Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2352–2369) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III: Translational Science
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
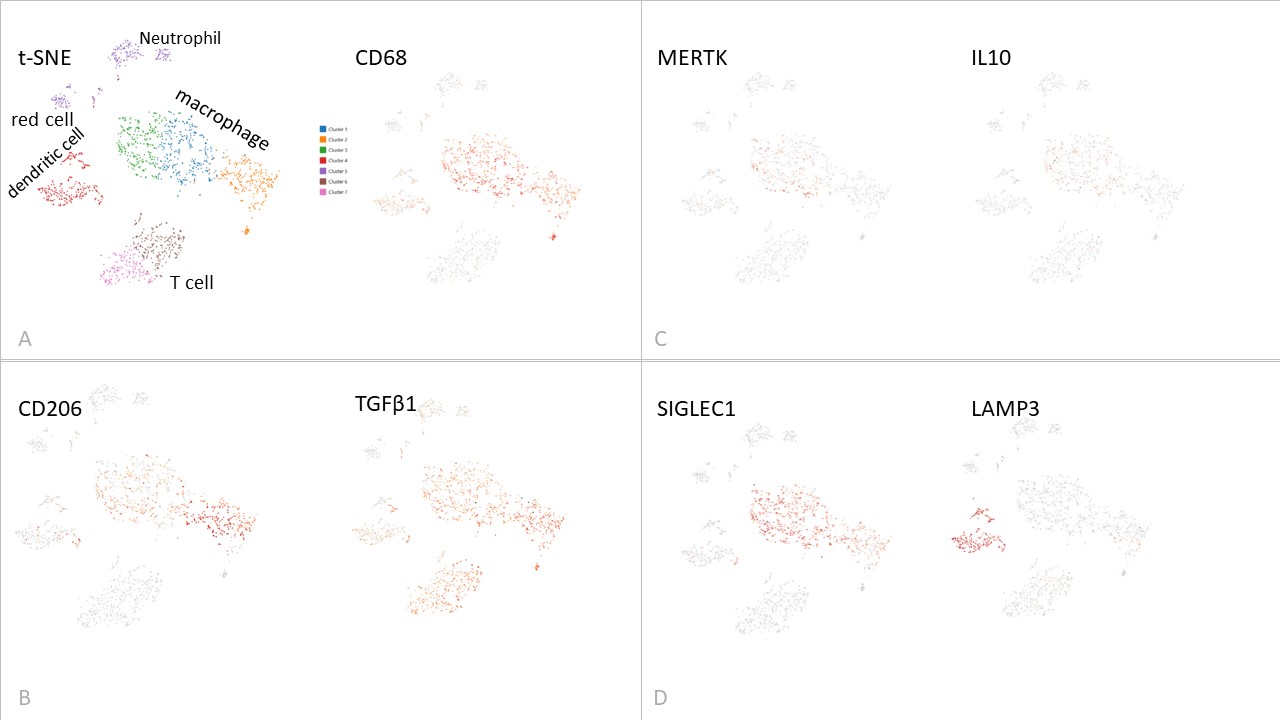
Background/Purpose: A spectrum of macrophage activation is seen in human pathologic conditions; M2-like CD206 positive macrophages are pro-fibrotic and proresolution, while M1-like macrophages are proinflammatory, as identified by polarisation in vitro. CD206 positive macrophages are under study as potential targets for inflammatory fibrotic conditions including systemic sclerosis (SSc). We investigated SSc lesional macrophages by single cell profiling and Akoya Multiplex immunochemistry and evaluated the effects of AUR300, a novel peptide therapeutic that targets M2 macrophages via CD206, the mannose receptor.
Methods: Suction blister fluid-derived cells from lesional skin were profiled by 10X RNAseq matched to AKOYA antibody staining to characterise the tissue resident immune cells, including the CD206 positive macrophages of interest (n=12 SSc patients and controls).Tissue culture modelling with patients’ blood monocyte-derived macrophages and disease fibroblasts (n=6 SSc cell lines), as well as bleomycin induced lung fibrosis as a model of organ involvement, were used to determine efficacy and mechanism of action of the therapeutic AUR300 peptide.Soluble CD206 (sCD206) (n=140 SSc and n=80 healthy control (HC) plasma samples) and cellular CD206 (n=17 SSc, n=9 HC macrophage lines) were investigated as potential biomarkers of SSc disease activity.
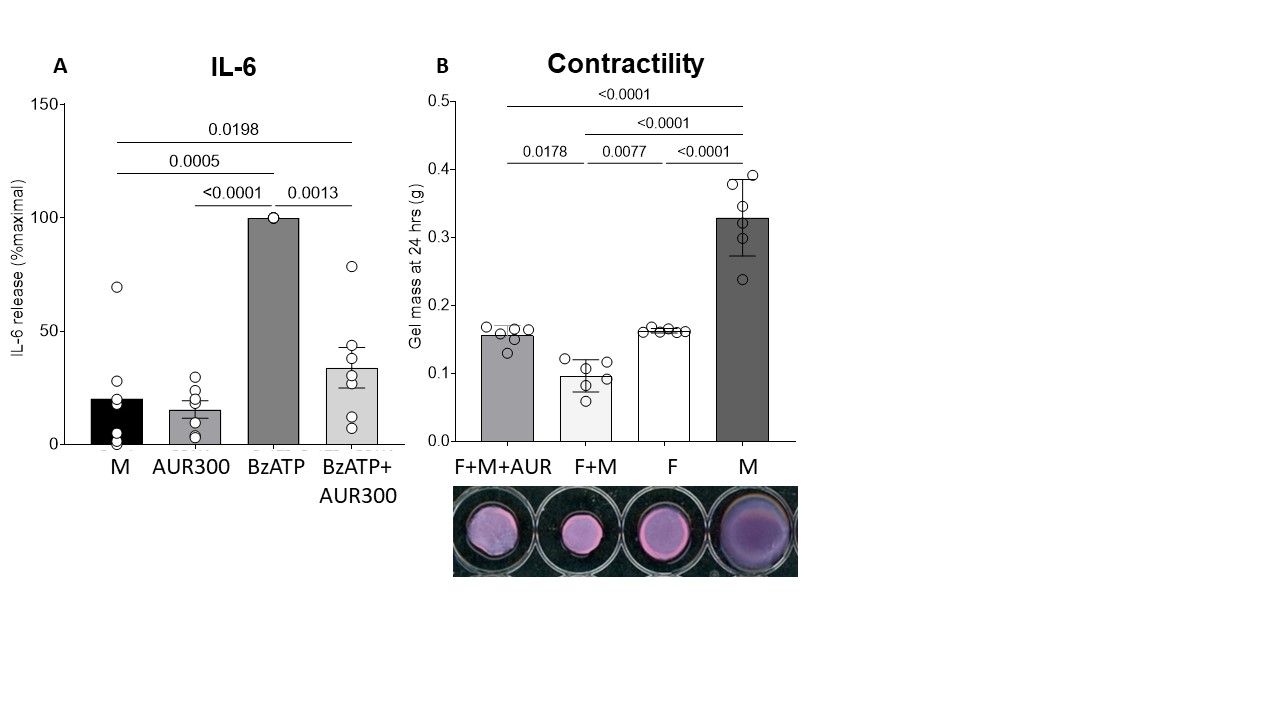
Results: CD206 positive macrophages were found in a spectrum of activation states varying from MERTK high CD206 low IL10 expressing regulatory cells, to CD206 high MERTK negative TGFβ expressing pathogenic cells (Figure 1) implicated in cross talk with fibroblasts, in the affected tissue and model systems. Exposure to disease microenvironments enhanced CD206 levels and triggered IL-6 release, reversed by the therapeutic AUR300 peptide (p < 0.05 for CD206, p< 0.0013 for IL-6, p< 0.018 for gel contraction, for effect of 10 µM AUR300) (Figure 2), which also attenuated inflammation and fibrosis in the bleomycin lung fibrosis model.Cross-talk with disease fibroblasts involved cytokines (IL-6, TSP-1) and growth factors (TGFβ and PDGF-BB) acting in concert. CD206 was elevated in plasma (HC 552±25, lcSSc 521±32, dcSSc 645±32, sCD206 pg/ml mean±SEM, P< 0.026 for dcSSc), tissue fluid (HC 31±3, SSc 48±6, pg/ml P< 0.041) and cells (HC 628, 485-729, SSc 663, 294-1932, median, range, fluorescence, P NS) as a biomarker, linked to severe resistant disease (highest in anti-Scl70 group).
Conclusion: In disease tissue, CD206 positive macrophages represent a spectrum of activation states, from pro-resolving MERTK IL-10 expressing cells, to pathogenic cells releasing profibrotic cytokines and growth factors in activating microenvironments. AUR300 reverses the activation state in SSc cell-based and murine in vivo models and represents a potential therapeutic for patients with strong CD206 positive signatures.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lopez S, Ahmed Abdi B, Lei L, Al-Oweidi A, Macfadyen C, Nagib L, Ive S, Kumar A, Collins T, Cross J, Denton C, Abraham D, Yates C, Garvin C, Lopez H, Martin G, Stratton R. Reversal of the Activation State of Pro-fibrotic CD206 Positive Macrophages by Therapeutic Peptide AUR300 in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reversal-of-the-activation-state-of-pro-fibrotic-cd206-positive-macrophages-by-therapeutic-peptide-aur300-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reversal-of-the-activation-state-of-pro-fibrotic-cd206-positive-macrophages-by-therapeutic-peptide-aur300-in-systemic-sclerosis/