Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid factors (RFs) are associated with disease activity and joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and thought to play a pathogenic role in disease. RFs have been measured for decades by nephelometry and/or solid-phase immunoassay, but these techniques are unable to resolve RF immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable (IGHV) composition at the level of the serum proteome. Here, we have performed the first quantitative mass spectrometry (MS) analysis of serum (secreted) IgH-RF repertoires in RA patients and reveal dynamic patterns of RF production after treatment.
Methods: Serum IgM-RFs from 16 patients with RF-positive newly diagnosed RA were purified by immunoprecipitation (1). IgH-RF V-region peptides were sequenced by LC-MS/MS followed by combined de novo amino acid sequencing and database matching using Peaks 8.0 software to determine IGHV composition. Full-scan multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) was used to quantitate expression of individual IGHV subfamilies in paired serum samples at baseline and after 6 months of tDMARD (n=9) or TNFi (n=7).
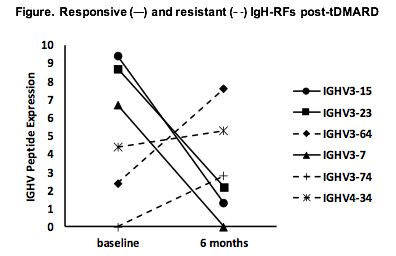
Results: High resolution MS sequencing of serum IgH-RFs demonstrated shared germline-encoded oligoclonal patterns with convergent usage of IGHV1-3, 1-69, 3-15, 3-23, 3-64, 3-7, 3-74, 4-34, and 5-51 subfamilies, although each patient had an individual IgH-RF peptide expression landscape. Six-month serum RF levels were decreased in 15/16 patients by routine nephelometry and correlated with falling IgH-RF expression levels by MRM/MS (P < 0.05 by Spearman rank). Molecular profiling of IgH-RFs by MS proteomics revealed that RF responses in each patient comprised two clonal populations: treatment-responsive (classified as a reduction of > 30% in expression levels), and treatment-resistant (classified as steady, an increase of > 30%, or newly emergent) (Figure). Commensurate with global reductions in RF levels after treatment, responsive IgH-RF clones comprised over 2/3rds of the RF clonal repertoire. On the other hand, patients co-expressed sizable numbers of resistant IgH-RF clones indicating molecular heterogeneity of RF responses. Newly emergent (de novo) clonal populations in treated patients were encoded by IGHV3 subfamilies not expressed at baseline.
Conclusion: RF production in RA is a dynamic, oligoclonal process comprising shared sets of IGHV subfamilies across unrelated patients. While most IgH-RF clonal populations are reduced by conventional therapies, the finding of resistant IgM-RF clones may reflect their production in protected niches in joints or tissues; or differences in selection and clonal expansion by immune complexes. MS-based quantitative proteomics of serum RFs offers a powerful approach for molecular characterisation of these prototypic diagnostic and pathogenic biomarkers in RA.
1. Wang et al., Arthritis Rheumatol. (2018) doi: 10.1002/art.40539
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang JJ, Murray-Brown W, Colella A, Smith MD, Chataway T, Walker J, Robinson WH, Wechalekar MD, Gordon T. Rheumatoid Factor Peptide Expression By Quantitative Proteomics Delineates Responsive and Resistant Clones after Treatment of Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-peptide-expression-by-quantitative-proteomics-delineates-responsive-and-resistant-clones-after-treatment-of-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-peptide-expression-by-quantitative-proteomics-delineates-responsive-and-resistant-clones-after-treatment-of-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/