinuation or switch, insurance disenrollment, death, or end of the study period. The primary composite CV outcome, was defined using inpatient claims for myocardial infarction or stroke. Cox proportional hazards models with propensity score fine-stratification weighting were used to generate hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) and accounted for over 60 potential confounders in each of the datasets. Fixed effects models with inverse variance were used to pool database-specific effect estimates. Secondary analysis was conducted by baseline cardiovascular disease (RWE cohorts only).
Results: In RWE study population, 28,568, 34,083, and 39,612 patients were identified from Optum, MarketScan, and Medicare, respectively, of whom 13.2%, 15.6%, and 9.5% initiated treatment on tofacitinib. The mean age was 55, 53, and 72 years in Optum, MarketScan, and Medicare, respectively. In RWE cohort, 13% of patients in Optum, 10% in MarketScan, and 31% in Medicare had a history of cardiovascular disease. The crude incidence rates of the primary CV endpoint per 100 person-years (95% CI) for tofacitinib and TNFI users were 0.73 (0.47-1.09) and 0.61 (0.51-0.72) in Optum; 0.75 (0.52-1.05) and 0.52 (0.44-0.61) in MarketScan; and 2.14 (1.66-2.70) and 1.86 (1.71-2.02) in Medicare. Overall, in the RWE cohort, the pooled HR (95% CI) for CV outcomes comparing tofacitinib with TNFI was 1.01 (0.83-1.23). Results from the RCT-duplicate cohort were in alignment with reports from the ORAL Surveillance trial (pooled HR: 1.24, 95% CI: 0.90-1.69 vs trial: 1.33, 95% CI: 0.91-1.94). Among RWE patients with baseline cardiovascular disease, the pooled HR (95% CI) was 1.27 (0.95-1.70). Consistent results were observed across other secondary and sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: This multi-database large population-based study did not find evidence for an increased risk of CV outcomes with tofacitinib, in comparison with TNFI, in the overall RA patient population treated in the real-world setting. However, similar to the reported results from ORAL Surveillance trial, tofacitinib, in comparison with TNFI, was associated with an increased, but statistically non-significant, risk of CV outcomes in RA patients with CV risk factors or a history of cardiovascular disease.
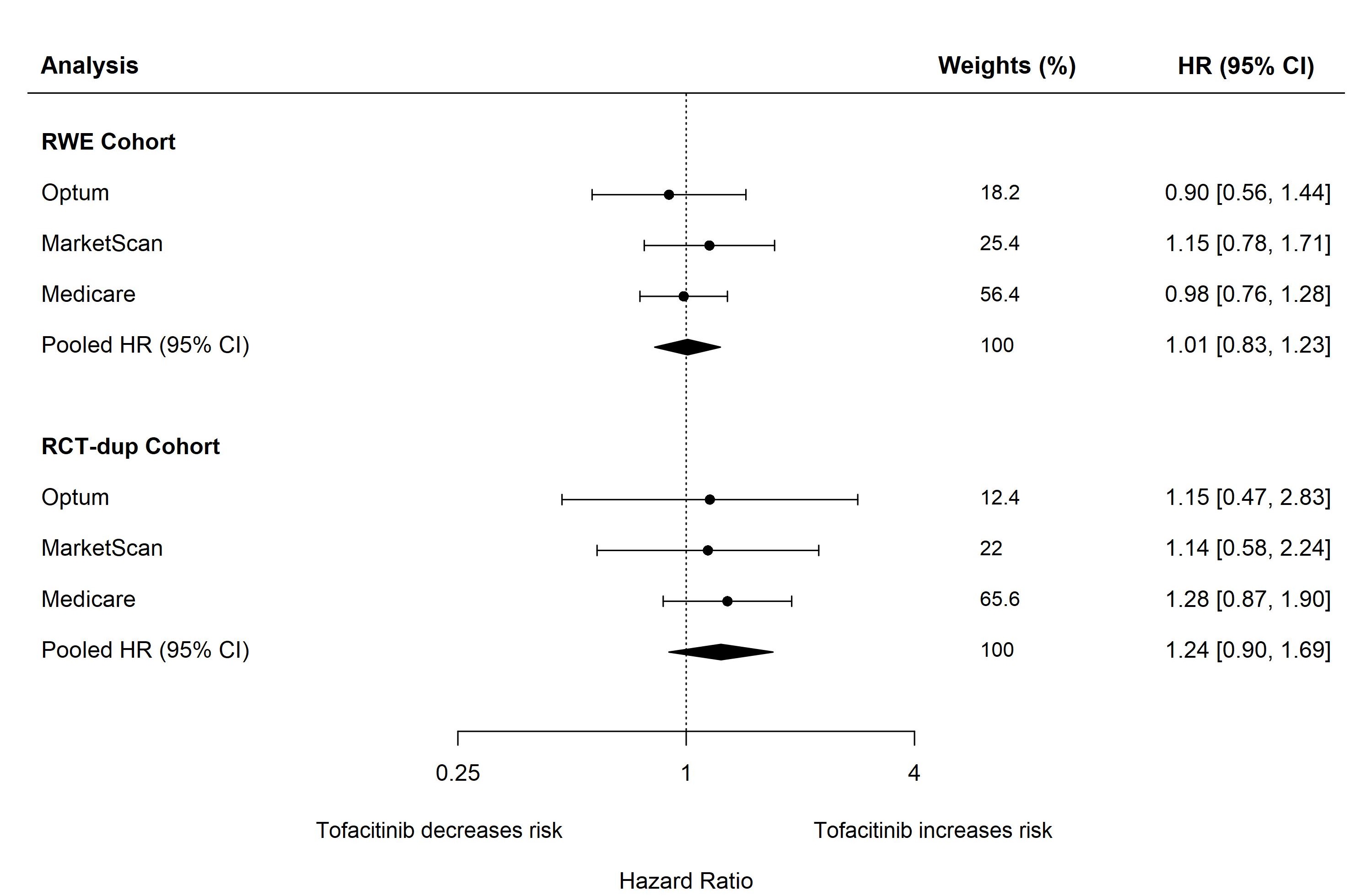 Figure. Risk of composite CV outcomes when comparing tofacitinib with TNF inhibitors (reference) in patients with RA.
Figure. Risk of composite CV outcomes when comparing tofacitinib with TNF inhibitors (reference) in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khosrow-Khavar F, Kim S, Lee H, Lee S, Desai R. Risk of Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients Treated with Tofacitinib: First Results from the Safety of TofAcitinib in Routine Care Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (STAR-RA) Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-cardiovascular-outcomes-in-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-first-results-from-the-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-routine-care-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-star-ra-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/risk-of-cardiovascular-outcomes-in-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib-first-results-from-the-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-routine-care-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-star-ra-study/
